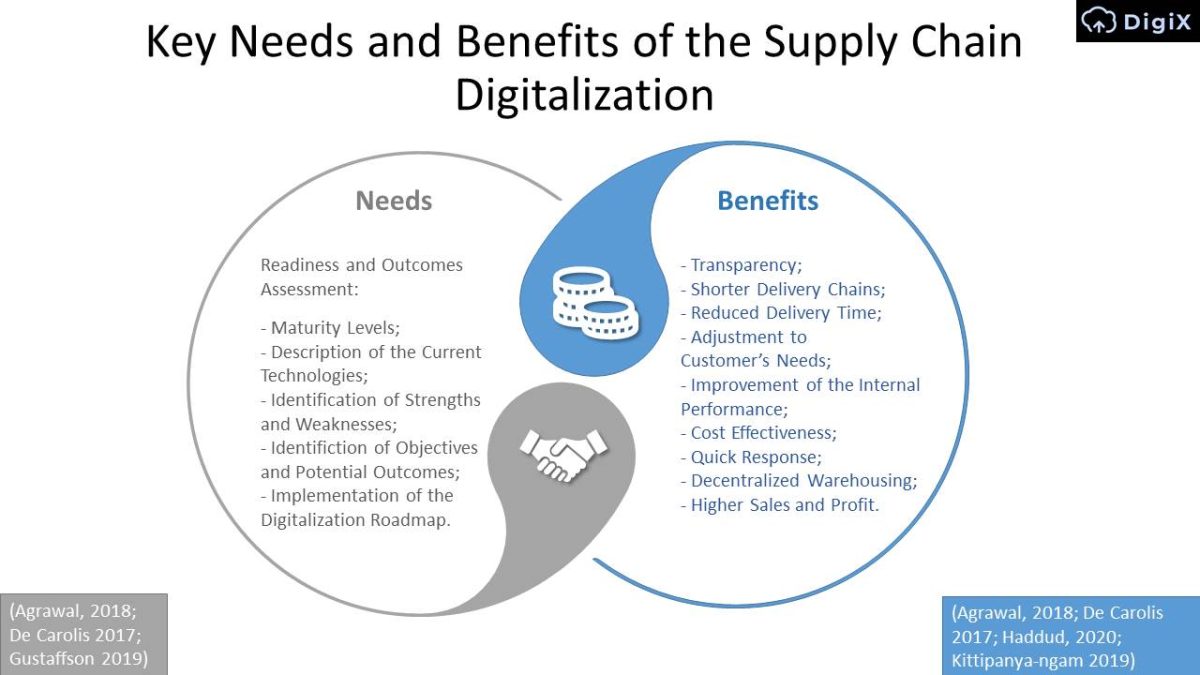
Key Needs and Benefits of the Supply Chain Digitalization
Needs
Readiness and Outcomes Assessment:
- Maturity Levels;
- Description of the Current Technologies;
- Identification of Strengths and Weaknesses;
- Identifiction of Objectives and Potential Outcomes;
- Implementation of the Digitalization Roadmap.
Benefits
- Transparency;
- Shorter Delivery Chains;
- Reduced Delivery Time;
- Adjustment to Customer’s Needs;
- Improvement of the Internal Performance;
- Cost Effectiveness;
- Quick Response;
- Decentralized Warehousing;
- Higher Sales and Profit.
