Introduction
There are many methods and strategies to improve working conditions and minimize the number of mistakes in the workplace. Consequently, root cause analysis (RCA) is one of the most effective instruments for understanding the contributing factors to the problem (Okes, 2019). It helps to comprehensively describe the issue, evaluate its impact, find correlations, and propose an effective solution (Okes, 2019). RCA is particularly beneficial in healthcare since every mistake might cause significant damage to a patient’s health or even lead to death. From these considerations, it is essential to conduct a thorough analysis to understand the causes of the cases and propose improvements to the work process. Ultimately, the current paper provides a root cause analysis for the case, describing the patient’s demise due to a medical error.
Concise Case Description
The examined scenario concerns the inadequate organization of the medical facility in regard to resuscitation orders. In healthcare, patients in rehab units are assigned codes based on the desire to survive near-death situations. For instance, DNR designates “do not resuscitate”, while Full Code implies the authority of the hospital to perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and make all necessary efforts to bring the patient back to life.
In the current case, the patient in the rehab unit started gasping for air during the third shift. The supervisor asked the Licensed Nursing Assistant (LNA) to check the patient’s code status. Consequently, LNA reported that the patient’s status was DNR, virtually prohibiting CPR in an attempt to save their life. The patient died shortly after, while the supervisor nurse could only administer oxygen to the patient and wait. However, when the nurse was examining the code chart afterward, she realized that the patient was under the Full Code policy, permitting the hospital full authority to save the patient’s life. As a result, the medical mistake of the LNA to report the correct status and the inadequate system of code status cost the patient their life.
Contributing Factors
There are several contributing factors to the examined tragedy; however, the primary focus should be on the inadequate organization of the code status. It is essential to identify the three elements of the RCA – problem, causes, and impact (Okes, 2020). Human errors, such as the mistake of the LNA, are significant factors of the RCA that should be accounted for. Moreover, the RCA does not assign blame to the individuals specifically, but human errors occasionally occur, and it is essential to identify their impact on the event. Answering these questions would allow an understanding of why the problem occurred and what could have been done to prevent it.
In the current case, the problem is an incorrect assessment of the code status, resulting in the patient’s death. There are several evident causes or contributing factors to this event. Namely, the inadequate regulation of codes, ineffective supervision system, and human error are the primary causes of the problem. Some of the secondary factors include the lack of communication between the supervisor nurse and the LNA, organizational failure to establish an effective system of codes, lack of specialized training, and many others.
Organizational Failure
The mentioned contributing factors eventually led to the tragic incident, and it is essential to analyze them in detail. The first primary cause is the inadequate regulation of codes, which signifies organizational problems in the facility. When a patient is redirected to a rehab unit, the hospital assigns a special code – either DNR, Partial Code, or Full Code. These are essential parameters since they directly impact the hospital’s decisions concerning CPR. Since codes are so vital to decision-making, the information about them should be accessible immediately in the rehab unit. The supervisor had to send the LNA to another location to check the codes, which is an unacceptable flaw in the facility’s organizational structure, resulting in the patient’s death. Furthermore, this system might malfunction because of communication issues, the LNA’s competencies, and other external factors, making it highly unreliable.
Consequently, assuming all the patients in the rehab units are commonly assigned Full Code, there has to be additional identification of the DNR code. For instance, if the hospital does not have sufficient funds to implement an effective notification system, it should at least mark patients with DNR codes. Thus, the supervisor nurse would know that if there is no specific note concerning the code status, she should assume the Full Code level and perform CPR. Even a simple notification in the rehab unit would significantly increase the speed of response and potentially save the patient’s life. As a result, the organizational system of codes is the primary cause of the incident and should be urgently revised to prevent future tragedies.
