Introduction
Honest Burgers is a well-known burger restaurant in the United Kingdom. It is best known for its high-quality goods, food, and services. However, the market has changed dramatically over time. Brexit and COVID-19, in particular, have altered the industry’s structure and consumer behavior. It is vital that Honest Burgers reassess its competitive strategies to its internal and external environment.
This report includes the introductory chapter and the literature review for the topic: how Honest Burgers are affected by ongoing external issues, and then to seek solutions for Honest Burgers to address the labor shortage and shifting consumer trends challenges the brand is currently experiencing. In order to address the topic sentence, a systematic literature review is conducted, which includes 20 valid and reliable sources. In addition, frameworks (PETEL, SWOT, Porter’s Five Forces, and VIRO) were researched and applied in conjunction with the company’s annual financial report to analyze the industry and company internally and externally.
The study’s goal is to figure out how HB will deal with the labour shortage and the challenges that the brand is currently facing in terms of consumer trends. A variety of models and theories are used to analyze these factors. They are PESTEL analysis for external assessment, Porter’s five force model for competition assessment, VRIO analysis for practice assessment and SWOT analysis for internal assessment.
Strategic issues
The entire world is dealing with the strategic issue of COVID-19 and its consequences. On top of COVID-19, the United Kingdom also is dealing along with another strategic issue Brexit, which is having a significant impact on the country’s economy and industries. The focus of this paper will be on how these two strategic issues impacted the hospitality industry.
COVID-19 pandemic, which hit the country on March 23rd, 2020, prompted the country’s first-ever national lockdown, forcing hospitality establishments to shut down (IFG, 2021). In addition to COVID-19, the hospitality industry was adversely affected by Brexit. Exiting the European Union on January 31st, 2020, imposed a significant burden on the hospitality industry, particularly in the supply chain and labour force (IFG, 2021).
For the past two years, the company has been dealing with the issue of covid and Brexit as a whole. A PESTEL analysis is carried out in order to comprehend the current state of the hospitality sector and gain insight into how Brexit and COVID-19 have reshaped the industry.
PESTEL Analysis
The macroeconomic environment is examined using the PESTEL framework. Performing a PESTLE analysis on an organization’s operations is a useful tool for investigating external factors that have an impact on the organization’s operations (Perera, 2017). As a result, the PESTEL framework is deemed appropriate for analysing HB’s current position in relation to its environment in this report.
Political
The hospitality industry is heavily influenced by external factors, most notably by the Brexit vote. Since Brexit, the company has faced numerous challenges as a result of the UK government’s implementation of a point-based immigration system for skilled workers from both the EU and outside the EU (Secretary of State,2020, p.7). Because more than 24% of hospitality jobs are filled by EU workers, the new post-Brexit employment law may exacerbate already-existing labour shortages in the industry (Clark, 2021). Staffing shortages are being experienced by HB, which is involved in the hospitality industry, as a result of the Brexit vote (company house, 2022).
Economical
Hospitality sector generated £59.3 billion in 2019 in the UK economy, of which food and beverage services accounted for 41.6 billion (Hutton and Foley, 2021, p.5). However, in the 2020-21 financial year, the COVID-19 outbreak reduced economic output by 59.8%. (IBISWorld, 2022). Some critical economic indicators that pose a short-term challenge to the hospitality industry include projected inflation of 7% by spring 2022 and a 0.75 percent interest rate (Bank of England, 2022), inflation, unemployment issues, and soaring UK energy prices (Romei, V., 2022). Despite this, takeaway and fast-food restaurant revenue is expected to grow at a compound annual rate of 3.3 percent to $24.2 billion over the next five years, from 2026 to 2027. (IBISWorld, 2021). Economic factors have a direct impact on HB because the company is dealing with challenges such as rising labour costs and material supply costs. (Annual report for 2022).
