Coronavirus Pandemic
About
The Coronavirus pandemic has become the main reason for discussion in the new decade. This is not surprising — the microscopic virus has caused more than 320,000 deaths worldwide in a few months and 92,000 in the United States (“Google News,” n.d.). Many politicians around the world have forcefully imposed restrictive measures to prevent the virus from spreading. Nevertheless, the pandemic has demonstrated the inadequacy of the health system.

Economic Indicators
GDP
The primary macroeconomic indicator: shows the total cost of all services provided and products manufactured in the country.
Employment
An employment relationship with an employer that brings economic benefits: the high level indicates the degree of prosperity of society.
Unemployment
A high level reveals a lack of balance between job seekers and actual jobs. Could cause an economic crisis.
Well-Being
Not a real economic indicator, but what citizens feel is a subjective picture of how they perceive the economic situation.

The Pandemic Macroeconomy
GDP
It is evident that the decline in enterprises’ productivity, the closure of service centers, and social service delivery points will eventually lead to negative GDP indicators.
Employment
The restrictive regime has resulted in many workers being remotely accessed — this has created a technological evolution of existing software tools.
Unemployment
However, some of the employees have been fired or dismissed: this leads to an increase in the number of consumers against the background of a decline in the number of production facilities, which causes a social and economic crisis.
Well-Being
The U.S. economic system has shown a paradoxical effect — on the one hand, the available reserves allow for cash transfers to citizens, and on the other hand, the lack of effective investment in health has led to high mortality rates.
Business crisis
The enterprises were not prepared for the crisis: the branches are closed, the finances are not coming in, the working personnel is being reduced.
The effects of the microeconomic crisis can be summarized as follows:
- oproduction cuts;
- othe drop in prices;
- ojob cuts;
- othe growth in the number of bankrupt companies;
- oa sharp drop in wages.


Socio Economic
The Coronavirus pandemic has the potential to cause more socio-economic severe consequences. Poverty among the population is predicted to increase for the first time since 1998 (Mahler et al., 2020).
The crisis has shown the immaturity of the U.S. health care system — lack of planning and risk management, lack of financial stability to scale up the work of clinics.
It is interesting to note that the rules of hygiene during self-isolation have brought new values into society’s life — the importance of health care, the possibility to limit social contacts, and visits public spaces.

Healthcare Organizations
WHO
Engaged in sponsoring research, public awareness, and laboratories. The main mouthpiece of the planet.
CDC
Less responsibility than WHO. However, CDC is accountable for monitoring and sharing information, resolving private situations, and transferring ambassadors and agents to hot spots.

Current Policies
Restrictive Measures
President Trump has introduced an emergency regime within the United States that involves the closure of public facilities, restaurants, parks, and beaches. This is a substantial measure, as many studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of quarantine conditions to curb the rate of infection.
Cash Benefits and Financial Assistance
Trump’s administration approved economic reform, according to which every American received more than $1,000 (Carney & Lane, 2020). This measure was aimed at stimulating the solvency of the population in the conditions of increasing unemployment in order to ensure the effective circulation of money in the market.
Easier Access to Hospital
The President urged U.S. medical organizations, including private ones, to provide free assistance in testing the population. The federal budget funds cover even the expenses of uninsured citizens (Abelson & Sanger-Katz, 2020).