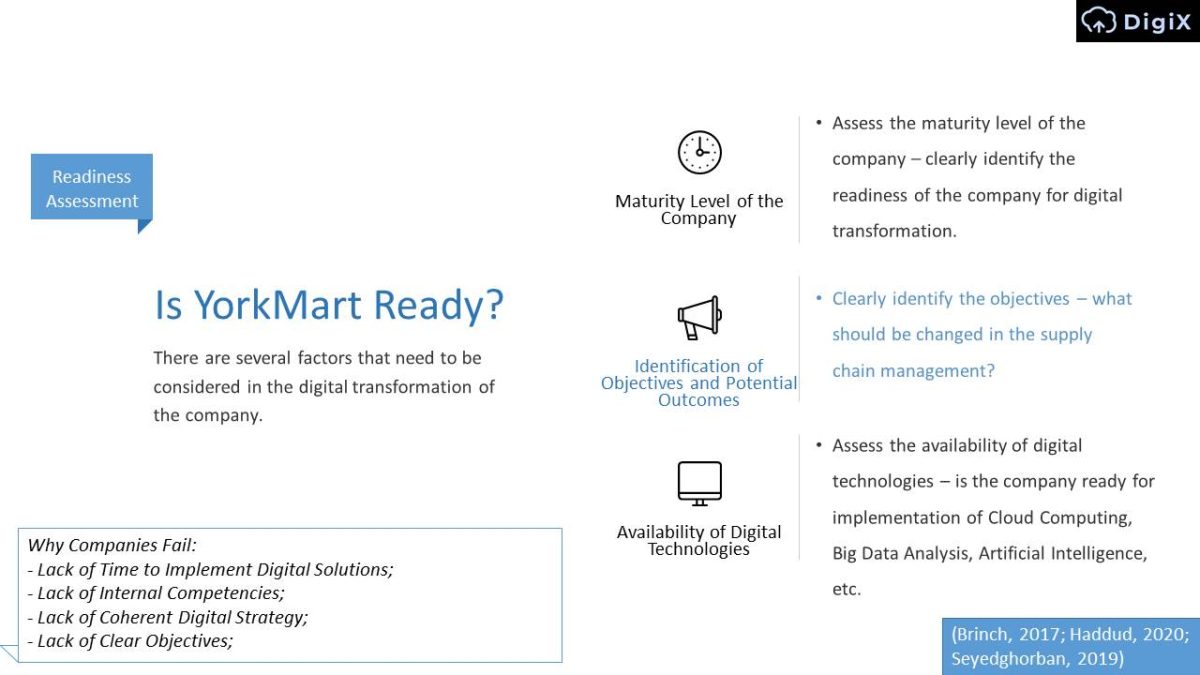
Is YorkMart Ready?
There are several factors that need to be considered in the digital transformation of the company.
Why Companies Fail:
- Lack of Time to Implement Digital Solutions;
- Lack of Internal Competencies;
- Lack of Coherent Digital Strategy;
- Lack of Clear Objectives.
Maturity Level of the Company:
- Assess the maturity level of the company – clearly identify the readiness of the company for digital transformation.
Identification of Objectives and Potential Outcomes:
- Clearly identify the objectives – what should be changed in the supply chain management?
Availability of Digital Technologies:
- Assess the availability of digital technologies – is the company ready for implementation of Cloud Computing, Big Data Analysis, Artificial Intelligence, etc.
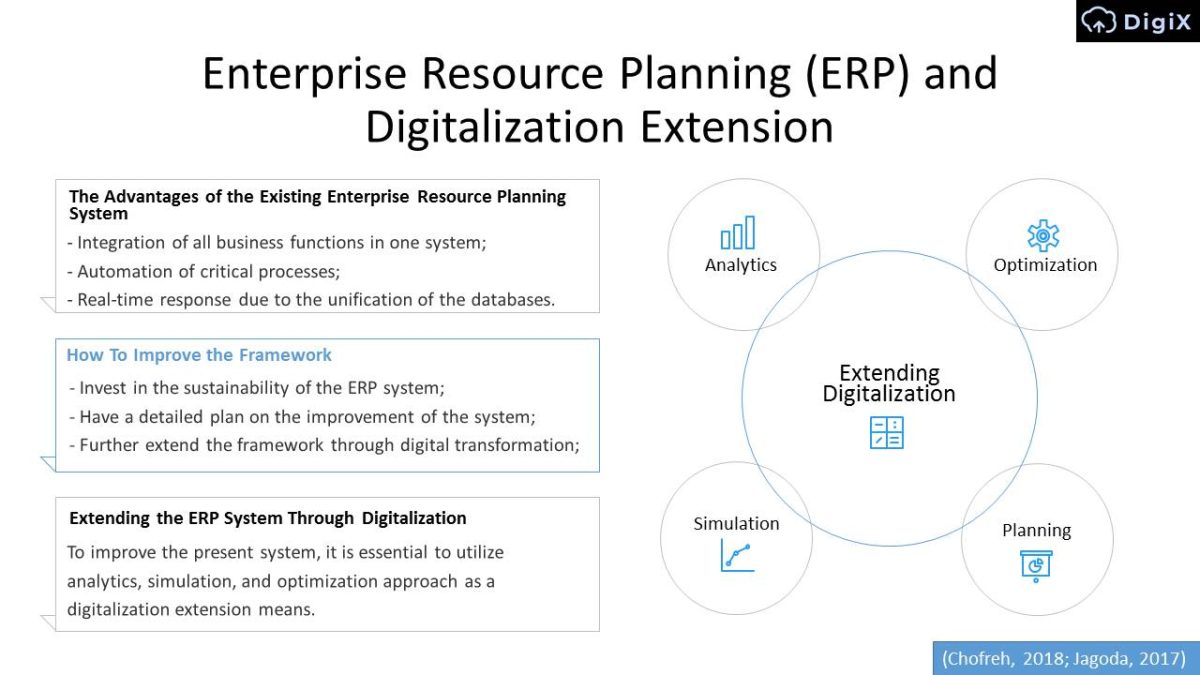
