The Purpose
The purpose of the article is to model how employer-provided training has a significant influence on the development of individuals, teams, and organizations.
The basis of the purpose is that employers usually provide training opportunities to their employees with the objective of boosting capacity and productivity of organizations.
As training and development of employees have costs and benefits, they determine the turnover rates.

Research Questions
Main Question
What is the relationship between employee training and individual, team, and organizational development, as well as employee turnover?
Sub-Questions
- What are the models that the Victorian Public Service (VPS) applies in training and development of employees?
- How do attributes of employees and organizations determine models of training and development identified?
- Do models adopted by the VPS have a differential influence on employee turnover?

Literature Review
- Training is an integral aspect of human resources management because it equips employees with relevant skills and boosts their productiveness.
- Improved performance, profitability, and competitiveness are some of the benefits organizations gain from training.
- Employer-provided training is an investment that improves individual, team and organizational development of skills.
- A survey conducted among 526 employers in Australia indicates that 87% plan to boost their expenditure on training to reduce turnover rates of employees.
- The human capital theory holds that employer-provided training improves performance, mobility, commitment, satisfaction, and retention of employees.

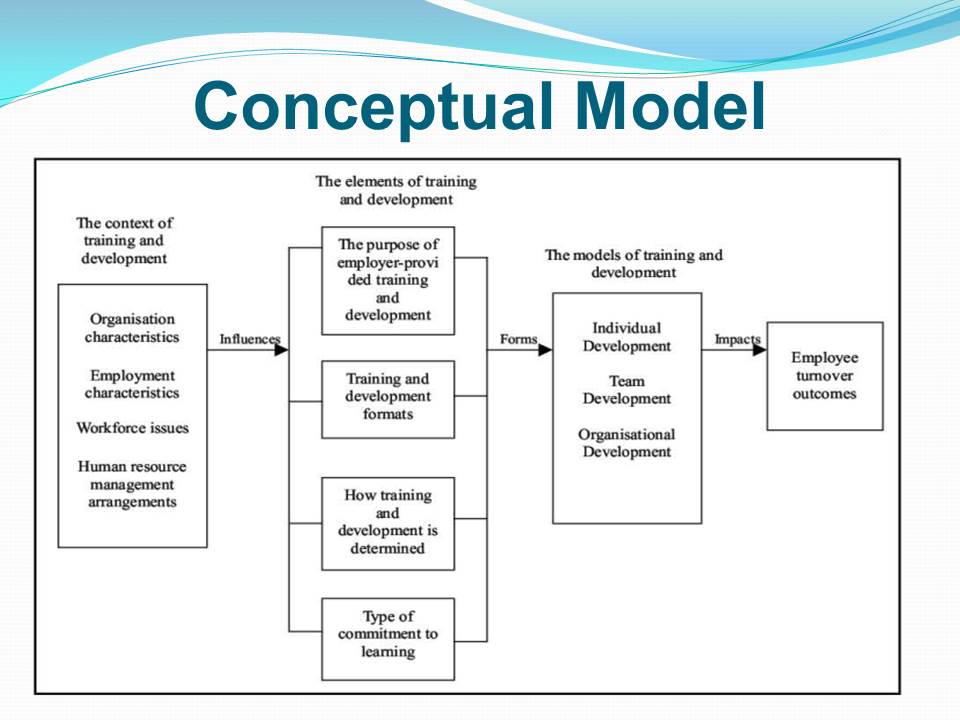
Conceptual Model
- Characteristics related to organization, employment, workforce issues, and human resource management are independent factors that influence training of employees.
- The elements of training entail purpose, formats, determinants, and learning commitment.
- These elements create individual, team, and organizational models of training, which determine turnover rates of employees.
- The correlation between training models and factors that affect turnover rates of employees valid the conceptual model.

Research Design
- The research employed a case study research design because it used the VPS in demonstrating the impact of training and development.
- The VPS reflected large organizations because it had 28 departments and more than 36,000 employees.
- The VPS is an appropriate case study because it experiences challenges of employee retention due to aging and shortage of skills.
- In sampling, six units of analysis (divisions) were selected from three departments of the VPS.
- The study used a qualitative approach in data collection through examination of records, interviews, and surveys of human resources managers, senior managers, and employees in various departments and divisions of the VPS.

