Introduction
Lake Tahoe, which is located between the Carson range and Sierra Nevada Mountains, ranks as one of the spectacularly clear and blue alpine lakes in the world. Its clean water enables a substantial amount of sunlight to reach greater depths. During the period ranging between 1968 and 2000, the lake’s clarity declined at an average rate of 9 inches annually.
This aspect pushed the lake into losing 33 per cent of its unique clarity. In 1975, a standard to improve the lake’s clarity with a margin of 100 feet was formulated. The lake’s decline in clarity hinges on an increment in the volume of pollutants.
Additionally, studies conducted by scientists reveal that Lake Tahoe is experiencing and environmental emergency. The emergency emanates from increased destruction of the watersheds and wetlands. Due to increased environmental degradation and pollution, it has become difficult for the lake’s ecosystem to cleanse itself (Schladow Para. 1).
Overview of the paper
The paper entails a comprehensive description of the environmental issues being experienced at Lake Tahoe by analyzing the clarity of the lake and the major pollutants causing loss of clarity. The paper also carries out an analysis of strategies to deal with the environmental issues coupled with describing an economic rationale of the strategies implemented and the available options to deal with the issue.
Description of the environmental issue
Clarity of Lake Tahoe: One of the main reasons that have contributed to Lake Tahoe’s clarity emanates from the fact that 40 per cent of rainwater falls directly on the lake’s watershed. The remaining water drains into the lake through meadows and marshes, which are very effective in filtering foreign particles. In 1968, the clarity was at its best with a depth of 100 feet.
However, developments within the lake basin are facilitating disturbance of the filtering system, hence culminating in a decline in the clarity of the lake water. Currently, one can only see up to a depth of 70 feet, which means that the lake is losing its clarity at an average rate of 1 foot per year (Schladow Para. 7).
Major pollutants causing Lake Tahoe’s loss of clarity
Recent research conducted on the quality of water at Lake Tahoe revealed that the lake is increasingly losing its clarity. Currently, Lake Tahoe is undergoing cultural eutrophication, which entails excessive algal growth. The main pollutants include fine sediment particles and algae production (Schladow Para. 4).
Over the past few years, Lake Tahoe has experienced an increment in algae production due to increased nutrients, which include phosphorous and nitrogen. The increment in the volume of fine sediments particles is increasingly reducing the amount of sunlight reaching deeper waters. The sediments deposited are microscopic with an approximate thickness of human hair.
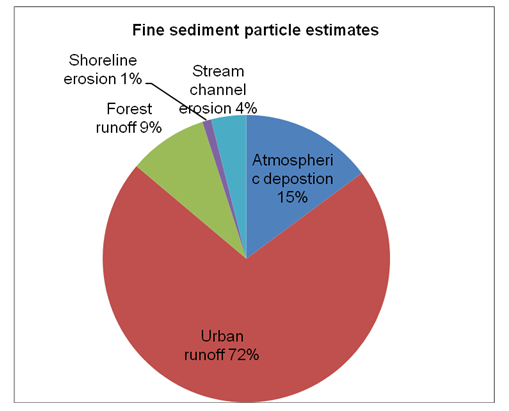
The fine sediment particles emanate from the watershed. In addition, the application of road abrasives and other activities causing soil disturbance are also leading to an increment in the volume of fine sediment particles deposited in the lake. The particles access the lake through various means such as through storm drains, air, stream channel erosions, runoffs, and atmospheric depositions.
Wood burning and road dust are also major causes of loss of the lake’s clarity. Findings of the Total Maximum Daily Load revealed that fine sediment particles are the major causes of the decline in Lake Tahoe’s clarity. This aspect arises from the fact that they remain suspended in the water rather than being deposited in the lake’s bottom, and thus the water is increasingly becoming brown and murky (Schladow Para. 3).
Additionally, production of algae is also reducing the amount of sunlight reaching deeper waters for sunlight is being scattered or adsorbed. Increased deposition of nitrogen and phosphorous is leading to an increment in the volume of free-floating algae. Over the past four decades, Lake Tahoe has experienced an increased algal growth.
