Introduction
To begin with, there is strong necessity to mention that the concept of business cycles is the concept aimed at analyzing the trends and processes in business sphere of a single company or the whole State. Originally, the analysis of GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment, as well as labor costs requires complex analysis, based on the various economic approaches. One of such approaches is the Real Business Cycle Theory, which is regarded as the macroeconomic model in which all the fluctuations in the numbers may be accounted in accordance with the real shocks.
Analysis
The fact is that, all the economic indicators, which may be analyzed with the help of Real Business Cycle concept, are regarded to be cyclic on default. It should be stated that the RBC theory presupposes several types of fluctuations: these are secular (trend), business cycle, seasonal, and random. Barlevy (2005) in his research states the following fact: “Unlike other leading theories of the business cycle, it sees recessions and periods of economic growth as the efficient response to exogenous changes in the real economic environment. That is, the level of national output necessarily maximizes expected utility, and government should therefore concentrate on the long-run structural policy changes and not intervene through discretionary fiscal or monetary policy designed to actively smooth economic short-term fluctuations”. In the light of this fact there is strong necessity to emphasize that the rates of unemployment, labor costs, GDP and other economic factors and indicators are so dependent on various factors that fluctuations often seem random, independently on the expected utility.
As for the real numbers of unemployment, Economic News Release (2009) states that in July 2009 the payroll employment rates continued to decline. The U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the unemployment rate of 9.4 percent. It is stated that the average monthly job loss during May – July period accounted half the average decline for November through April (-331,000 in comparison with -645,000). The job losses continued in July in numerous industrial sectors and in total up to 15 million people stayed unemployed. As for the numbers, Economic News Release (2009) gives the following image of the unemployment rates: “Among the major worker groups, unemployment rates for adult men (9.8 percent), adult women (7.5 percent), teenagers (23.8 percent), whites (8.6 percent), blacks (14.5 percent), and Hispanics (12.3 percent) were little changed in July. The unemployment rate for Asians was 8.3 percent, not seasonally adjusted. Retail trade employment declined by 44,000. Job losses in the industry had averaged 27,000 per month over the prior 3 months. Employment in wholesale trade fell by 19,000 in July, with the majority of the decline occurring among durable goods wholesalers.”
The increase of the unemployment rates causes the liberation of the labor force, and the labor market becomes overfilled with unemployed specialists. The fact is that, this causes an immediate decline of the labor costs. However, on the other hand, this is the main reason of productivity increase in lots of manufacturing sectors. The fact is that, the main output and hours in manufacturing, which is about 11 percent of business sector in the USA, has a strong tendency of varying from quarter to quarter in comparison with the indicators of aggregate business and nonfarm sector of US business.
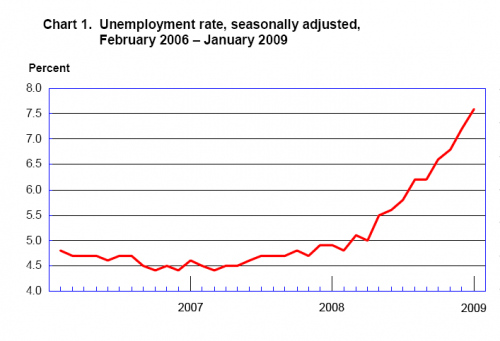
The chart represents the dynamics of the unemployment rate, and the main reason of these dynamics is covered mainly in the financial occasions in the world economy. According to the forecasts, the unemployment is close to its peak; nevertheless, it will be still growing for some time, as momentum of the process is rather powerful, thus, some time will be needed to stop the increase.
Economic News Release (2009) describes the overall tendency in the sphere of employment, and how it is related to the issues of GDP changes: “Business sector output per hour increased 6.3 percent from the first quarter to the second quarter of 2009, as output decreased 1.8 percent and hours of all persons engaged in the sector–employees, proprietors, and unpaid family workers–fell 7.5 percent (seasonally adjusted annual rates). The productivity increase was the largest since the third quarter of 2003, when output per hour increased 8.4 percent.” From this perspective there is strong necessity to emphasize that from the second quarter of 2008 to the second quarter of 2009 the rates of productivity grew up to 1.9 percent in the business sector. The output, in its turn, fell 5.4 percent and hours fell 7.1 percent. In average, the annual rate of business sector productivity had increased up to 2.6 percent for the period 2000 – 2008.
Criticism and Alternatives
Originally, all the similarities and tendencies, represented in the research of the economic indicators, can not be regarded as deterministic. The same may be stated about the fluctuations of the trend, nevertheless, the burning issue of all these considerations is covered in the statement that people mostly prefer economic booms rather then recessions, nevertheless, recessions are generally explained by human actions, and, it is stated that mostly human actions control business cycles in macro and micro economic scales. From this point of view, it is necessary to give the statement by Knoop (2004), who claims that macroeconomic indicators are closely linked with the matters of mainstream economic policy, performed by people: “Real Business Cycle Theory is a major point of contention within macroeconomics (Summers 1986): RBC theory categorically rejects Keynesian economics and real effectiveness of monetarism, which are the pillars of mainstream macroeconomic policy, while such noted mainstream economists as Larry Summers and Paul Krugman categorically reject RBC theory in turn”. However, it is necessary to mention, that the followers of Keynesian economic approach claim that business cycles of the US economic development are often correspond to the concept of effective demand, which fully contradicts the Real Business Cycle Theory, and its concept of supply-side. Consequently, the critical feature of the fluctuations, which defines the commercial convulsions of the market are regarded to be the common variations of the widely diffused economy and the commercial dealings and its tangles of finance.
Conclusion
Finally, there is strong necessity to mention that the fluctuations in the GDP rates, unemployment and labor cost can not be explained by some appropriateness or regularity. Business cycles have their own reasons and their own consequences, nevertheless, these reasons are so numerous, that all the occasions are close to random occurrence. Still, Real Business Cycle Theory explains the necessary basics for these fluctuations, and helps find the interconnections between several factors of macroeconomic activity.
References
- Barlevy, G. (2005). The Cost of Business Cycles and the Benefits of Stabilization. Economic Perspectives, 29(1), 32
- Economic News Release (2009) Employment Situation Summary, Bureau of Labor Statistics. Web.
- Economic News Release (2009) Productivity and Costs, Second Quarter 2009, Preliminary. Bureau of Labor Statistics. Web.
- Knoop, T. A. (2004). Recessions and Depressions: Understanding Business Cycles. Westport, CT: Praeger.