Introduction
Orange is a leading French telecommunication company, which operates in 29 countries and it has more than 263 million customers (“Orange – 2017 Consolidated Financial Statements”). It offers mobile telecommunication services to individuals and businesses, fixed telephone services, and communication application development, integration, and management services.
Stock Price Information
The company’s stock symbol is ORA, and it is listed on Euronext Paris. It has issued 2,660 million shares (“Orange – 2017 Consolidated Financial Statements”), and its current market capitalization is €36.935 billion. The selected period for analyzing its stock performance starts from 1 January 2017 till 31 December 2017. It could be noted that the opening stock price was €14.57 and the closing stock price was €14.475, which indicated a capital loss of 0.65% (“Orange”).
It affected the value of equity invested in the company’s stocks. The investors should not panic as the change was small, and the management undertook various business decisions that would contribute positively to the growth of its business in the coming periods. It was reported by Mayeri that Orange’s business services segment achieved more than 200,000 customers in December 2017, which was a positive sign for the growing business of Orange (Mayeri). The stock price trend is analyzed based on Orange’s announcements during this period and the assessment of risks associated with its business. The stock price trend could be observed from Fig. 1 given below.
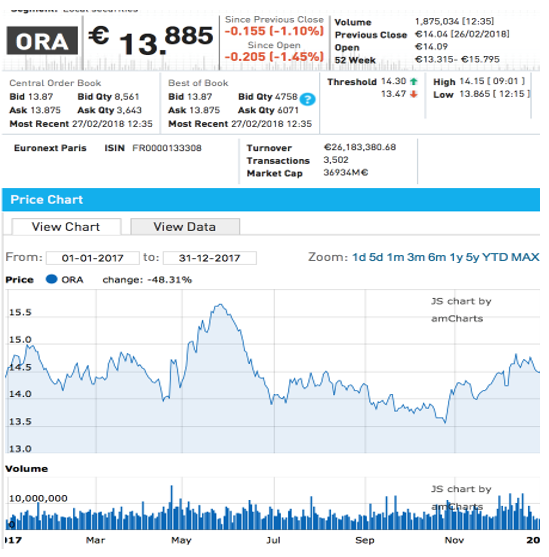
It could be noted from Fig. 1 that the company’s stock price peaked it’s 52-week highest on 29 May 2017 (i.e., €15.735) and its lowest on 25 October 2017 (i.e., €13.565) (“Orange”). Moreover, the fluctuations in the stock price were low, and its beta value is 0.76, which means that the changes in the stock price were less than those observed in the index value (“Orange”).
Assessment of Risks
Orange faced tough competition from other mobile operators in different markets. The competition in the market-implied a tradeoff between low pricing for customers and investment for business development. The rivalry between companies poses a great risk for Orange as the demand for new and better technologies is increasing, which require significant investments by telecommunication companies.
Therefore, managing competition is crucial through effective marketing and developing customer loyalty. The business needs to renew its relationships with corporate clients as it has generated the largest proportion of its revenue from corporate sales. Based on this strategy, Orange company integrated the IT network and structure of ZF and TRW and renewed its contract for the next four years (“Orange Business Services Integrates Global Network”).
It could be noted that it is focused more on business development, which would generate positive outcomes in the later periods. Orange announced on 26 October 2017 that it would acquire Business & Decision, which is a listed company, to accelerate its growth in data management (“Orange Signs Agreement to Acquire Business”). The announcement had a positive impact on its stock price. The management’s decision to acquire Business & Decision was also part of its strategy to boost its position in the data management services industry. It could help the company to generate more value from its operations in different markets particularly France.
Orange prepares its financial statements on a consolidated basis, which means that it operates various subsidiaries and brands in different countries. One of the risks associated with international business operations is the currency exchange risk. It hedged its foreign currency positions by using different risk management techniques including forwarding contracts, swaps, caps, and floors. Its cash flows were not only affected by the exchange risk but also interest rate, inflation, and other market conditions prevailing in countries of operation. The management’s ability to finance business operations could be affected by adverse changes in the value of these economic variables, which would also hurt the stock price.
It was indicated that Orange would incur a loss of €161 million if the interest rate increases by 1% (“Orange – 2017 Consolidated Financial Statements”). The sensitivity of the company’s liquidity and solvency position could have negative effects on its stock price. The investors can protect their equity by investing in a diversified portfolio. It implies that they can buy stocks of companies operating in different industries. The risk-level of investors determines companies that match their risk profiles.
The credit rating of Orange’s bonds indicated that the credit rating agencies did not expect it to face any major problems with debt management. They determined a low-risk profile because of its strong business position and diversification of revenue streams. Therefore, it could be stated that investment in the company’s stocks suits those investors who have a low-risk tolerance. They can invest in this stock and expect a low return on investment. The recommendation was also supported by the stock price trend observed in Fig. 1 as the price volatility remained low, which means that the stock price movements remained within a small bandwidth.
The economic conditions of Europe and other global markets could also affect the company’s business. Its major earnings were generated from its business in European markets. Therefore, it could be stated that any adverse change in the economic factors could reduce Orange’s revenue and increase its expenses. The management could mitigate this risk by investing in marketable securities in those markets that are economically stable.
It would ensure that the company maintains sufficient liquidity to finance its operations during the economic downturn. On the other hand, it is indicated that investors are at high risk of losing their investment value. The market risk cannot be systematically eliminated by all investors. Therefore, they should keep this in mind while investing in the company’s stocks whose main business depends on European markets.
Orange also faced litigation risk, which was due to different court cases against it in different countries. There is a case pending in the Egyptian Court related to the contracted rates of interconnection between NTRA and Orange. Another case filed against Orange Bank could lead to a loss of €480 million to be paid in a settlement deal (“Orange – 2017 Consolidated Financial Statements”). The company did not recognize the loss provision in its financial statement.
Moreover, there were pending cases related to a tax audit, which could also result in penalties. All these cases could affect its earnings, which means that the profit attributable to common shareholders would reduce. Investors are unlikely to get protection against these claims. Therefore, they should be ready to experience a decline in the value of their investment in Orange’s shares.
Conclusion
It could be concluded Orange had a stable financial position in 2017. It faced minimum risks and investors can also expect a low return on their investment in Orange’s shares.
Works Cited
Mayeri, Elizabeth. “Orange Business Services Surpasses 200,000 User Subscriptions for Cisco Spark.” Business Wire. Web.
“Orange.” Euronext, 2018. Web.
“Orange Business Services Integrates Global Network and IT Infrastructure of ZF and TRW.” Orange. 2017. Web.
“Orange – 2017 Consolidated Financial Statements.” Orange, 2018. Web.
“Orange Signs Agreement to Acquire Business & Decision and Accelerate Orange Business Services’ Growth in Data.” Orange. 2017. Web.