Social
The marketing strategy and business operations of a hospitality company are heavily influenced by social factors. COVID-19, which prioritizes well-being, value, and identity as major trends, has unquestionably shaken consumer confidence and purchasing power (Mintel, 2021). As a result, Customer demand for plant-based products is also on the increase (Petropoulos, 2021). Consumer research conducted by CGA in March 2021 found that 54% of respondents intend to go out more frequently, 22% to spend more money on eating out and drinking than they did before COVID-19, and 26% to increase their purchases of healthy food from local vendors once things return to normal (IBISWorld, 2021). Delivery and takeaway orders in 2021 increased in comparison to the same period in 2019 because of the nationwide lockdown (UK Hospitality 2021). Another negative impact of COVID-19 is that many people have lost their jobs. Over 342,000 people lost their jobs, with 81 percent of them employed in the hospitality and food services industry (Department for Business, Energy & Industrial Strategy, 2021, p.9).
Technology
The hospitality industry has always relied heavily on technology, and it is one of its most important characteristics. Now, the use of technology in this sector has accelerated as a result of COVID-19. Ninety-five percent of business leaders polled by CGA (UK Hospitality, 2021, p.8) said they expect technology to be critical following the pandemic. According to the Go Technology report, 26% of consumers orders food and beverages on their mobile devices while dining out in 2021, up from 14 percent in July 2019. (UK Hospitality, 2021), Additionally, 32% of customers used their phones to look up menus, 19% ordered drinks, and 18% paid their bills (IBISWorld, 2021).
Legal
Legal issues have an impact on all industries. Restaurants in the United Kingdom are required to adhere to a set of rules and regulations. To ensure food safety and quality, the Food Standards Agency (FSA) has to approve strict standards and inspections for food safety, health, and food grading (Gov.UK, 2022). This means that HB has to follow all FSA regulations as well.
Environmental
In every industry sector, environmental factors have become increasingly important. Analysts (IBISWorld, 2021) believe that the presence of COVID-19, which is caused by environmental disaster, is the most significant reason for the UK hospitality industry’s worker shortage. The impact can be seen in the case of HB, which lost a large number of employees as a result of the disaster (Annual report, 2022).
Challenges
For the past two years, the company has been dealing with the issue of covid and Brexit as a sector. Consequently, these issues are putting pressure on the industry and the business. We will focus on two major challenges that HB is currently facing as a business: labour shortages and changing consumer trends. To analyze these challenges, a variety of models and theories are used, such as Porter’s five force model, which is used to prioritize them and assist HB’s management in rethinking their internal strategy and finding solutions to gain a competitive advantage, VRIO for practical assessment, Stakeholder’s theory in relation to HB, as well as a financial overview of the company.
Porter’s five forces
Traditionally, Porter’s five forces model has been based on five significant forces: buyer power, supplier power, new entrant power, competitor power, and substitute power, all of which can either pose a challenge to a business or enable it to control these five forces (Lasserre, 2017). Porter’s five forces can help you figure out who has the most influence in a business decision. This is useful for determining the severity of a company’s current competitive environment and the viability of a future strategy.
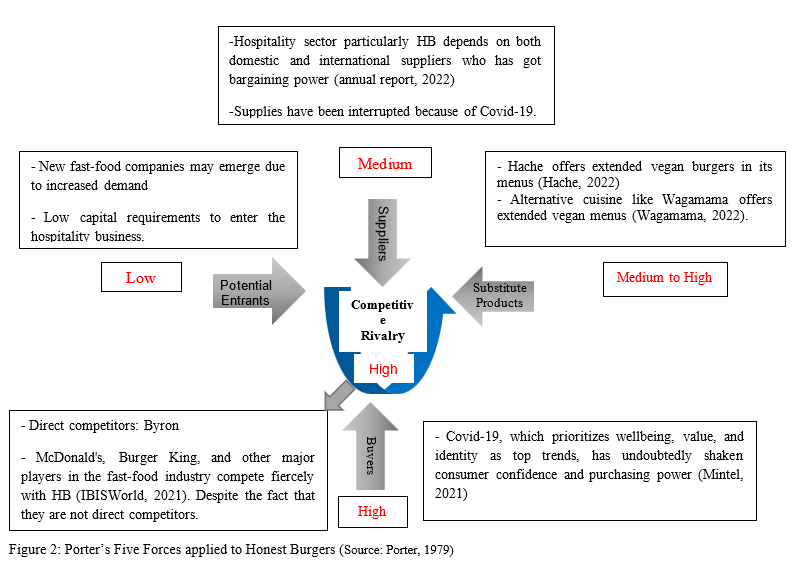
Potential entrants: low capital requirements make it easier to enter the restaurant industry (Evans, 2020, p.295). However, in London’s financial heartland, where population density and rental prices are higher, this becomes a low to medium level (IBISWorld, 2021). As majority of HB’s business in central London, the risk of potential entrants is low to medium.