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Digitalization Extension
The Advantages of the Existing Enterprise Resource Planning System:
- Integration of all business functions in one system;
- Automation of critical processes;
- Real-time response due to the unification of the databases.
How To Improve the Framework:
- Invest in the sustainability of the ERP system;
- Have a detailed plan on the improvement of the system;
- Further extend the framework through digital transformation.
Extending the ERP System Through Digitalization:
- To improve the present system, it is essential to utilize analytics, simulation, and optimization approach as a digitalization extension means.
Extending Digitalization
- Analytics.
- Optimization.
- Simulation.
- Planning.
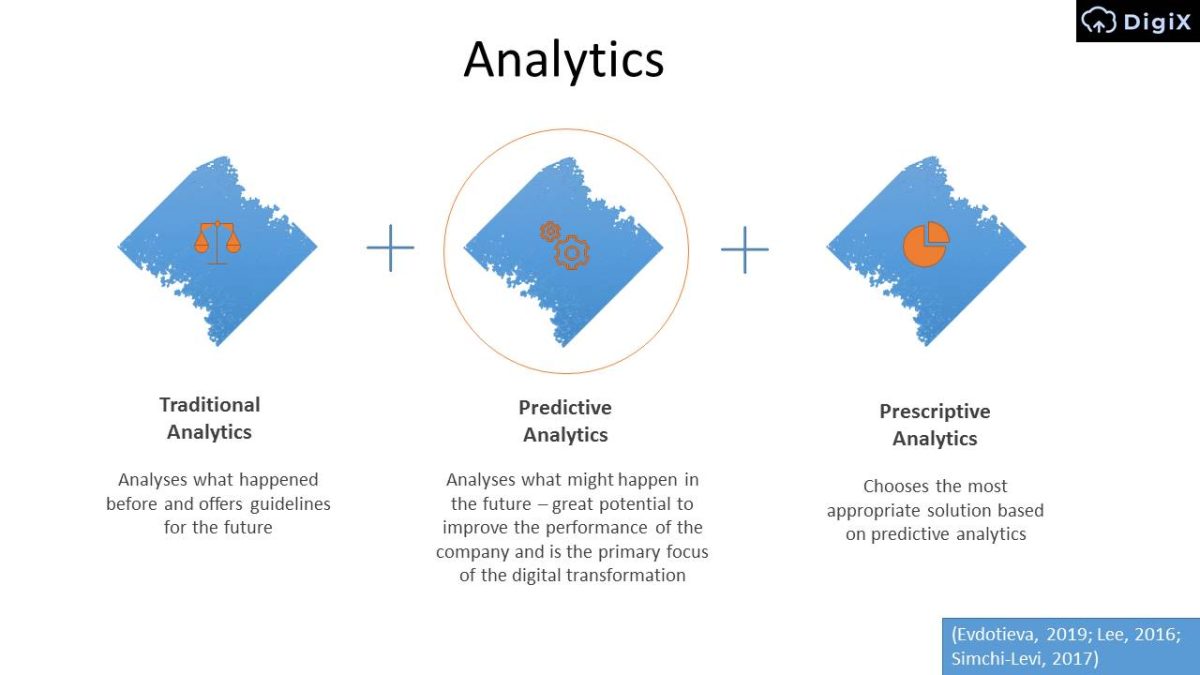
Analytics
Traditional Analytics: Analyses what happened before and offers guidelines for the future.
