Introduction
Marks and Spencer (M&S) is a leading British Multinational Company with its headquarters in London. Thomas Spencer and Michael Marks established the company in 1884. Today, M&S has over 700 shopping outlets in the United Kingdom. It also has its presence in over 40 nations globally. Currently, the MNC markets a wide range of products such as clothes, food products, and house furnishings.
In the recent past, “the company has been a major competitor in the apparel and luxury food industries (Sadler, 2007, p. 21)”. The company has a strong equity.
This explains why the consumers trust the company’s products and services based on their quality and value. M&S has a proper organisational structure thus making it a leading competitor in the country and globally. This discussion offers a detailed strategic analysis of this multinational company.
Current Strategic Issues Facing the Company’s Industry
Marks and Spencer operates in different business sectors. Some of these include the food and apparel industries. In the recent past, certain changes have taken place thus making it necessary for the company to re-organize its strategy (Bevan, 2008).
There are current trends and issues affecting the food industry. These issues affect the business of various companies such Tesco, Wal-Mart, Aurora, and Pudding Lane, among others. The current strategic issues facing the company are as follows:
Competition
The outstanding observation is that M&S is facing competition from various competitors. The competitors are operating different business segments. The company is also losing its market share and profitability (Tallman, 2010). It is notable that M&S markets products such as food materials and clothes. That being the case, M&S is facing competition from different companies (Grant, 2007).
For instance, some apparel companies such as Top Shop, Guess Company, and Hugo Boss continue to dominate the European Union (EU) market. As well, different food chains and restaurants such as Wal-Mart, Tesco, and Sainsbury are providing affordable and quality food products to their consumers. This explains why M&S should work hard in order to cope with these changing trends in the market.
Global Financial Crisis
Many companies are recovering from the credit crunch of 2009. As well, companies should embrace the idea of “forward-thinking” in order to emerge successful. M&S should therefore deal with issue in order to emerge successful (Tallman, 2010).
Obesity and Health Issues
In the recent past, consumers have become aware and conscious of their health needs and expectations. Governments are implementing new interventions and policies to promote healthy business practices.
Food Safety
The world is presently experiencing the problem of bioterrorism and food insecurity. The local food industry also faces similar challenges thus affecting the performance of different companies (Sekhar, 2009). This situation calls for Marks and Spencer to address the issues in order to be successful.
Consumer Demands
The needs of consumers are changing. Their spending and purchasing habits are also changing. The younger generation is purchasing more foods than ever before. Companies such as M&S will be required to examine such changes in order to address the needs of the consumers (Williamson & Jenkins, 2013).
Fashion Changes
It is agreeable that more customers are aware of their clothes and fashion needs. The current changes continue to affect the performance of different businesses. M&S should consider such changes in order to realize its potentials.
Technological Changes
Many companies in the industry are using modern technologies than ever before. Modern technology is needed to promote the best practices for service delivery, product development, and customer satisfaction (Burns, 2008). Companies in the industry are required to embrace new technologies in order to emerge successful.
Marks and Spencer Strategic Position
From the above issues facing the industry, it is agreeable that (M&S) is currently doing business in a very competitive environment. M&S Company continues to encounter numerous challenges than ever before. As well, the company is no longer benefiting from its “cores values”. These values include “quality, affordability, and efficient service” (Sekhar, 2009).
Some apparel companies such as Top Shop, Guess Company, and Hugo Boss continue to dominate the European Union (EU) market. As well, different food chains and restaurants such as Wal-Mart, Tesco, and Sainsbury continue to provide affordable and quality food products to the consumers.
This explains why M&S should work hard in order to cope with these changing trends in the market. The company has continued to lose its market share and competitiveness (Verdin & Heck, 2009).
The level of competition makes it hard for the company to realize its goals. Since M&S operates in many business segments, it has to deal with many competitors. For example, different retailers such as Debenhams, The Gap, Top Shop, and Next Company continue to dominate the apparel market.
Certain food chains such as Sainsbury and Tesco are marketing frozen food products and fast foods thus making it hard for Marks and Spencer to emerge successful in its business. The outstanding observation is that M&S is facing competition from different business segments.
At the same time, the company has failed to change its business strategy in order to remain competitive in the industry. The company is slowly by slowly losing its market share and profitability (Tallman, 2010).
In the recent past, the company has been working hard to regain its market share and profitability. However, the company’s weaknesses continue to affect its business. The company has consistently focused on its clothes and foods as their main brands.