Due to the increment in the rate of climate change, the Lake’s surface water is becoming warm. Warm water is lighter when compared to cold water. This element creates an opportunity for algae to sink to greater depths, hence reducing water clarity thus a decline in water clarity (Masterson Para. 1).
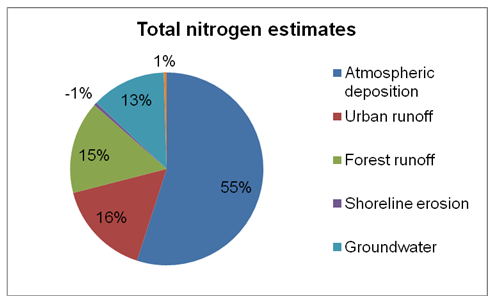
Through scientific modeling and monitoring, it has become possible to estimate the amount of each pollutant being deposited in the lake. A study conducted in 2004 revealed that the total fine sediments deposited amounted to 481×1018 particles. Most of the nitrogen deposited in the lake originates from urban areas (Schladow Para. 6). Vehicle emissions also form another source of nitrogen deposits in the lake.
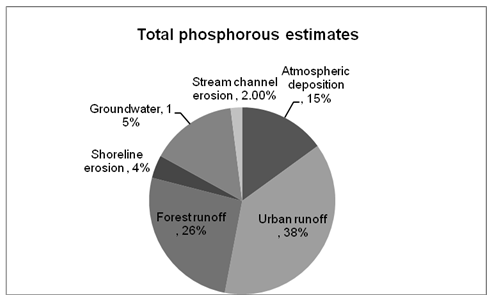
The nitrogen gets into the lake through atmospheric means. In 2004, the total volume of nitrogen that was deposited in the lake amounted to 397 metric tons. Most of the phosphorous deposited in the lake emanates from urban areas and fertilizers used in farmed areas.
Forests within the Tahoe basin are also a major source of phosphorous deposited in the lake. The phosphorous generated from the forest is mainly deposited in the lake through runoff. Approximately 80 per cent of Lake Tahoe’s basin is constituted of forest cover. Consequently, generation of phosphorous is a major issue, which should be addressed (Schladow Para. 9).
In an effort to improve water clarity, the various parties interested in improving the Lake’s clarity are focusing on reducing the sediments deposited in the lake especially from the urban areas around the lake basin. In a bid to achieve this goal, the strategies aimed at reducing pollutants emanating from and transported via forests, streams, and runoffs.
As aforementioned, through scientific modeling, it has become possible to determine the various methods through which the various pollutants are deposited in the lake as illustrated by figure 1 to figure 3.
Findings of a study conducted by UC Davis scientists, who have continuously studied the lake for more than 4 decades, revealed that the decline in the lake’s clarity has slowed over the past decade. However, its clarity has continued to be poor compared with past decades.
Despite the high rate of precipitation experienced in the area during the period ranging from 2007 to 2009, Lake Tahoe’s clarity remained constant. The Lake’s clarity in 2009 was better with 10 feet compared to 2008. In an effort to improve the Lake’s clarity, numerous projects are in place currently (Schladow Para. 7).
Some of the parties engaged in these projects include public agencies, UC Davis, and academic institutions. One of the public agencies involved in improving the Lake’s clarity is Tahoe Regional Planning Agency. The objective of the projects is to restore and conserve Lake Tahoe’s basin ecosystem. The projects focus at reducing the amount of fine sediment particles being deposited and algal growth in the Lake (Schladow Para. 9).
Courtesy of the efforts undertaken by the above parties, the Lakes’ clarity has continued to improve. In 2011, the Lake’s clarity improved with a margin of 3.7 feet. Additionally, the projects have led to a decline in the rate at which the Lake was losing clarity over the past few years.
According to UC Davis scientists, the Lakes clarity in 2010 declined to 64.4 feet compared to its 68.1 feet clarity in 2009 (Schladow Para. 11). Scientists associate loss of lakes’ clarity to the high rate of climate change and algae growth (Sumi, Fukushi, and Hiramatsu 56).