Predictive Analytics: Analyses what might happen in the future – great potential to improve the performance of the company and is the primary focus of the digital transformation.
Prescriptive Analytics: Chooses the most appropriate solution based on predictive analytics.
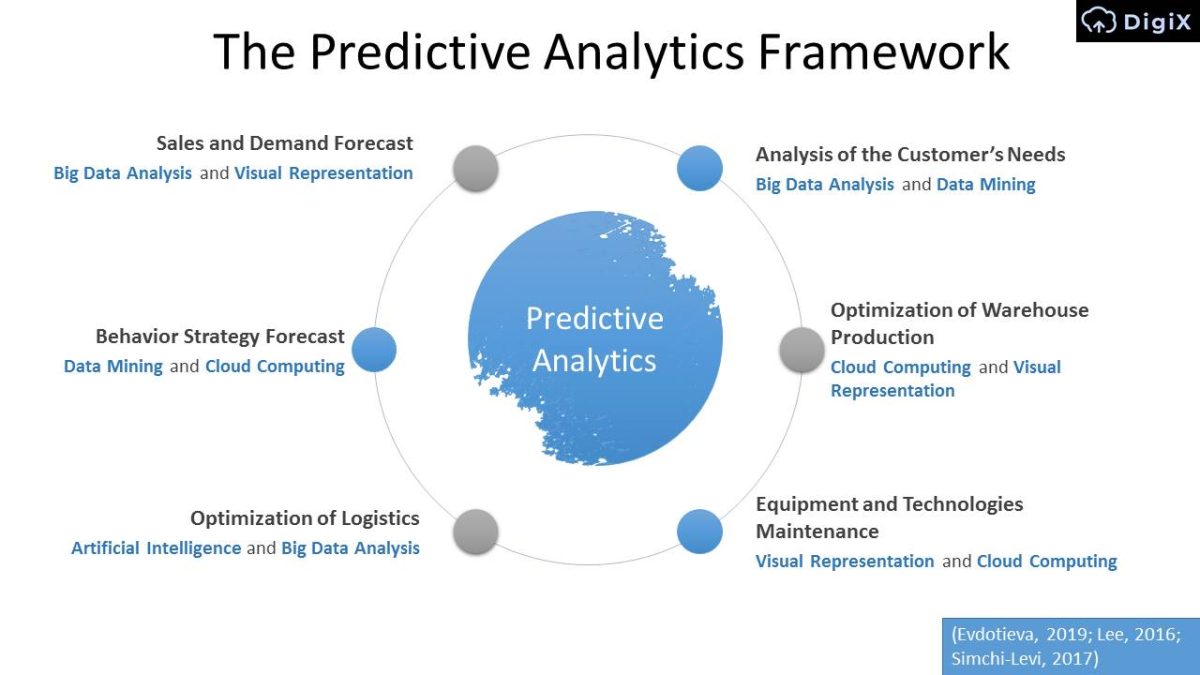
The Predictive Analytics Framework
Predictive Analytics
- Sales and Demand Forecast: Big Data Analysis and Visual Representation.
- Behavior Strategy Forecast: Data Mining and Cloud Computing.
- Optimization of Logistics: Artificial Intelligence and Big Data Analysis.
- Analysis of the Customer’s Needs: Big Data Analysis and Data Mining.
- Optimization of Warehouse Production: Cloud Computing and Visual Representation.
- Equipment and Technologies Maintenance: Visual Representation and Cloud Computing.