Supplier power: When it comes to the hospitality industry, suppliers’ negotiating power is low because of the large number of suppliers and lack of differentiation among suppliers (Evans, 2020). As a result of the industry’s reliance on both local and international suppliers, supplier bargaining power in the hospitality industry, particularly in HB, is low to medium.
Buyer power: There is a high potential for buyer bargaining power in the hospitality industry, and HB is no exception. Moreover, consumers’ negotiating power has increased as a result of COVID-19’s shift towards sustainability, well-being, and veganism (Dinev, 2021).
Competitive Rivalry: The hospitality industry is characterized by intense competitive rivalry. There is a lot of competition because there are a lot of fast-food restaurants that serve similar food, but they aren’t direct competitors (IBISWorld, 2022).
Substitute products: In the hospitality industry, there are many competitors who offer alternative menus, so substitute products are medium to high in demand (IBISWorld, 2021). Many existing competitors, such as Hache, already have vegan menus, and a new entrant could emerge to take advantage of the new market opportunity.
On the basis of Porter’s 5 forces analysis, the challenges facing the hospitality industry, particularly HB, are Brexit and COVID-19. Now, health-conscious consumers want more vegetarian and vegan restaurants (Dinev, 2021). As a result, Honest Burger can fully capitalize by expanding vegan menus, and recently opened a fully vegan restaurant (McAllister, 2022). A new entrant may emerge to capitalize on the altered market opportunity. This framework will help Honest Burgers rethink their internal strategy and find ways to gain a competitive advantage.
VRIO
Organizations can use the VRIO framework to better identify the resources and capabilities that will provide them with a long-term competitive advantage. Over time, businesses gain a competitive advantage by implementing strategies that capitalize on internal strengths, respond to environmental opportunities, neutralize external threats, and avoid internal weaknesses (Barney, 1991, p.99). The goal of VRIO is to determine how HB can gain a competitive advantage through the use of internal resources. In order for companies to turn resources into long-term competitive advantages, they must have four characteristics:
Valuable: Resources must be valuable before they can be of any use. A company’s resources are only valuable when they contribute to long-term competitive advantage. It’s important to figure out if a resource is valuable to HB.
Rare: There must be a scarcity of resources in order for this to work. If only a few companies have access to a resource, it is considered rare. If all players in an industry have access to a valuable resource, they can all use it in the same way. If this is the case, none of the players will gain any benefit from this resource. This condition is referred to as competitive parity or competitive equality (Barney, 1991).
Inimitable: Even if a company can pursue strategies that other companies can’t because of a lack of resources, it doesn’t guarantee a long-term competitive advantage. Resources should be difficult and expensive to duplicate or substitute in order to gain a long-term competitive advantage. If other companies copy it, the company will gain a competitive advantage for a limited time.
Organizational Support: In order to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage, a company’s resources must be properly organized. If a company is unable to organize a valuable, rare, and difficult-to-imitate resource, it will gain an unused competitive advantage.