That being the case, the expectations and demands of the customers has been changing thus making it impossible for Marks and Spencer to remain competitive in its business environment. According to a study by Seth and Randall (2011), M&S has been getting most of its revenues and sales from the United Kingdom.
This means that the company has mainly focused on the UK market. The increasing cost of living is making it harder to the consumer to purchase most of the company’s products. From the analysis, the biggest question is how M&S can change its strategy in order to succeed in its business environment.
Marks and Spencer Environmental Analysis
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
- M&S markets high quality and competitive products.
- The company has good relationship with employees.
- The company’s stores and outlets are strategically located across London.
- Marks and Spencer is one of the most profitable companies in the United Kingdom and across the globe. This explains why the company has a growing market share (Williamson & Jenkins, 2013).
- Marks and Spencer has established the best supply chain processes and strategies with its suppliers (Williamson & Jenkins, 2013).
- The company has the best business practices and financial strengths.
Weaknesses
- One thing about Marks and Spencer is that it relies mostly on local suppliers in the United Kingdom.
- At Marks and Spencer, the marketing strategy does not embrace new ideas and changes (Verdin & Heck, 2009).
- The company does not consider the expectations of its customers. This explains why more customers are buying products from its competitors.
- The company does not market to the young generation.
- At Marks and Spencer, “the customer is no longer getting the best support and services (Seth & Randall, 2011, p. 87)”. For instance, the company does not provide “loyalty cards” and “gifts” to its customers.
Opportunities
- Marks and Spencer can use e-business in order to compete against the other leading companies (Seth & Randall, 2011). Modern companies can use new technologies to improve their supply chain processes and provide the best customer support.
- It is agreeable that people are looking for new fashions and designs. The company stands a better chance to benefit from this new development (Tallman, 2010).
- The European Union (EU) continues to show signs of stability in the coming years.
- The company is currently expanding its business to different countries and cities.
Threats
- The modern consumer is becoming very sensitive about fashion.
- As more companies continue to use the internet for marketing, Marks and Spencer continues to lose it customers.
- The level of competition is always increasing because the company operates in different segments.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
The Porter’s Fiver Model examines the business environment of a company. “It explores the unique challenges and issues for an organisation to address in order to become successful (Verdin & Heck, 2009, p. 86)”. This analysis explores the current position of Marks and Spencer.
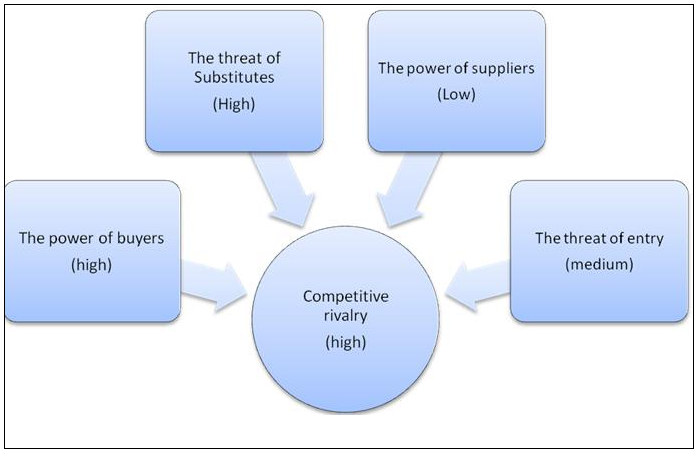
Fig 1: Porter’s Five Forces
Competitive Rivalry
The level of competition in the business is very high. In the clothing sector, M&S is facing competition from Gap and Next Companies (Bevan, 2008). As well, the company is facing high completion from Sainsbury and Tesco Companies in the food sector.
Bargaining Power of the Buyers
It is agreeable that the company is facing numerous threats from its buyers. The buyers are demanding for quality and proper service. The company is required to worker harder in order to provide better products to its consumers (Bevan, 2008).
Suppliers’ Bargaining Power
Currently, the bargaining power of Marks and Spencer’s suppliers is low. This is the case because there are more suppliers in the existing market.
Threat of New Entrants
Most of the competing companies and retailers have already established their businesses in the country (Tallman, 2010). This explains why there are minimum threats from new entrants into the market.
Threat of Substitutes
In the UK, there are more companies importing their products from other countries. Such products are usually cheaper and address the needs of the customers. This poses a threat to the company’s business practice (Sekhar, 2009).