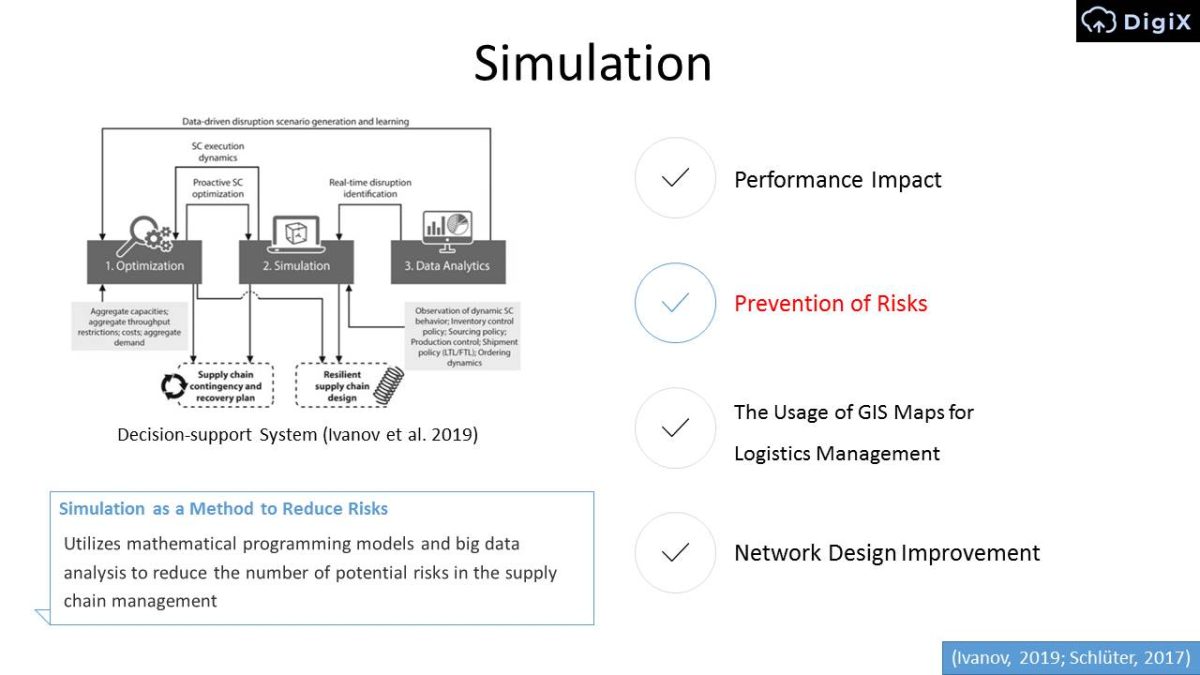
Simulation
- Performance Impact.
- Prevention of Risks.
- The Usage of GIS Maps for Logistics Management.
- Network Design Improvement.
Simulation as a Method to Reduce Risks
Utilizes mathematical programming models and big data analysis to reduce the number of potential risks in the supply chain management.
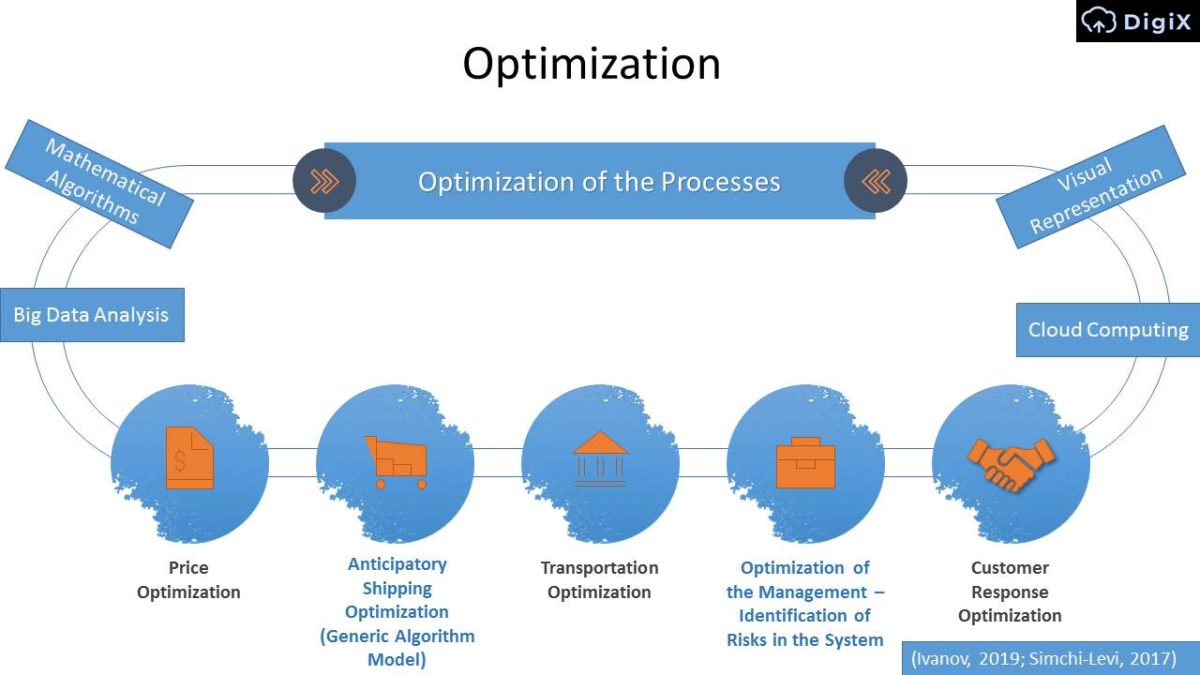
Optimization
Optimization of the Processes
- Mathematical Algorithms;
- Big Data Analysis;
- Price Optimization;