Strategies implemented to improve the Lake’s clarity
By 2025, the involved parties seek to improve Lake Tahoe’s clarity to 80 feet. In an effort to improve the lake’s clarity, a number of strategies are in place contemporarily. Some of these strategies relate to reducing urban runoffs through innovative measures, methods, and new technologies.
One way through which the strategy intends to achieve this goal is by using erosion control projects for example passive and wetland filtration basis, road vacuum cleaning, and media filters. The strategy also intends to deal with the runoff problem by implementing effective storm water infrastructures.
Reducing urban runoff – Treating the runoff water using advanced water technologies will lead to a significant decline in the level pollutants drained into the lake. In a bid to increase Lake Tahoe’s clarity to 80 feet within one year, the urban runoff should reduce by a margin of 34 per cent from the 2004 level. Additionally, the fine sediments draining into the lake should reduce with a margin of 74 per cent from the 2004 levels.
Atmospheric depositions- Efforts to improve the Lake’s clarity also entail reducing the volume of dust generated within the vicinity of Lake Tahoe. This move will be realizable by incorporating technologies, measures, and methods that will contribute towards the reduction of the amount of dust emanating from construction sites, parking lots, and roadways.
Some of the central technologies for these strategies entail advanced vacuum cleaning technologies. It is also paramount for the involved parties to eliminate dirt roads. Sediment deposits due to atmospheric forces should reduce by 55 per cent.
Forest runoff- It is important for the involved parties to control surface runoffs from the forest areas for disturbed forest areas release fine sediment particles, which can easily drain into the lake through surface runoffs.
Stream channel erosion- in a bid to improve the lake’s clarity, it is vital for the involved parties to focus on restoring the stream. This element is one of the most effective ways through which Lake Tahoe can experience a decline in the volume of fine particles being deposited into the lake. Through stream restoration, it will be possible to improve the lakes’ clarity for it will result into minimization of erosion of streambeds and banks.
Economic rationale for the issue
Restoring and preserving the clarity of Lake Tahoe is an important aspect that authorities and residents of the Lake Tahoe’s basin should take into account. One of the economic rationales for restoring and preserving the lake’s clarity associates with the fact that it is a major tourist attraction destination. The lake’s perfect beauty has served as a tourist attraction point for centuries.
The lake ranks as the deepest and largest lake in Nevada and California. Approximately 200,000 domestic and international tourists visit the lake on a classic summer weekend (Schladow Para. 1). As a result, the lake basin has experienced economic growth due to the establishment of various types of businesses such as restaurants and hotels.
The environmental emergency facing the lake presents a major threat to the survival of tourism within the lake’s vicinity. Losing its clarity means that there is a high probability of the region losing its tourist attractiveness. Consequently, most of the businesses established within the region will experience a decline in their sales revenue and hence their profitability.
Decline in profitability may stimulate some businesses to implement survival strategies such as downsizing, which will increase the rate of unemployment within the lake’s basin, hence reducing the consumers’ purchasing power. Ultimately, the region will experience a decline in the rate of its economic growth.
The rationale of the above environmental issue can also be explained in terms of the opportunity cost involved. In an effort to restore the lake’s clarity, the US government, through the Forest Service Bureau of Reclamation, the EPA, the US Wildlife and Fish Service, and the Congress, developed a ten-year Lake Tahoe’s Basin restoration program in addition to allocating $ 300 million to facilitate the program.
Other agencies interested in restoring Lake Tahoe’s clarity have invested a substantial amount of money in an effort to achieve their goals. For example, the UC Davis has invested more than $13 million in establishing an education and research center. The objective of the research center is to create awareness to the public regarding the importance of restoring the Lake’s clarity (Schladow Para. 4).
The decision to invest such a substantial amount of money by the US government and other interested agencies represents an opportunity cost. This aspect arises from the fact that the US government could have utilized the money in other economic avenues that can directly contribute to the country’s economic growth.
Summary of available options
Implementation of control programs
In a bid to enhance the clarity of Lake Tahoe, the involved parties can consider a number of options. One of these strategies entails the establishment of control programs. The control programs implemented should focus on a number of aspects. One of these aspects touches on controlling human activities that can contribute to increased soil erosion (Cooperative Extension 6).