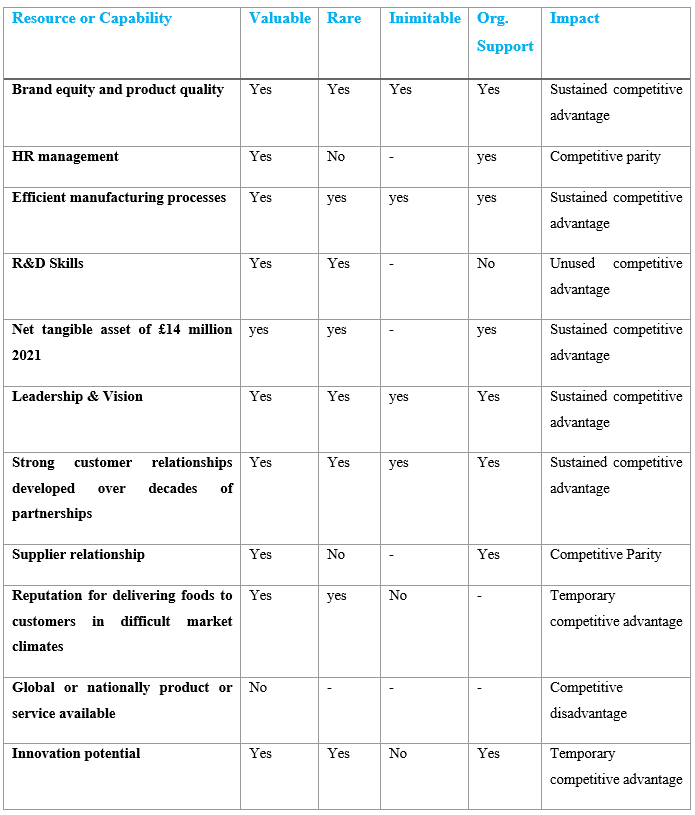
According to VRIO, HB’s brand identity is its strength. Quality products, strong customer relationships and innovation potential are its most significant strengths. Using internal resources and capabilities, avoiding internal flaws, and neutralizing external threats gives a company a competitive advantage (Frynas and Mellahi, 2015). It’s rare that HB has its own butchery supply chain, which makes 90% of the menu from scratch. In addition, HB has spent a significant amount of money on research and development for its own manufacturing process. It would be expensive for any competitor to develop a system that produces such high-quality products. In the future, newcomers may enter the market with similar food and service, as competitors such as Byron do. As a result, HB may lose a long-term benefit. HB’s shortcoming is that, despite recent initiatives, it is not yet well organized to enable skilled human resources to succeed. Its leadership and vision aren’t well-organized either. Furthermore, the majority of HB’s restaurants are located in London, which is a disadvantage, but this could change in the future with strategic management.
Stakeholder’s theory
The stakeholder theory is a business ethics and organizational management theory that looks at morals and values in the workplace. A stakeholder is a person, group, or organization who is interested in or concerned about a company. Creating value and benefits for all stakeholders, not just shareholders, should be the goal of businesses (Freeman et al., 2010, p. 4-10). Stakeholders have the ability to influence or be affected by the organization’s actions, goals, and policies. Friedman, on the other hand, disagrees with Freeman’s approach, claiming that a company has a moral obligation to increase shareholder profits “as long as it follows the rules of the game” (Ronnegard and Smith, 2013, p. 184).
As a result of Brexit and COVID-19, the business has been reshaped as customers’ purchasing attitudes have shifted. As a result, in stakeholder theory, customers play an important role. Consumer confidence and purchasing power have unquestionably been eroded as a result of COVID-19, which prioritizes well-being, value, and individuality as major trends (Mintel, 2021). Furthermore, in the hospitality industry, employees and supply chain play a critical role, particularly in a changing environment. Employees in the food service and delivery industries have been designated as the “most important stakeholders in the business” by both COVID-19 and the Brexit referendum (Crane and Matten, 2021, p.280).
HB believes in the importance of long-term business success. The company’s behavior is in line with the expectations of its employees, customers, shareholders, and communities, as well as society as a whole (Annual report, 2022).
Financial overview of Honest Burgers Ltd
HB is a well-known fast-food company. According to the company’s five-year revenue report, revenue increased significantly from 2017 to 2020 (fame, 2022). The company’s financial performance benefits key ratios like liquidity, solvency, and profitability. (Danese and colleagues, 2018). However, the situation did not hold in 2021 due to the arrival of the COVID-19 pandemic and the UK government’s national lockdown strategy. According to the financial statement for the 2020-21 financial year, the company’s turnover decreased by £13.1 million from the previous year. In 2021, the company made a huge loss of £ 3,185,261 compared to a profit of £ 1,154,031 in 2020, and COVID-19 can be seen here.
