Introduction
Biscuits are some of the common snacks found within Australian market. The products mostly target the young people but can be consumed by any anybody regardless of age or gender. The consumers of biscuits are therefore varied. However, there are concerns about the biscuits on health; it is medically proven that too much consumption of snacks like biscuits have the potential of causing toothache, and since they contain sugar they can increase sugar level in the body. This is one of the main factors determining the amount of consumption of biscuits as snacks. This report examines the biscuit industry within Australia (Tiezzi, 2006).
Market Background
The biscuit market in Australia has undergone lots of transformation since the first time biscuits were manufactured in Australia. The first biscuits to be introduced in Australia appeared in the 17th and 18th centuries; they were hard and were referred to as ‘sea biscuits’ because they were mostly used by sailor at sea. Since then, the biscuit products have evolved to become one of the easiest snacks to eat within the Australian market and beyond.
Since the introduction of biscuits in Australia, so many market players have entered the industry and the competition has been increasing tremendously. Currently, the leading biscuit manufacturing company in Australia; it has over forty years of experience in biscuit production and supply. Nonetheless, the whole biscuit market within Australia has been characterized with lots of acquisitions and mergers within the past decade. This has been due to the fact that producers seek to increase their market share and increase their base with commercial synergies. The market industry has three major competitors which are the Arnotts Biscuits Holdings Pty Limited, Goodman Fielder Limited and Kraft Foods (Australia) Limit. Their market shares are as follows:
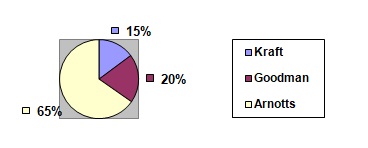
Looking at the pie chart, it is clear that Arnotts Biscuits Holdings is leading with 65% of the market share. This owes to the fact that the company is the first amongst the initial biscuits companies to operate in Australia. The second largest company in the market is Goodman Fielder Limited with 20% and the last is and Kraft Foods (Australia) Limit with 15%. However, it is important to note that there are over 400 biscuit companies whose products access the Australian biscuits market industry (Dun & Bradstreet, 1995).
Environmental Factors
There are a number of environmental factors affecting the biscuit industry in Australia. The prices of biscuit products are influenced by several political factors. One of the factors is the Goods and Service Tax which accounts for approximately ten percent of most transactions across all the industries. It is also important to note that the prices of biscuits are vulnerable to any government decisions with regard to prices and production policies.
Economic factors have the most potential effects on the production of biscuits. Kin case of economic slow down, whether global or domestic, the biscuit industry is most likely to experience its negative impacts in terms of productivity and consumption. During economic slowdowns, organizations and individuals tend to cut on their expenditures; they limit such expenditure to basics only. Another economic factor that has negative effects is inflation and currency fluctuations which can possibly destabilize the market prices for biscuits.
In the 21st century, effective and efficient productions are facilitated by increased level of technology. Therefore, it is important to note that increase in related technology is likely to enhance the production of biscuits with the Australian market. This greatly depends on how fast the biscuit companies adopt the new technological inventions and innovations.
Culturally, the consumption of biscuits and other snacks has been on the increase within the Australian market. The number of consumers of these products is rising tremendously. It implies the consumption of such snacks is strongly becoming part of the Australian population. Therefore, the biscuit industry is set to gain more in terms of revenues and profit margins.
Nestle Company
Background
The Nestle Company was started in 1860s by a trained and experienced pharmacist who did lots of experiments with a view of coming up with an alternative nutrition for mothers who were not able to breastfeed their babies. In 1905, the company was formed after a merger and operated under the name Nestle and Anglo Swiss Milk Company. It ultimately expanded to other nations like the United States, Spain, Germany and Britain in the period running from 1905 to 1918 (Nestle, 2010).
The company experienced increased sales during the First World War; however, after the end of the wars, the company experienced slowed sales due to the fact that most consumers went back to purchasing fresh milk. After the Second World War, the company came up with workable strategies that saw the company expand its operations. Never the less, the end of World War Two resulted into the drop of its revenues and profit margins.
Despite the slowed financial performance of the company, it began to expand its operations globally by establishing its plant in developing countries. The consequent of this expansion was the recovery of its high performance in which its productions and sales increased impressively. Its expansion has included acquisition and mergers with other like minded companies (Nestle, 2010).
Nestle Operations
The company operates on global scale; it has presence in both developed and developing nations where its products are being produced and consumed. It has international human resources, huge capital base and a large number of customers spread across the world. The company has diversified its brands besides investing in unrelated products. It owns 30 percent of the L’Oreal Cosmetic Company. However, the company owns brands like Kit Kat, Pickled Plum, Bubblegum and Onctueux amongst other many brands.
The operations of the company include collecting fresh milk from farmers and store the fresh milk with a limited period of time before using it as raw material for the production of its varied brands. The company manufactures its products, keeps its own inventory and ensures that its final products are largely distributed in the market for final consumptions. In addition, the company is also involved in other unrelated operations through its Corporate Social responsibilities. Apart from participating in environmental sustainability campaigns; it also supports local activities in regions of its operations.
Mission Statement
The Nestle Company believes that use of research for its products can ensure it provides it consumers with better quality life. The company is committed in providing the consumers of its products with quality and safe food items; the food products that meet the optimum physiological needs of the consumers. Moreover, the company ensures its products are tasteful and pleasurable.
Nestle SWOT Analysis
Strengths
The company has several strengths that are able to keep it as the market in its industrial operations. The company has international presence hence making it easy for it to penetrate more market segments. Besides, the company has large capital base for its expansion. The company also enjoys a large number of customers for its range of products giving it a competitive advantage over its competitors. The company’s other strengths include having a well experienced and focused Chief Executive Officer and strong research team with the ability to conduct though research and come up with quality innovations (Castel Articles, 2005).
Weaknesses
The main weakness of the company is that its expansion to other countries has not been successful. This is due to tight competition and business policies existing in those countries. For instance, its LC1 was not as successful in France as the company wished it should have been. This might have been due to the possibility that consumers might have considered the LC1 division as being scientific and therefore might have misunderstood the products to be food instead of drug (Castel Articles, 2005).
Opportunities
The health-based goods are becoming very common in the global market. This is attributed to growing health concerns in which consumers are becoming more sensitive than ever with what they consume in terms of food (Castel Articles, 2005).
Threats
A number of markets in which the company plans to enter are already occupied by strong competitors. Besides, the company is prone to effects of economic slowdowns. Another threat to the company is the possible entry of new players into the market. This is likely to flood the market and hence destabilize prices in the industry. Moreover, political instabilities and currency fluctuations in its countries or regions of operations may adversely affect its operations (Castel Articles, 2005).
Reference List
Castel Articles. (2005). Nestle SWOT Analysis. Web.
Dun & Bradstreet. (1995). Jobson’s year book of Australian companies, Volume 66. Australia: Riddell Information Services
Nestle. (2010). History. Web.
Tiezzi, E. (2006). The sustainable city IV: urban regeneration and sustainability. Volume 93 of WIT transactions on ecology and the environment. Australia: WIT Press.