Proposed Policies
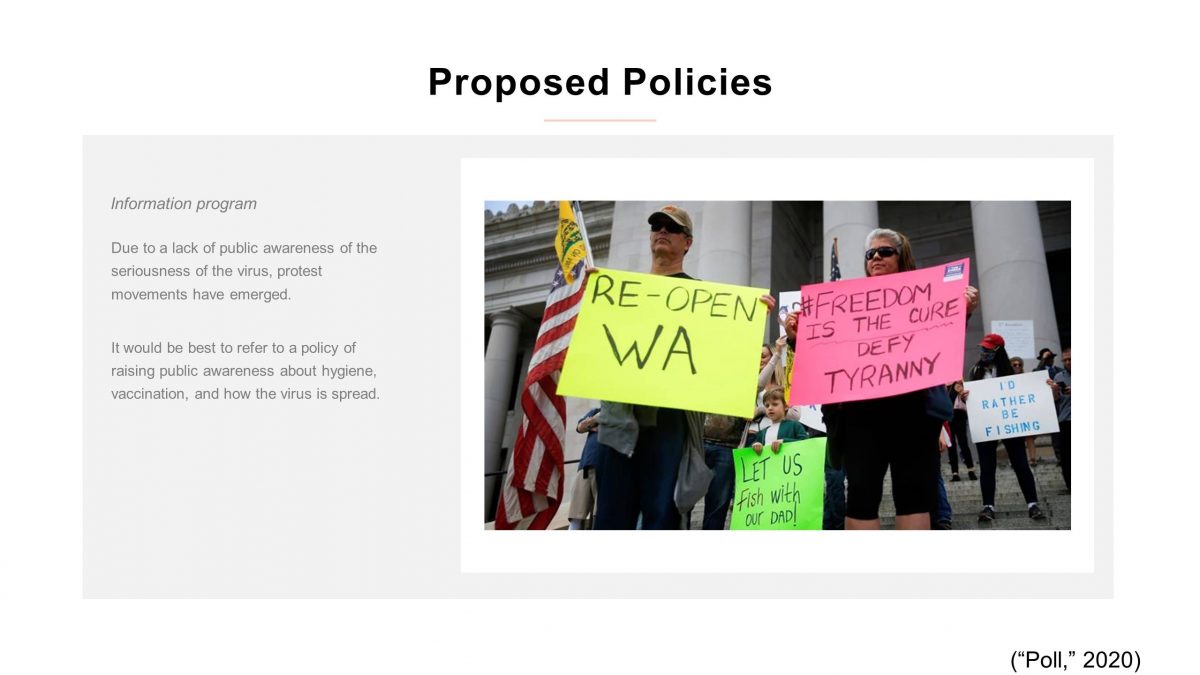
Information program
Due to a lack of public awareness of the seriousness of the virus, protest movements have emerged. It would be best to refer to a policy of raising public awareness about hygiene, vaccination, and how the virus is spread.
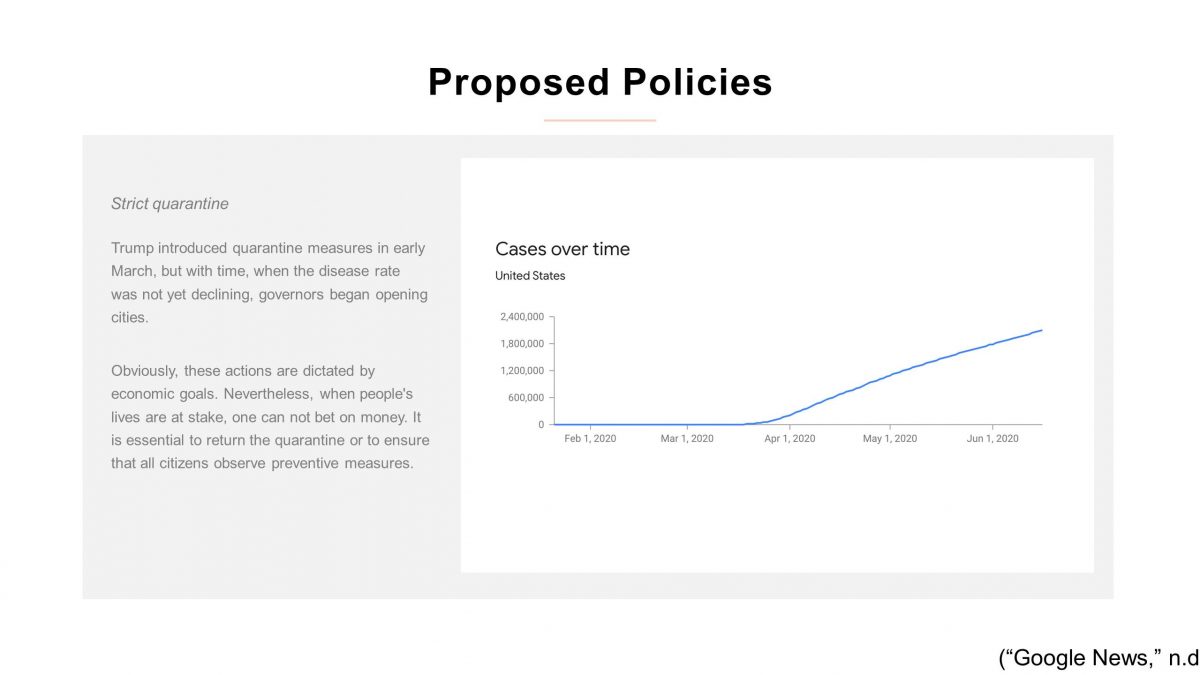
Strict quarantine
Trump introduced quarantine measures in early March, but with time, when the disease rate was not yet declining, governors began opening cities. Obviously, these actions are dictated by economic goals. Nevertheless, when people’s lives are at stake, one can not bet on money. It is essential to return the quarantine or to ensure that all citizens observe preventive measures.
Socioeconomic Support
Field Tests
The creation of free mobile testing points could solve geographical distance problems from clinics, reducing the likelihood of social interaction.
Clinic Support
Often Americans go to private clinics because they are closer, more accessible, or provide better services. The authorities must help the private sector at this time.