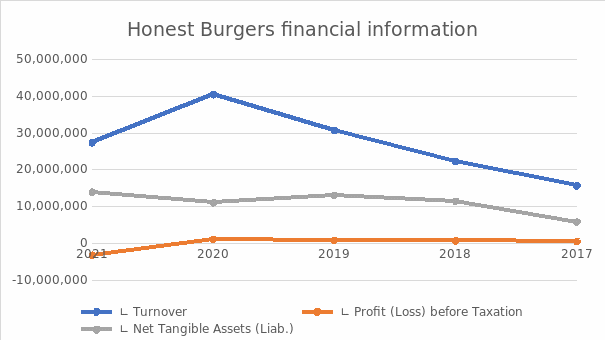
Another significant financial weakness that calls the company’s viability into question, such as a £4.2m bank loan that must be paid back soon or the company will breach its agreement with the bank (Annual report, 2022). Despite the fact that the company has strong tangible assets of 13,937114 in 2021, which is a 26% increase over last year (Fame, 2022).
Labour shortage
Due to Brexit and COVID-19, HB has been facing a staffing shortage. It currently has 639 employees compared to 726 in 2020 (fame, 2022). ONS (2021) reports a high of 102,000 hospitality vacancies in June 2021, up from 19,000 in February 2021, indicating a tight labour market. This is due in part to Brexit and the UK’s new employment legislation regarding the recruitment of EU citizens. According to new legislation, only “highly skilled scientists and researchers” with no job offer can work in the UK under the global talent scheme, and outside of highly skilled scientists and researchers’ minimum salary threshold of £25,600 for a work permit in the UK (Gov.uk, 2022). Because most jobs in the hospitality industry are classified as “low-skilled” and pay less than £25,600, the labour shortage is expected to worsen (Clark, 2021). As a result, when the new legislation took effect in 2020, the hospitality industry, particularly HB, began to experience staff shortages. According to Caterer (2021), more than 300,000 EU hospitality workers have left and returned to their home countries since March 2020.
Furthermore, the company suffered from a staffing shortage as a result of the environmental disaster COVID-19, as many EU citizens left the UK when the company was closed during the national lockdown and did not return (Annual report, 2020-21).
Consumer trends
Customers’ needs and lifestyles have changed as a result of Covid -19, as people are now more health conscious than ever before. Consumer demand for “innovative food and drink formulations” and enhanced dining experiences that boost mental and emotional health and reduce stress has shifted as a result of COVID-19 (Mintel, 2020). Furthermore, customers are demanding ingredients that are sustainably sourced, as well as a variety of vegetarian and vegan options (Petropoulos, 2022). As a result, consumers’ increased health consciousness, faster lifestyle changes, and spending attitudes will pose a significant challenge to Honest burgers in the future.
However, it may be an opportunity for honest burger to develop an appropriate strategy to keep up with the changing market dynamics. In addition, the pandemic boosted the delivery and takeaway sector, which saw a 345 percent increase in sales in April 2021 compared to April 2019. (UK Hospitality, 2021, p.6). Since then, Honest Burger has taken full advantage of the situation, operating 10 restaurants on a delivery basis during those times and reporting higher sales than they did the previous year at the same time (Annual report, 2020-21).
Solutions
The solutions related to the staffing shortage experienced by HB and caused by the consequences of Brexit and COVID-19 should address resourcing and retention. According to the UK’s new employment legislation regarding the recruitment of EU citizens, a considerable number of them cannot work in the hospitality industry of the country. On the one hand, fast food restaurants, including HB, may pay new salaries that meet the standards on a new regulation, however, this initiative may be regarded as almost non-realizable due to economic challenges imposed by the pandemic. On the other hand, HB may attract local citizens, and for this, the company should reevaluate its working conditions. As a matter of fact, the majority of people do not want to work in fast food restaurants due to inappropriate conditions, workloads, and the absence or respect from management. In this case, HB should revise its regulations and attitude to employees to create a healthy atmosphere. For instance, HB may promote its improved working conditions, articulate them in the workplace, and ask employees to provide feedback in social media – in this case, local citizens will know that HB cares about its workers and differs from other fast-food facilities.