- Anticipatory Shipping Optimization (Generic Algorithm Model);
- Transportation Optimization;
- Optimization of the Management – Identification of Risks in the System;
- Customer Response Optimization;
- Cloud Computing;
- Visual Representation.
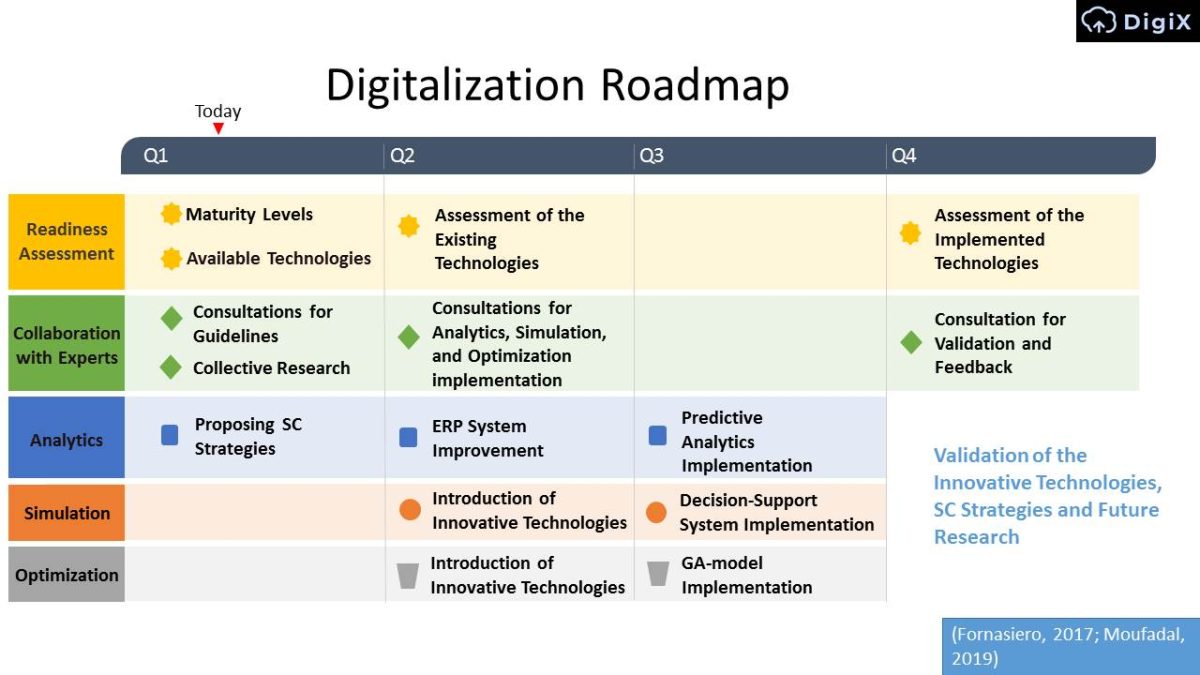
Digitalization Roadmap
Supply Chain Digitalization is Inevitable
In the contemporary market, digital transformation provides a high number of advantages for the company, and the traditional supply chain management cannot handle the competition.
