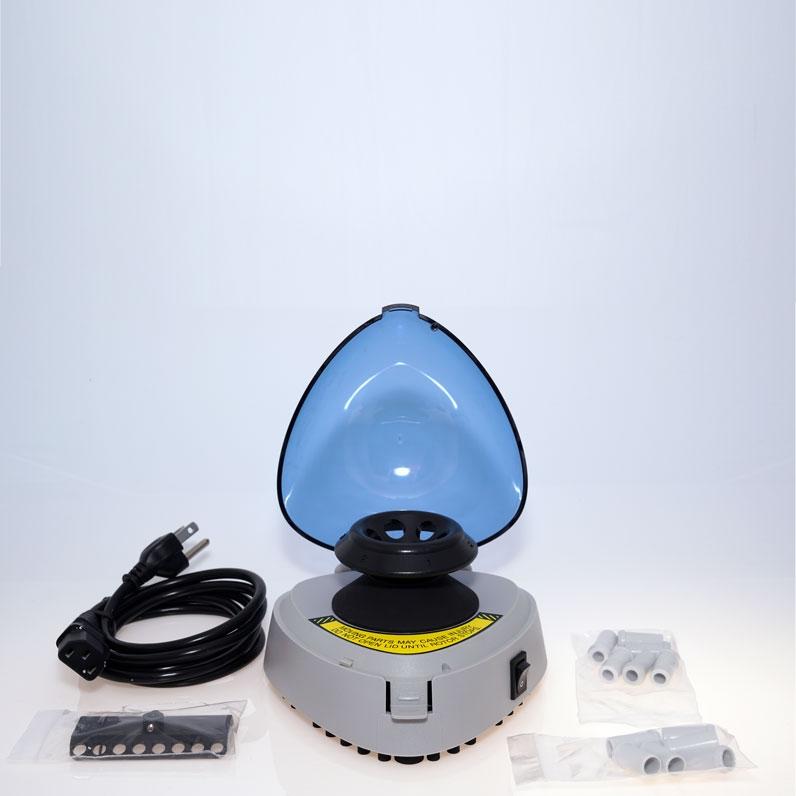
Overview
A tabletop centrifuge is a laboratory device, which is used in day-to-day research activities for simple and quick centrifugation of chemical or biochemical solution mixtures. These devices are multifunctional and mostly utilized for routine laboratory activities (see Fig. 1). Tabletop centrifuges are primarily used for immunological, cytological, and biochemical analyses, where the research involves the separation of a mixture’s contents on the basis of elements’ molecular weight. The outcome of centrifugation is manifested in having a solution with distinctive stripes, where each stripe represents a set of molecules with a certain molecular weight.

Safety
Before using the device, make sure that all parts are not defective since the rotatory parts reach a substantial rotational force, which can cause physical harm if the device is not operational. Dangerous objects must not be placed near the device in order to avoid hazardous interactions. The centrifuge must be kept at an optimal temperature, preferably a room temperature, ranging between -20C and +60C. Only original accessories and parts must be used in all aspects of operating the device. A faulty or low-quality part or accessory can lead to malfunction and endanger people present in its proximity. The voltage of a power supply must match the specified voltage value. Make sure that the power source is in close proximity in order to have easy access to it (see Fig 2.).

Operation
A tabletop centrifuge can only be operated after the rotor was properly fixed. Fixation of the rotor must be done with a 15 mm wrench only, which comes with the equipment. When fixating the rotor, ensure that the leading hand is holding the wrench horizontally to the surface of the rotor. The non-leading hand needs to hold the rotor at the base of the central rotor holder. Avoid holding the rotor at its sides and vial holders as it will permanently damage the vial holders, and it also can cause improper rotor fixation, which will make the device malfunction.