Factors Leading to Human Error
The second direct cause is the LNA’s human error of misinterpreting the patient’s code status. Without assigning blame to the individual, there could be multiple reasons for this mistake. Namely, inadequate training, lack of experience, mislabeling of codes, or, perhaps, the LNA’s stress and sleep deprivation. While human factors are difficult to identify, it is essential to mitigate the organizational risks that led to LNA’s mistake. In other words, the hospital must thoroughly inspect the proficiency of nurses and LNAs concerning the code charts and other crucial processes. It specifically concerns cases when a single mistake might cost the patient’s life. Ultimately, healthcare is a high-risk industry, and the hospital needs to ensure that all nurses have sufficient competencies and experience.
Root Cause Analysis Diagram
Consequently, it is possible to use a Fishbone Diagram to illustrate the contributing factors that led to the problem. The chart demonstrated below presents a thorough overview of primary and secondary causes. The factors are classified into three categories: organization, management, and people. The hospital needs to acknowledge its structural flaws, and all contributing elements need to be thoroughly analyzed and revised by the facility to prevent future tragedies.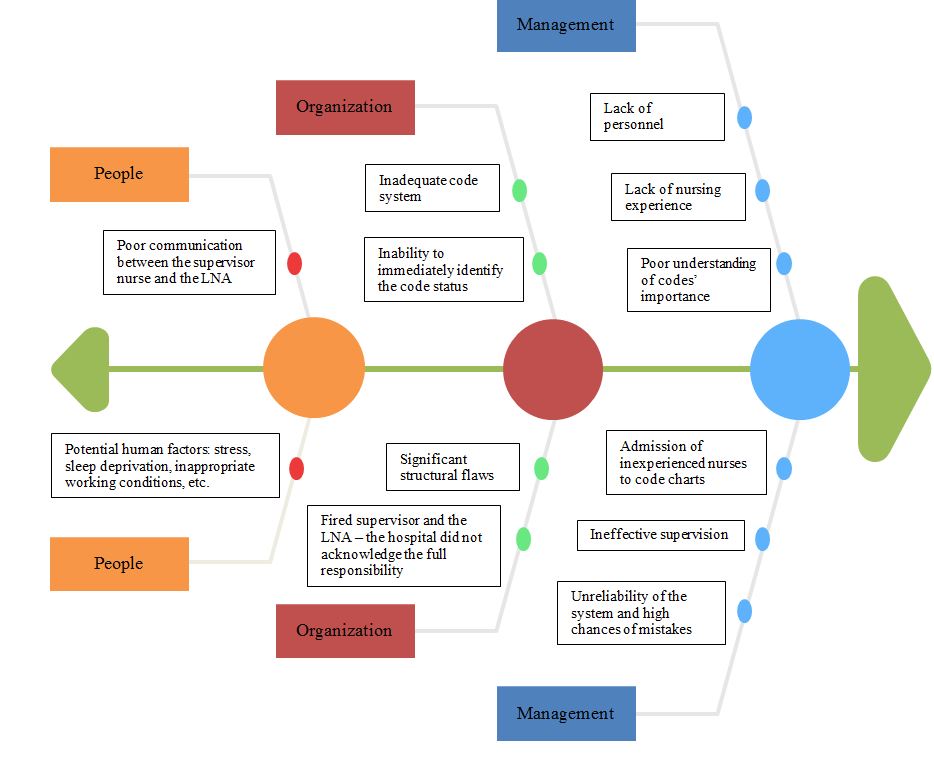
Conclusion
The current paper has demonstrated the effectiveness of the RCA in establishing the connection between the causes and the effect. The examined case is a tragic event, describing the patient’s death due to the organizational incompetence of the facility and human errors. It is essential to thoroughly analyze such problems to prevent similar mistakes in the future and improve the overall quality of the provided services in healthcare. Furthermore, the hospital needs to acknowledge its organizational problems concerning code statuses. The facility fired the supervisor nurse and the LNA; however, the RCA demonstrated that problems are more deeply ingrained, and the hospital needs structural changes. Ultimately, the RCA is a useful tool for recognizing the causes of the problem and proposing an effective solution.
Reference
Okes, D. (2019). Root cause analysis: The core of problem-solving and corrective action. ASQ Quality Press.