Advantages
A high number of advantages, such as cost and delivery time reduction due to predictive analytics, optimization of logistics, and prevention of risks due to simulation models.
Implications
Compared to the traditional form of supply chain management, digitalization allows for a better position in the market.
Results
The development of all functions included in the SC management and the revenue growth.

References
Agrawal, P., & Narain, R. (2018). Digital supply chain management: An Overview. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, 455 (pp. 1-6). Bristol, England: IOP Publishing.
Brinch, M. and Stentoft, J. (2017), “Digital supply chains: Still more ‘wannabe’ than practice”, DILF Orientering, Vol. 54 No. 2, pp. 22-28.
Chofreh, A. G., Goni, F. A., & Klemeš, J. J. (2018) Sustainable enterprise resource planning systems implementation: A framework development. Journal of Cleaner Production, 198, 1345–1354.
De Carolis, A., Macchi, M., Negri, E., & Terzi, S. (2017). Guiding manufacturing companies towards digitalization a methodology for supporting manufacturing companies in defining their digitalization roadmap. In 2017 International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (pp. 487-495). Milan, Italy: Politecnico di Milano.
Evtodieva, T. E., Chernova, D. V., Ivanova, N. V., & Protsenko, O. D. (2019). Business analytics of supply chains in the digital economy. In S. Ashmarina et al. (Eds.), Digital transformation of the economy: Challenges, trends and new opportunities (pp. 329-336). Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG 2020.
Fornasiero, R., Marchiori, I., Pessot, E., Zangiacomi, A., Sardesai, S., Barros, A. C., Thanous, E., Weerdmeester, R., & Muerza, V. (2017). Paths to innovation in supply chains: The landscape of future research. In R. Fornasiero, S. Sardesai, A. C. Barros & A. Matopoulos (Eds.), Next generation supply chains: A roadmap for research and innovation (pp. 169-234). Switzerland: Springer Nature Switzerland AG.
Gustafsson, E., Jonsson, P., & Holmström, J. (2019). Digital product fitting in retail supply chains: Maturity levels and potential outcomes. Supply Chain Management: An International Journal.
Haddud, A., & Khare, A. (2020). Digitalizing supply chains potential benefits and impact on lean operations. International Journal of Lean Six Sigma, 11(4), 731–765.
Ivanov, D., Dolgui, A., Das, A., & Sokolov, B. (2019). Digital Supply Chain Twins: Managing the Ripple Effect, Resilience, and Disruption Risks by Data-Driven Optimization, Simulation, and Visibility. Advances in Manufacturing Technology, 309–332.
Jagoda, K., & Samaranayake, P. (2017). An integrated framework for ERP system implementation. International Journal of Accounting & Information Management, 25(1), 91–109.
Kittipanya-ngam, P., & Tan, K. H. (2019). A framework for food supply chain digitalization: lessons from Thailand. Production Planning & Control, 1–15.
Lee, C. K. H. (2016). A GA-based optimisation model for big data analytics supporting anticipatory shipping in Retail 4.0. International Journal of Production Research, 55(2), 593–605. Kittipanya-ngam, P., & Tan, K. H. (2019). A framework for food supply chain digitalization: lessons from Thailand. Production Planning & Control, 1–15.
Moufaddal, M., Benghabrit, A., & Bouhaddou, I. (2019). Industry 4.0: A roadmap to digital Supply Chains. In 2019 1st International Conference on Smart Systems and Data Science (ICSSD). Durham, England: University of Durham.
Schlüter, F. F., Hetterscheid, E., & Henke, M. (2017). A Simulation-Based Evaluation Approachfor Digitalization Scenarios in Smart SupplyChain Risk Management. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Management Science, 1, 179–206.
Seyedghorban, Z., Tahernejad, H., Meriton, R., & Graham, G. (2019). Supply chain digitalization: past, present and future. Production Planning & Control, 1–19.
Simchi-Levi, D., & Wu, M. X. (2017). Powering retailers’ digitization through analytics and automation. International Journal of Production Research, 56(1-2), 809–816.