Introduction
The present laboratory work is devoted to studying the phenomenon of equilibrium force, which is formed when several forces directed in different directions are exerted on a case. A net force is a force that has an equal effect on a body to all the applied forces and, therefore, is the result of their vector addition (DPA 17). The Force Table was used to evaluate this property, which allows the application of several different forces to the body and the establishment of visual equilibrium. The variables in such an experiment were the values of the suspended weights as a characteristic of the value of the applied forces and the angles at which the sample was held approximately in the center of the circular table. Thus, the laboratory work was designed to evaluate the equilibrium force using vector addition of the applied forces and to determine whether the specimen was in proper equilibrium.
Data

Procedure
To collect data, a sample was placed on the Force Table to which three to four strands were tied and threaded through pulleys placed on the edge of a circular table; values of different weights were placed on the pulleys until the sample visually maintained equilibrium in the center of the table.
Results
Table 1 shows the primary results collected directly from the experiments. For each test, the values of the suspended weights and the angles at which the thread with the weight was placed to achieve some equilibrium state on the Force Table were collected. In the third experiment, unlike the first two, four threads were used, so the number of measurements was higher.
Table 1. Results of the experiments performed
The same data were converted into vector form, for which the vector length was determined by weight. Figure 2 shows the results of vector summations for all three experiments. An important observation is that not all vector sums were able to add up, and visually, this can be seen as a discrepancy between the end of one vector and the beginning of another. Such a discrepancy determines the absence of an equilibrium force on the Force Table.
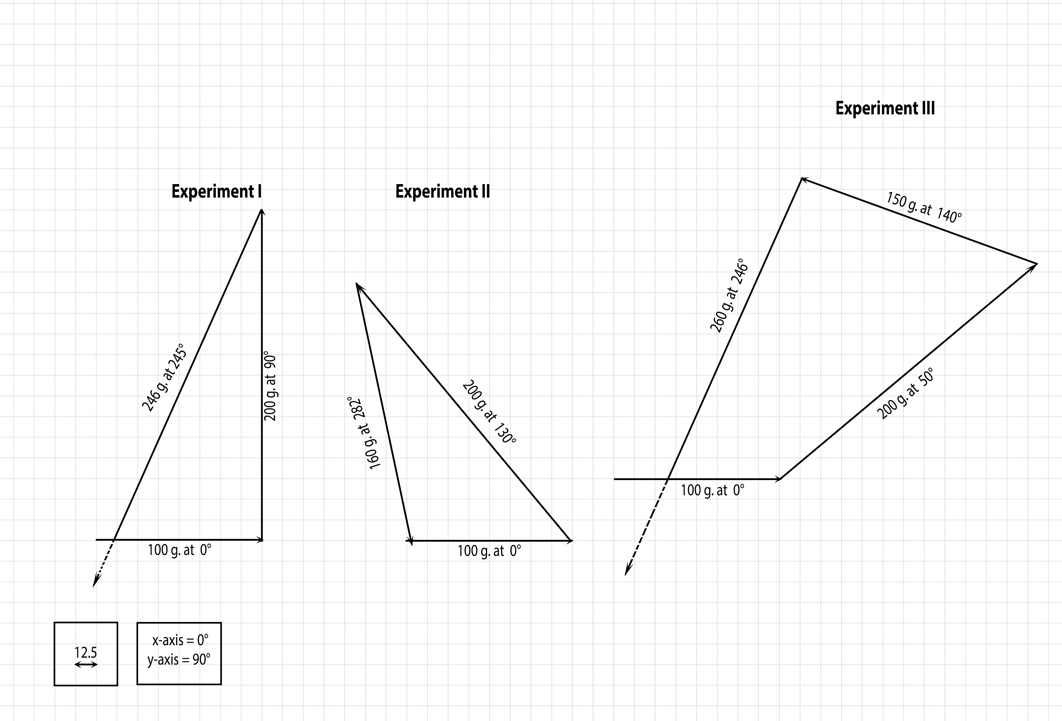
Calculations
The vector sum (Figure 2) and the algebraic sum of coordinates can be used to determine whether the sample was in proper physical equilibrium. Calculations [1]-[3] show the value of the final force: a divergence from the zero value determines that the system is not in equilibrium. As the calculations show, neither system was in equilibrium. Hence, each of the three objects has a resultant force, which causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the resultant force.

Conclusion
In this laboratory work, a Force Table was used to determine the equilibrium force for three and four applied forces. The calculations demonstrated that in none of the experiments were the specimens in equilibrium, and a resultant displacing force acted on them. Both the vertical and horizontal components of this force were calculated. More significant uncertainty corresponded to lesser data accuracy, so one source of error could be considered some uncertainty in the results.
Work Cited
DPA. “Laboratory Manual.” Herbert Lehman College, Web.