It is a statutory requirement for limited companies to publish audited financial statements. Shareholders, government, employees, community, and creditors among others use these financial statements. Published financial statements provide the potential users with narrow insight in to the financial strengths and weaknesses of a business. This is because published reports do not give information on all financial areas. For instance, published financial statements do not give trend analysis of a company for a period of five years (Siddiqui 623). Such a comprehensive view of a business is important as it would influence users’ decisions on whether to continue their association with the business or not. Ratio analysis is an important tool for analyzing performance of a company. Results of ratio analysis give adequate information for evaluating a business (Brigham and Joel 56). This paper carries out DuPont analysis for four companies and compares their results.
DuPont analysis
DuPont analysis breaks down return on equity into three components. These components are asset turnover, leverage factor and profit margin. It is a quick way of checking strengths and weaknesses of a business. It shows efficiency in use of inputs to generate profits, use of capital to generate gross revenue and how a business leveraged debt capital. Return on assets gives information on net income, sales and total assets. Return on equity gives information on net profit, equity, pretax profit, EBIT, sales, and assets (Gibson 37). The table below shows a summary of DuPont ratios.
Table showing ratios of company C and D.
Comparison of the two companies
The trend of return on assets and return on equity can be shown on a graph. Graphs often give a good depiction of movement variables within a period of time.
Graph Showing return of assets and equity for company C and D.
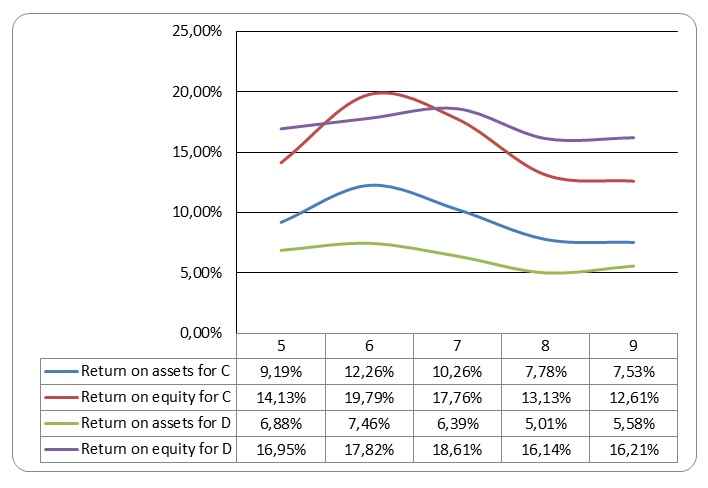
From the graph above, it is evident that return on equity for both companies is higher than return on assets. The graph also shows that both return on equity and assets for the two companies increased in 2005 and 2006. Thereafter, it took a declining trend. Company C generates more revenue from assets than company D while company D pays more returns to their shareholders than company C.
The table below summarizes results of company E and F.
Graph Showing return of assets and equity for company E and F.
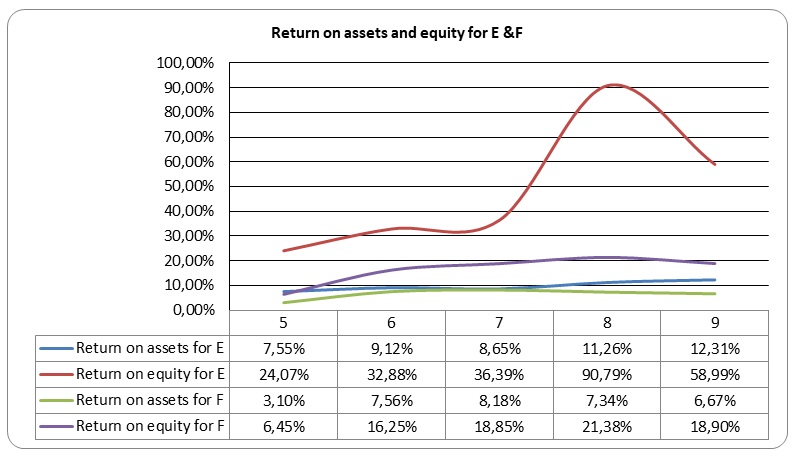
From the graph above, both companies had an upward trend on return of assets and equity. Performance of company E is better than that of F. Company E pays very high returns on equity as high as 90%. These high rates may attract potential investors. From above comparisons, it is clear that DuPont analysis gives a quick view of performance of an entity
Works Cited
Brigham, Ehrhardt, and H. Joel. Fundamentals of financial management, USA: South- Western Cengage Learning, 2009. Print.
Gibson, Charles. Financial reporting and analysis: using financial accounting information, United States of America: South-Western Cengage Learning, 2010. Print.
Siddiqui, Siddiqui. Managerial economics and financial analysis. New Delhi: New Age International (P) limited, 2005. Print.