Socioeconomic Barriers
Difficult to Inform
Inserting advertising banners, videos, and posts are effective for younger audiences, but older Americans do not trust the Internet. During the pandemic, it was not easy to organize training courses for retirees and to encourage them to be more sensitive to coronavirus news.
Cost of Treatment
Even with cash benefits, not all Americans can afford expensive treatment and prevention. Despite Trump’s words, not all clinics provide free treatment. In addition, the daily purchase of gloves, masks, and disinfectants strongly affects citizens’ financial reserves.

Benefits for Healthcare Organizations
Increasing the Culture
First, broad public awareness will result in an improved scientifically proven culture, which will result in an improved nation’s health indicators.
Reducing the Burden on Clinics
Second, the strict quarantine will reduce the burden on health care organizations by allowing them to postpone to remain operational.
More Resources
Third, increased economic support from the state will give clinics more resources to implement successful and efficient medical care.

It is time to reevaluate achievements in the field of health and look at a new day. Our system has shortcomings, and the proposed policy will solve them!
References
Abelson, R., & Sanger-Katz, M. (2020). Trump says hospitals will be paid for treating uninsured coronavirus patients. The New York Times. Web.
Authers, J. (2020). Pandemic panic is natural. But try to resist it. Bloomberg Opinion. Web.
Beck, T. (n.d.). What’s the big deal? Experts unpack the coronavirus outbreak. Cal Alumni Association. Web.
Carney, J. & Lane, S. (2020). Cash assistance for Americans gains steam as coronavirus roils economy.The Hill. Web.
Chen, P.G.. (2020).Integrating behavioral health services into medical practices faces culture and financial barriers. Objective Analysis Effective Solutions. Web.
Coronavirus crisis lays bare the risks of financial leverage, again. (n.d.) Financial Times. Web.
Google News. (n.d.). Coronavirus (COVID-19) [Data set]. Web.
Mahler, D.G., Laknerr, C., Aguilar, A. C., Wu, H. (2020).The impact of COVID-19 (Coronavirus) on global poverty: Why Sub-Saharan Africa might be the region hardest hit. WorldBankBlogs. Web.
Poll: Most Americans favour lockdowns to curb coronavirus. (2020) Aljazeera. Web.
Poon, L. & Holder, S. (2020). The ‘new normal’ for many older adults is on the Internet.Bloomberg. Web.
Regan, H., Renton, A., McGee, L., & Wilkinson, P. (2020). Coronavirus pandemic: Updates from around the world.CNN World. Web.
Taylor, D. B. (2020). Is the coronavirus an epidemic or a pandemic? It depends on who’s talking. The New York Times. Web.
Vembu, V. (2020). The economic impact of the coronavirus pandemic. The Hindu Business Line. Web.