The solutions brought forward are built on the premise that COVID-19 shows employees and consumers as important stakeholders of the industry. With the sector struggling to fill 159,144 vacancies as of August 2021 (ONS, 2021(b)) improving HR practices is important. In this case, the updated conditions of work should be articulated for recruitment and employees may be provided with a minimum 0f 50% from their salaries during the pandemic even if they do not work due to self-isolation. In addition, the workers of HB may participate in a specific program of labor exchange created during the pandemic where they may work in other companies when operations in HB are temporarily unavailable. Finally, new development programs should be implemented to ensure employees’ retention. People should be provided with an opportunity to gain and share new knowledge and skills.
Design Learning and Development Programs integrated in HRM
The staffing shortage experience in the UK hospitality sector cannot only be solved through the old means of increased pay and better benefit. HB should use sustainable and long-term solutions to ensure that it attracts the most skilled employees and retains them in their company. Human resources are one of the most critical components in a company, and therefore HB administration should ensure that it prioritizes the human resource sector.
One of the main strategies that HB can use to address the problem of staff shortage is the learning and development function. L&D will help HB meet the changing needs of the industry by formulating an ambitious vision for L&D (Brassey, Christensen, and Dam, 2019). The main advantage of L&D is that it will help HB attract and retain top talents. As the competition of skilled hospitality staff in the UK intensifies, more employees are looking for workplaces where they can improve their skills. Unlike in the traditional employment system where employees were employed based on productivity, employers have now shifted to contract bases where employees are retained as long as they are productive (Brassey, Christensen, and Dam, 2019).
Therefore, employees are looking for learning and development chances to increase their skills and knowledge in the hospitality industry and make them more attractive to employers. Employees have more control of their professional development, and that is why they are looking for workplaces that will provide them with L&D opportunities. If HB implements a functional and effective L&D, it will attract more skilled employees who want to advance their skills and profession in the hospitality industry. It shows that HD should use L&D as a solution to its staff and labor shortage.
Example of programs that can be adopted by HB includes the informal training approach. This is training that the management or immediate supervisor members will do daily. This training will be based on informal induction programs, which give the employees the ability to solve diverse challenges in the industry (Calinaud, Kokkranikal, and Gebbels, 2020). Additionally, HB can train their employees on customer service, which involves how the employees can professionally engage customers. This training will improve employee satisfaction on the job (Aharon et al., 2021). Another relevant training that HB can provide to its employees is the product and service-specific training. For instance, due to the high demand for vegan menus, HB can train its chefs on how to prepare vegan foods in the hotels.
Other relevant training programs can include quality and standards maintenance. In this training program, the employees will be trained on the guidelines to maintain consistency in the hotels’ services and products (Aharon et al., 2021). HB can train its employees on generic courses such as self-development. This entails training the employees on how to invest in themselves and building their knowledge, experience, and skills. The training will help them be proactive, set SMART goals, and work hard towards them. For immigrant employees, training them in different languages can significantly help them maintain good intercultural practices (Calinaud, Kokkranikal, and Gebbels, 2020). Therefore having paid language courses for them would be an appropriate way to enhance L&D in the hotel company.
HB will therefore have to ensure that as they conduct the L&D program, they recruit more employees in the company to curb the problem of labor shortages. Additionally, HB needs to ensure that all its recruited employees pass through the L&D program. It will enable to reduce the turnover rate and ensure that only employees who are dedicated to the company will be retained. For instance, through information training with the supervisors, they will be able to know employees who need to be retained depending on how they engage and work in the hotel.
Implementation
Design Learning and Development Programs integrated in HRM
Fig 1: SMART evaluation of Learning and Development Program.