Such programs will lead to a reduction in the volume of fine sediment particles drained into the lake. The control program should also focus on the rate of urbanization. The high rate of urbanization is a major factor that is contributing to the increment in the volume of fine particle sediments being deposited in Lake Tahoe.
Additionally, the establishment of control programs is much more effective in reducing the production of algal in the lake given the fact that algal growth is dependent on nutrient availability in the water.
Implementation of carbon tax- In its effort to improve the clarity of Lake Tahoe, the US government should focus on strategies aimed at reducing the rate of climate change. One of the aspects that the US government should focus on entails global warming.
Carbon emissions fall in the category of the major causes of global warming. Currently, studies conducted by scientists are associating climate change with the decline in the clarity of Lake Tahoe. The increasing rate of global warming is culminating in an increment in the surface temperature of Lake Tahoe, and thus increasingly stimulating growth of algal.
The US government should implement carbon tax in order to deter carbon emission from various parties such as vehicles and industries located within the lake’s basin. The US government should also set the carbon tax at a relatively high point in order to deter carbon emissions. Reduction in the rate of global marketing will culminate in a decline in the rate of algal growth within the lake.
Assessment of the options
There is a high probability of the above options succeeding in improving the clarity of Lake Tahoe. Firstly, by implementing control programs that target reduction of the volume of nitrogen and phosphorous deposited in the water. Nitrogen and phosphorous are some of the major ingredients that stimulate algal growth, which is associated with the decline in Lake Tahoe’s clarity.
Additionally, control programs will lead to a reduction in the volume of fine sediment particles deposited in the lake. Implementation of control programs will result in significant improvement in the lakes clarity.
On the other hand, implementation of carbon tax will play an important role in reducing the rate of climate change, which associates closely with the loss of clarity in Lake Tahoe. Carbon tax will stimulate the involved parties within Lake Tahoe’s lake basin to adopt strategies aimed at reducing carbon emissions.
Despite the benefits associated with the above options, there are also some costs involved. Firstly, implementing control programs will require the US government to allocate a substantial amount of money in the lakes restoration and preservation program.
Additionally, controlling the rate of urbanization presents a major challenge to the authorities involved for they have to redesign the urban areas around the lake in addition to formulating policies aimed at controlling urbanization. On the other hand, the success of carbon tax will be dependent on the effectiveness with which the government implements strategies to determine the amount of carbon emissions from various parties.
Data sources to conduct cost-benefit analysis
In a bid to conduct a cost-benefit analysis effectively on the effectiveness of the strategies implemented, the involved parties should consider various sources of data.
Some of these sources relate to previous studies conducted by various public and private institutions such as the Tahoe Regional Planning Agency and the UC Davis. The benefits achieved from dealing with the environmental issue experienced in Lake Tahoe can be monetized by enhancing the region’s rate of economic growth. One way to achieve this goal is by restoring tourism in the lake’s basin.
Recommendations
In a bid to improve Lake Tahoe’s clarity, it is important for the involved parties to consider the following aspects:
- Improving the lakes clarity is a challenging task. Consequently, it should be a joint task. Some of the parties who should be involved include the federal and state regulatory agencies and the land management agencies.
- The involved stakeholders should continuously review and monitor whether the implemented strategies contribute to the reduction in the volume of each pollutant within the lake. One of the main aspects subject to review relates to the evaluation of whether the technologies, methods, and measures implemented are contributing towards the improvement in the lake’s clarity. Constant monitoring will aid in determining the costs and benefits of every method.
- The stakeholders involved in improving the lake’s clarity should stick to the timeline formulated in order to attain the intended benefits.
Works Cited
Cooperative Extension 2009, Programs to preserve environmental quality at Lake Tahoe. PDF File. Web.
Masterson, Kathleen. Climate change could reduce Lake Tahoe clarity, 2011. Web.
Schladow, Geoff. UC Davis: Lake Tahoe clarity dips slightly, 2010. Web.
Sumi, Akimasa, Kensuke Fukushi, and Ai Hiramatsu. Adaptation and mitigation strategies for climate change, Tokyo: Springer Verlag, 2010. Print.