Introduction
The chain of infection is a theory that aims to explain how an individual could acquire an infection from another. In many instances, the chain of infection theory presents a way for epidemiologists to collect the relevant information they need for preventing the disease from spreading or eliminating its occurrence.
Chain of Infection Theory
Consisting of six links, the chain requires each link to be suitable to the organism in order for a disease to continue spreading. This means that the breaking of only one link in the chain can intervene with an epidemic (Juraja, 2007). The following is the explanation of each link involved in the chain of infection:
- Infectious agent. Infection agents are organisms that act as infiltrators of organisms and turn them into hosts.
- Host. A host is the infectious chain link that acts as a receiver of an infection. Hosts can have different susceptibility levels based on their genetic and immunity factors that influence their resistance to pathogens.
- Reservoir. Reservoirs refer to environments where infectious diseases can live, grow, or multiply. They can differ based on the characteristics of infection.
- Transmission Mode. An infection can be transmitted to a host through different transmission modes such as direct and indirect. Direct modes include droplet spreads and direct contacts while indirect are associated with airborne, vectorborne, and vehicle-borne transmission.
- Portal of Entry. This chain link is associated with the way in which a harmful pathogen enters a host.
- Portal of Exit. This chain-link refers to the way in which a pathogen exits the host and is usually connected to the location of the pathogen.
For public health, understanding the processes involved in the chain of infection presents numerous positive implications such as the introduction of control measures targeted at the management of infectious diseases. Because of this, health care providers will be able to develop an action plan for addressing a problem; among such interventions are vaccinations to developing antibodies, isolations of hosts to prevent direct transmissions, protective equipment for shielding portals of entry.
Example of an Infectious Disease
To understand the mechanism behind chains of infections, it is important to provide an example of a specific disease. For instance, malaria is among the most common infectious diseases that can be applied to the chain of infection theory. Understanding the mechanisms involved in the diseases is important because health care costs for managing malaria are expected to reach $8.7 million by 2025 (Patoillard, Griffin, Bhatta, Ghani, & Cibulskis, 2017). Malaria is a dangerous and even life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease caused by parasites called Plasmodium (Malenga et al., 2017). The chain of infection graph below shows the cycle of malaria’s development:
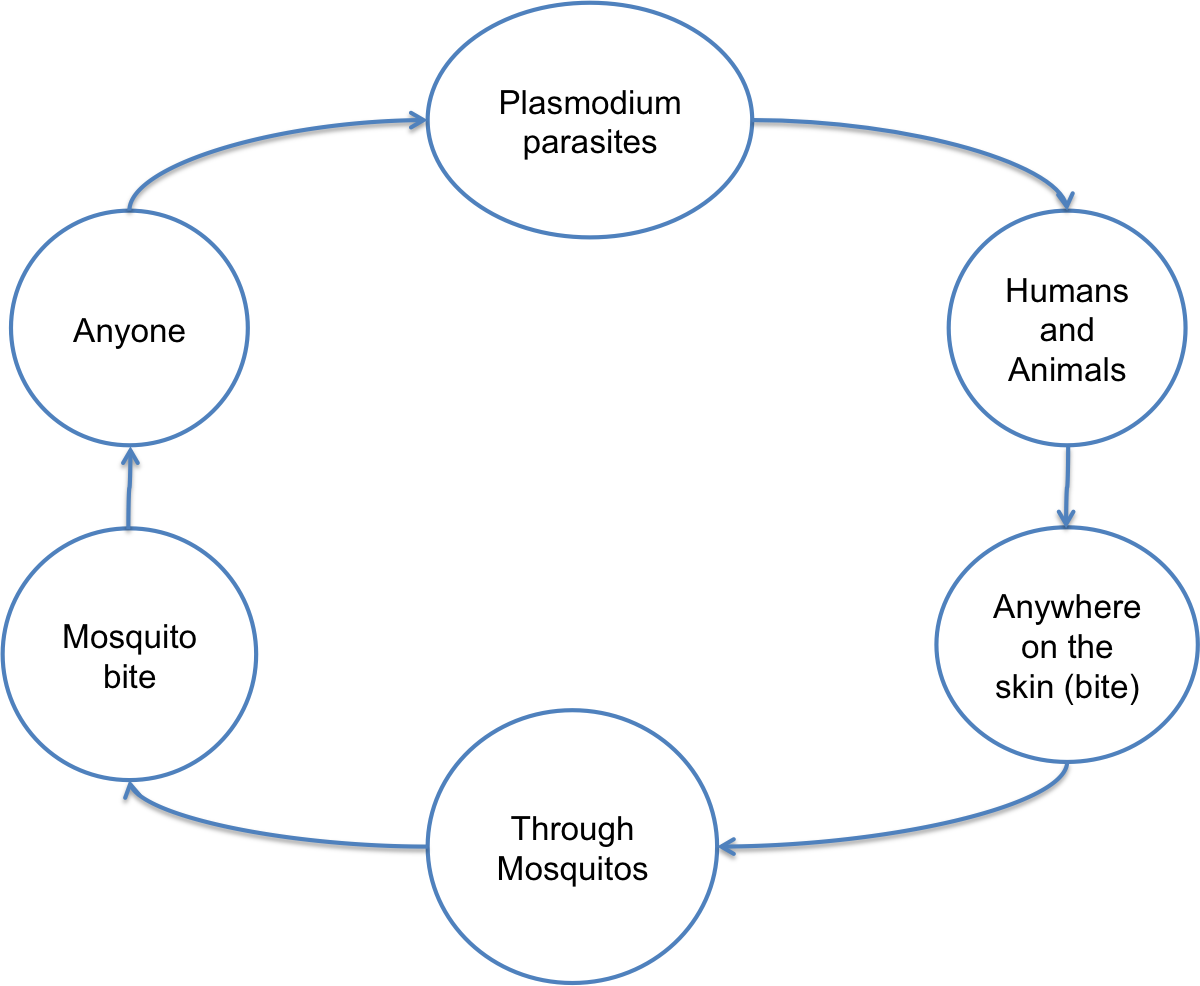
As seen from the chain of infection above, any human or animal can be affected by Plasmodium parasites that get transferred through mosquito bites. Importantly, both humans and animals can suffer from the disease, although, it is only possible to get infected through a bite and none other portals of entry. According to Brooks, Jean Paul, Claude, Mocanu, and Hawkes (2017), prevention strategies that target malaria can be as simple as using bed nets; however, the use of preventative medication or educational programs can also be highly effective. Implications of understanding the mechanisms involved in the development of the disease include strategies that prevent malaria from occurring.
References
Brooks, H., Jean Paul, M., Claude, K., Mocanu, V., & Hawkes, M. (2017). Use and disuse of malaria bed nets in an internally displaced persons camp in the Democratic Republic of the Congo: A mixed-methods study. PloS One, 12(9), 1-17.
Juraja, M. (2007). The missing link in the chain – the infection control link nurse. American Journal of Infection Control, 35(5), 110-111.
Malenga, T., Kabadhe, A., Manda-Taylor, L., Kadama, A., McCann, R., Phiri, K., …van den Berg, H. (2017). Malaria control in rural Malawi: Implementing peer health education for behavior change. Globalization and Health, 13, 84-94.
Patouillard, E., Griffin, J., Bhatt, S., Ghani, A., & Cibulskis, R. (2017). Global investment targets for malaria control and elimination between 2016 and 2020. BMJ Global Health, 2(2), 1-7.