The learning and development program for Honest Burger Limited is targeted at all the 639 employees of the company. Employees, management, and invited instructors will be involved to develop and implement the program. It should be aligned to ensure that it meets its strategic goals, including developing, attracting, and retaining top talents to reduce labor shortages. This study will use the Kellogg Logical Model below to implement and measure the impact of the learning development program. The costs of the program’s implementation will be determined after the invitation of educators and final corrections. In relation to technologies, it will require standard tools for presentations and the creation of documents that can be read, printed, and distributed.
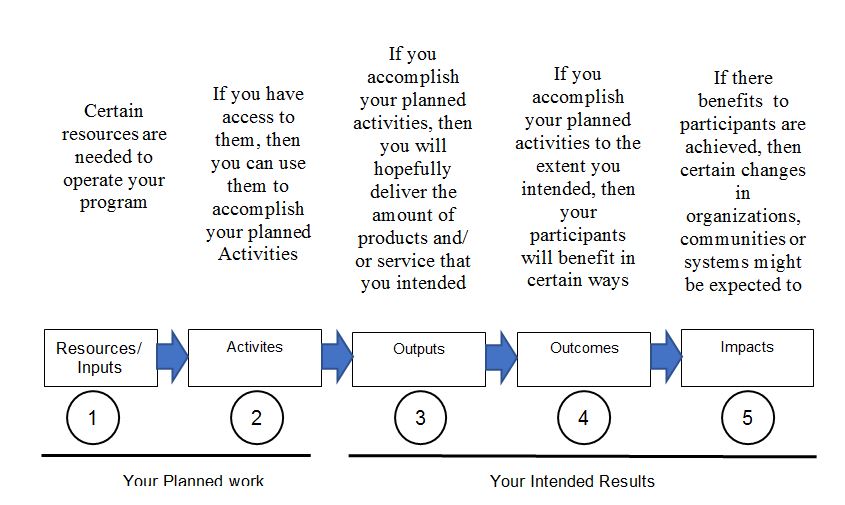
The first step will be assessing the resources that are required to actualize the learning and development program for Honest Burgers Limited. These include the financial, human, and organizational resources that will directly help in the learning and development program (Kellogg Foundation, 2004, p 10). The company will need funding, collaboration with external training companies, learning equipment such as employee handbooks, and other supplies for this program.
Next are the activities which will be involved and can be used to achieve the stated goal. These may include the technologies, tools, and techniques required to accomplish the training program (Langley et al., 2020, p 23). This L&D program will include informal learning, face-to-face training, seminars, workshops, and classes to train the employees on new skills.
The next step will be determining the outputs. These are the immediate products of the training programs (Robinson, 2018). From the L&D program, it is expected that more employees will achieve positive attitude their work. Employee job satisfaction levels are expected to rise, and will be evaluated through improved service delivery and higher customer satisfaction. Additionally, employee turnover is expected to reduce within those three months as job applications to HD increase.
Next will be measuring the outcomes of the project. These include the specific changes in behavior occurring within Honest Burger’s limited (Daviding, 2018). The expected outcomes are increased customer satisfaction in the hotel, low employee turnover, and increased revenue for Honest Burgers. These will be indicators of the positive impact of the learning and development program.
The final step is ascertaining the impact of the learning and development program. This includes both the intended and unintended changes that will occur in Honest Burgers. With good employee experience, Honest Burgers will expect to attract more top talent employees in its pool which will help to cut the job shortages in the hotel (Taylor, 2018). In addition, the results of the program should indicate that employees do not want to leave the company as their professional skills are valued and developed.
References
Aharon, D.Y., Jacobi, A., Cohen, E., Tzur, J. and Qadan, M. (2021). COVID-19, government measures and hospitality industry performance. PLOS ONE, [online] 16(8), p.e0255819. Web.
Barney, J., 1991. Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage: Journal of Management, Vol. 17, No. 1, 99-120.
Brassey, J., Christensen, L. and Dam, N.V. (2019). Essential components of a learning and development strategy | McKinsey. [online] Web.
Calinaud, V., Kokkranikal, J. and Gebbels, M. (2020). Career Advancement for Women in the British Hospitality Industry: The Enabling Factors. Work, Employment and Society, p.095001702096720.
