A tariff is a duty enforced by the state on imports or exports. It increases the cost of imported products thus making them expensive compared to local products. They are imposed to protect domestic industries from external competition; protect local consumers from harmful products, promote employment creation activities, enhance national security and for retaliation purposes.
Effect of a tariff on import market
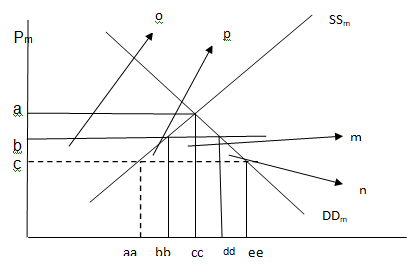
Where:
SSm = domestic supply of solar panels
DDm = Domestic demand for solar panels
Pw=c= is the world price
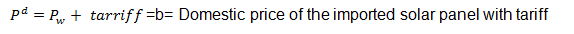
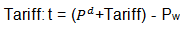
It is clear that any tariff will cause the quantity and volume of imports demanded to fall and the consumer price to increase thus reducing the price received by foreign exporters. Under free trade, the world price of solar panels are Pw . At this point, the domestic demand exceeds local supply levels by the amount equivalent to Qs (aa) less Qd (dd). This demand gap is filled through importation.
If the government levies a tariff of say 30 percent, the new price will be higher with the same percentage. The new price now including tax will be
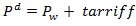
These higher prices discourage consumers from consuming and thus lowers consumer surplus (n) but raises the government revenue levels by (m).
The net welfare change will be: (losses+ gains). The decline in consumer surplus will be o+p+m+n, producer surplus will increase by (a) and government revenue will be (m). The net welfare decline will therefore be o+p+m+n- (p+n) =p+n.
The label (p) is dead weight loss or production inefficiency created by increasing prices thereby shifting available resources away from the intended sector and towards solar panels. The label (n) is the dead weight loss/ consumption inefficiency created as a result of increased prices of panel.
Overally, because U.S.A is a small economy in consideration to the world prices, there will be no effect of a tariff on the terms of trade. Therefore, world price will continue to exist at. Tariffs increases the prices of goods by the same margin of the tax.
For example, a 50 percent tariff will increase the prices by 50 percent. Such initiatives make the local producers competitive but will reduce the demand for the imported varieties. In fact, the local demand for imported goods falls while domestically produced goods prices increase.
In our situation, the local consumers which happen to be solar power companies will reduce the importation of Chinese solar panels due to increased prices coupled with low demand have narrowed their margins and may in most cases result in losses to the firm.
Non tariff barriers are used as a cover up for protectionist or discriminatory motives of states and to limit competition from imported goods. Examples include: subsidies, import quotas, voluntary export restraints, import licensing and technical standards, environmental and health-related standards, packaging requirements, variable levy and government export restraints.
The government should resort to import quota- a restriction on quantity imported. This measure will hike the prices of imported products above their world price levels thereby resulting in rents which accrue only to participating importers (Deardorff, 1999).
The International Trading Commission (ITC) is obliged to determine the domestic industry suffering due to material injury from imports of subsidized commodities. In its decision, it considers industry’s output, market share, sales, profits and employment.
This type of request falls under section 701 of subsidized imports which focuses on production, manufacturing and exports. However, the proof of material injury lies with the actors. Under this act, the ITC is responsible for injury determination while ITA is charged with subsidy determination (Coughlin, 1991).
The ITC imposed antidumping and countervailing duties. Such policies have been effectively used in steel manufacturing, industrial equipment, computer chips manufacturing, textiles and consumer product manufacturing.
Requirements for filing Countervailing or Antidumping Duties Petition
For petition application to be considered appropriate, first, it must be filed by local interested parties or unions within the local producing industries for the import competing product under investigation. Secondly, the petitioners should represent a minimum of 25 percent of local production levels.
Third, the act demands that the petition contain information concerning conditions of U.S. market and local industry and an evidence of unfair subsidization or dumping.
World Trade Organization (WTO)
The WTO was established in 1995 to replace General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). Its mission is to encourage smooth flow of trade by lowering trade barriers and solving trade related disputes as they arise between members. It therefore facilitates efficiency in conducting business amongst producers, importers and exporters.
The organization is governed by first, the principle of no discrimination to trade – countries should not discriminate against their trading. Secondly, it supports free trade through negotiation to reduce custom duties, import bans or quotas.
Third, it encourages investment opportunities through stability and predictability arrangements. Fourth, it promotes just trade competition and finally it encourages economic reforms and development.
The main functions of WTO include: controlling WTO trade agreements, handling disputes related to trade, facilitate trade negotiations forums, enhance cooperation with international organizations, overseeing national trade policies and finally, offering technical assistance to less developed countries.
Challenges of WTO
First, WTO has many controversial rules concerning intellectual property, investment and service which have a far reaching implication on developing countries. Second, although WTO decision making is by accord, the organization agreement does provide for the possibility of decision-making by majority vote.
Third, although the organization has a worldwide connection, bilateral trading agreements like European Union have grown and have had a strong enforcement mechanisms compared to WTO therefore they impose higher standards on developing countries. Fourth, the organization is well known for hidden and undemocratic decision making processes making complexing it for less developed countries to reflect their interests.
Fifth, the organization also has no formal connection with Non Governmental Organizations. Sixth, WTO rules are in consistent with most human rights acts but they are applied for the betterment of human beings. Finally, the working of WTO allows some tariffs and non tariff barriers thus limiting its principle of fair.
References
3dthree, (2004).The World Trade Organization: Human rights and peoples’ diplomacy training. Web.
Chapter 8: Analysis of tariffs and other barriers to free trade. Web.
Coughlin, C. C. (1991). U.S. trade remedy laws: Do they facilitate or hinder free trade. Web.
Deardorff, A. V. (1999). Nontariff barriers and domestic regulation. Web.
World Trade Organization report. (2011). Understanding the WTO. Web.