PESTEL Analysis
For M&S to succeed in its business, it needs to be aware of the changing trends in its environment. PESTEL Analysis makes it easier to measure the organization potential according to the major environmental factors (Verdin & Heck, 2009). This part presents the company’s external environment.
Political Factors
The company operates in the UK. This means it operates in a stable political environment. However, the major threat is from terrorism. The region has the best political structure, tax system, and labour administration thus making the environment attractive.
Economic Factors
The United Kingdom has a good economy. With proper management, the company can succeed in this economy. The company can embrace the best short and long-term goals because the economic situation in the United Kingdom is favorable for business practices (Verdin & Heck, 2009). The company should concentrate more on the younger generation because it has disposable income on tertiary goods such as clothes and fashion.
Social Factors
The changing socio-cultural aspects in different countries affect many businesses today. With the company operating in many countries today, there is need to address such factors and consumer expectations (Burns, 2008). As well, it should examine other aspects such as mortality rates, cultural changes, and consumer expectations. The approach will make it easier to market the best products to the consumers.
Technological Factors
The company is today operating in a competitive environment. The company should embrace modern technologies in order to widen its potentials and deliver quality to its customers (Verdin & Heck, 2009). The competitors have embraced the use of modern technologies thus posing a major challenge to the company.
Environmental Factors
The world is today becoming sensitive about the environment. Marks and Spencer will be required to examine its practices and use environmentally friendly practices for marketing and production. This is the only way for the company to remain successful.
Legal Factors
The current legal provisions require that business organizations embrace the best practices. Various consumer legislations, labor laws, and business ethical practices determine the practices of modern businesses today (Worth, 2007). M&S will have to reconsider its practices in order to be successful.
The Company’s Strategic Direction: The Ansoff Matrix
The Ansoff Matrix identifies the best direction for a company. The matrix helps the business managers make the best decisions based on the company’s products, market share, and consumer expectations.
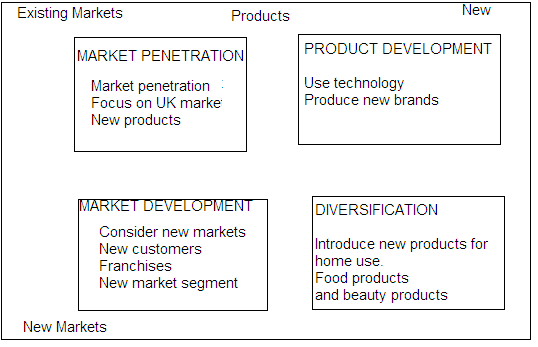
Fig 2: Ansoff Matrix
The above assessment indicates that Marks and Spencer has some strengths and weaknesses. The company has been moving away from its leading values. The level of competition is also increasing (Tallman, 2010). As well, the consumers are becoming aware and sensitive about quality and service delivery.
The consumers have been moving to other competitors such as Tesco, Wal-Mart, Hugo Boss, and Sainsbury, among others. These companies continue to provide cheaper and quality products to the customers. That being the case, M&S should design a new strategy and products in order to address the growing competition and rivalry in its business.
Conclusion
With the combination of the existing strengths, M&S will be able to turn its threats and weaknesses into opportunities. Personally, I believe the company should diversity its products in order to tackle the issue of competition. Diversification will make it easier to provide quality products to the existing shareholders.
Since the current strategy at the company is not effective, there is need to use new ideas and come up with new products. The approach will make it easier to address the changing needs of the modern customer. As well, the company should also provide quality products and services to its customers.
Reference List
Bevan, J 2008, The Rise and Fall of Marks and Spencer: And How It Rose Again, Oxford University Press, Oxford.
Burns, P 2008, Corporate Entrepreneurship: Building an Entrepreneurial Organization, Palgrave Macmillan, Basingstoke.
Grant, R 2007, Contemporary Strategy Analysis, Sage, London.
Sadler, I 2007, Logistics and Supply Chain Integration, Longman, London.
Sekhar, S 2009, Business Policy and Strategic Management, Wiley, New York.
Seth, A & Randall, G 2011, The Grocers: The Rise and Rise of the Supermarkets Chains, Longman, London.
Tallman, S 2010, Global Strategy, Longman, London.
Verdin, P & Heck, N 2009, From Local Champions to Global Masters, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Williamson, D & Jenkins, W 2013. Strategic Management and Business Analysis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Worth, R 2007, Fashion for the People: A History of Clothing at Marks & Spencer, Longman, London.