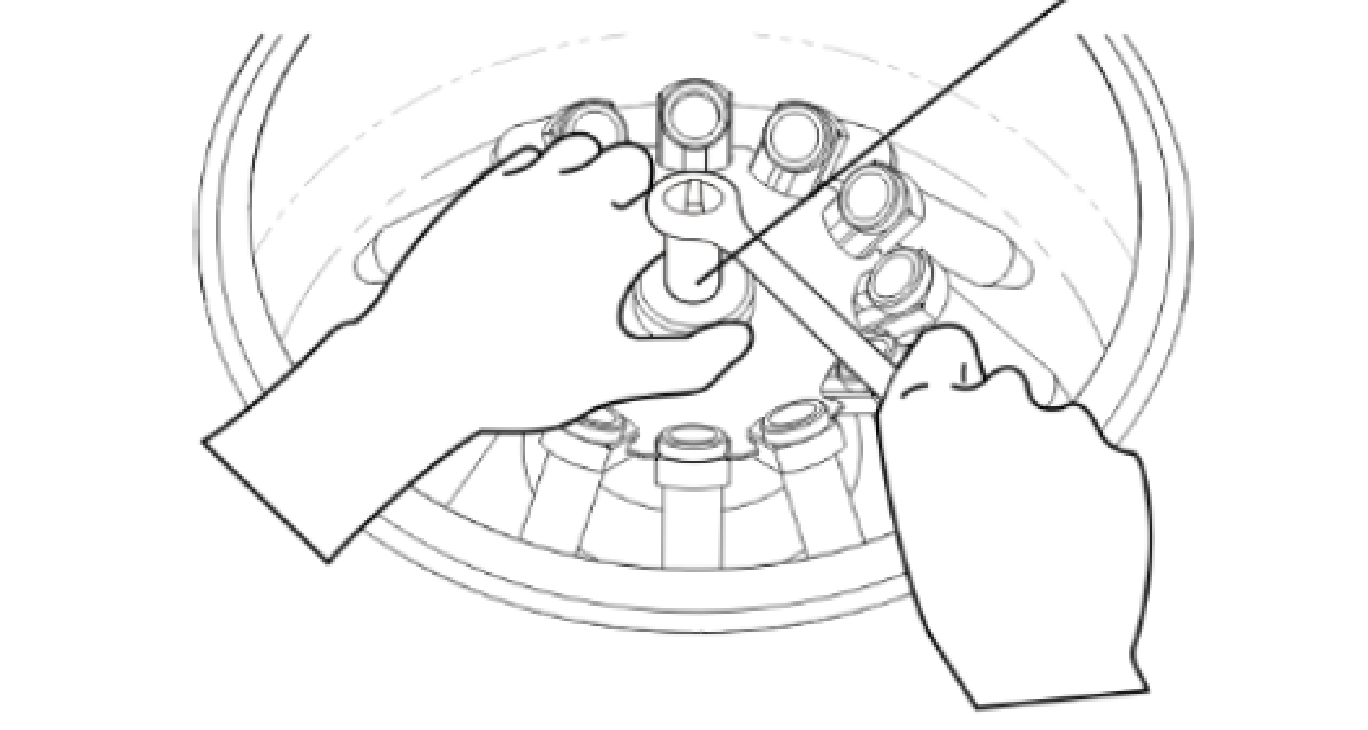
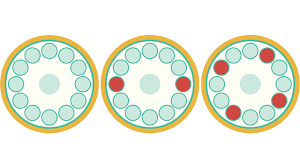
The next step involves the placement of the vials, which need to be placed at the opposites side around the rotor. Always make sure that an even number of vials are placed in the device. In case of having an odd number of vials, use an additional one with water to provide a counterbalance. The first vial can be placed anywhere in vial holders. The second vial is placed directly on the opposite side of the first vial. The following two vials are placed in a similar fashion but perpendicularly (see Fig. 4). Vial weight counterbalance is critical for the proper functionality of a tabletop centrifuge. The incorrect vial placement will lead to rotor rotation at an angle, which will damage the spinner and the device itself.
After vials are placed accordingly, make sure to close the centrifuge by locking the cap. Set the RPM or rotations per minute to the desired value, which will depend on the content of the vials and desired separation goal. A higher range of rpm will result in faster molecule movement towards the bottom of the vial. Larger molecules always move faster than smaller molecules, which is why a proper range needs to be set in accordance with the research needs. The start button needs to be pushed to initiate the process.