Data Analysis
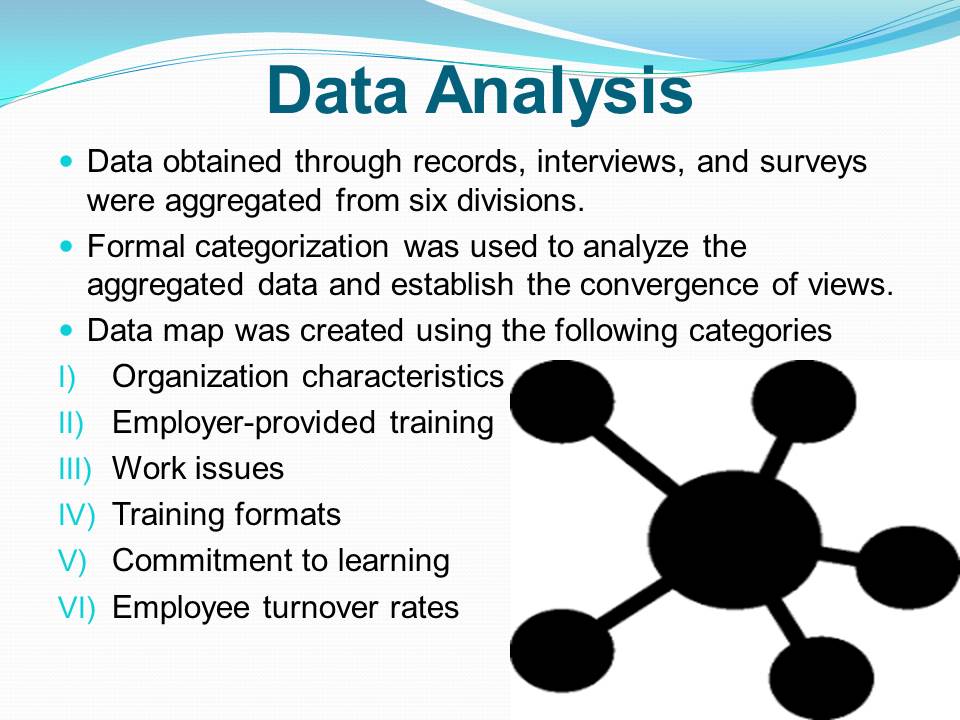
- Data obtained through records, interviews, and surveys were aggregated from six divisions.
- Formal categorization was used to analyze the aggregated data and establish the convergence of views.
- Data map was created using the following categories:
- Organization characteristics;
- Employer-provided training;
- Work issues;
- Training formats;
- Commitment to learning;
- Employee turnover rates.
Findings
- Models of training have differential impacts on the turnover rates of employees.
- Divisions that employed individual development model registered the highest turnover rates due to lack of growth opportunities.
- The adoption of the team development model lowered turnover rates among divisions with high-performance practices.
- Where there were poor commitment and role clarity, the organizational development model reduced turnover of employees.

Limitations
- The study has a low external validity due to the focus on the public service and restraining the application of findings in other industries and organizations.
- Since the study used a small sample size of six divisions in three departments, it excluded important cases that would contribute to elucidation of the models.
- The use of cross-case analysis provides partial information because it fails to identify turnover rates of employees over time.

Conclusion
- The study demonstrated that training and development are critical in the development of capacity and retention of employees.
- Individual and team development models increased and reduced turnover rates of employees respectively.
- The use of external tertiary education has a short-term rather than a long-term retention of employees.
- Team development model improves job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and retention rates.
- The application of high-performance practices decreased the rate of employee turnover.

Works Cited
Kennett, Geraldine. “The Impact of Training Practices on Individual Organization, and Industry Skill Development.” Australian Bulletin of Labor, vol. 39, no. 1, 2013, pp. 112-135.