Caterer, 2021. The impact of Brexit and Covid on the UK hospitality workforce. [online] Web.
Clark, J., 2021. The Impact of COVID-19 and Brexit on Hospitality Supply Chains. UK Hospitality, [online]. Web.
Companies House, 2022. Honest Burgers Ltd, [online] Overview. Web.
Crane, A., and Matten, D., 2021. COVID-19 and the Future of CSR Research. Journal of Management Studies, 58(1), pp.280-284.
Danese, P., Manfe, V., & Romano, p. (2018). A systematic literature review on recent lean research: state-of-the-art and future directions, International Journal of Management Reviews, 20(2), 579-605.
Department for Business, Energy, & Industrial Strategy (DBEIS), 2021. Hospitality strategy: reopening, recovery, resilience. [pdf] Web.
Dinev. K., 2021. Takeaway and Fast-food restaurants in the UK. [pdf] IBISWorld. Web.
Evans, N., 2020. Strategic Management for Tourism, Hospitality and Events. [e-book] Oxon and New York: Routledge.
Fame, 2022. Honest Burgers Financial statistics. [online] Bureau Van Dijk. Web.
Freeman, R. E., Harrison, J. S., Wicks, A. C., Parmar, B. L. and De Colle, S., 2010. Stakeholder Theory. The State of the Art. [e-book] New York: Cambridge University Press. Web.
Frynas, J, G., and Mellahi, K. (2015). Global strategic management. Oxford University Press, USA.
Gov.uk, 2020. New Immigration system: what you need to know. [online] Home Office. Web.
Gov.UK, 2022. Food Standards Agency, Government of the UK. Web.
Gov.UK, 2022. Recruiting people from outside the UK. [online] Home Office. Web.
Hache, 2022. Hache at home. [online] Web.
Honest Burgers, 2022. Honest Burgers About us, Honest Burgers Ltd. [online] Web.
Hospitality and Catering News, 2021. The changing shape of hospitality’s workforce: Exodus of 25-40year-olds. [online] Web.
Hutton. G. Foley, N., 2021. Hospitality industry and COVID-19. [pdf] London: House of Commons Library. Web.
Institute for Government, 2021(IfG). Timeline of UK coronavirus lockdowns, [pdf] Web.
Lasserre, p., (2017). Global strategic management. Macmillan International higher Education.
McAllister, J., 2022. BigHospitality. Lates opening: V Honest. [Online] Web.
Mintel, 2021. Covid 19 and Foodservice: A Year on -Market report 2021. [online] Mintel. Web.
ONS, 2021. Job vacancies. [online] Office for National Statistics. Web.
Perera, J., (2017). The PESTEL analysis.
Petropoulos, P., 2022. Full-Service Restaurant in the UK. [pdf] IBISWorld. Web.
Phadermrod, B., Crowder, R.M., Wills, G.B., 2019. Importance-Performance Analysis based SWOT analysis: International Journal of Information Management, Volume 44, February 2019, Page 194-203.
Porter, M. E., 1998. Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance. [e-book] NY: Free Press. Web.
Romei, V., 2022. UK inflation climbs to 30-year high of 5.5%. Web.
Ronnegard., D. and Smith, N. C., 2013. Shareholders vs Stakeholders: How Liberal and Libertarian Political Philosophy Frames the Basic Debate in Business Ethics. Business and Professional Ethics Journal, 32(3-4), pp.183-220.
Sanchez, R., 2008. A scientific critique of the resource-based view (RBV) in strategy theory, with competence-based remedies for the RBV’s conceptual deficiencies and logic problems” In A Focused Issue on Fundamental Issues in Competence Theory Development. Emarald Insight. P 3-78. Web.
Secretary of State, 2020. The UK’s Points-Based Immigration System. Further Details. [pdf] London: HM Government. Web.
The Bank of England, 2022. Monetary policy report – London.
Wagamama, 2022. [online] Web.
Wood, S., 2018. Work–life balance supports can improve employee well-being. [online] Web.