Agriculture is the backbone of Indian economy. It accounts for nearly 20 percent of the aggregate output. To be specific, nearly half of the population depends on agriculture for their livelihood (Government of India, 2010, p. 6). Contribution of the agricultural sector to the economy is declining, however other sectors thrive.
For example, approximately 45 percent of the total output was obtained from the agricultural sector in the early 70s,. The figure has dropped to less than 20 percent in the last decade. Nonetheless, agriculture still remains a significant source of employment for many Indians. It provides jobs to over half of the country’s population (Government of India, 2010, p. 12).
The dwindling agricultural production has led to a decrease in agricultural exports and an increase in agricultural imports. The ratio of agricultural exports to the total exports dropped to 10 percent in 2010 compared to 20 percent in the early ’90s. On the other hand, the ratio of agricultural imports to the aggregate imports grew by approximately 6.6 percent in the last three decades (Government of India, 2010, p. 13).
The decrease in agricultural production and the increase in agricultural imports have been a cause of major concern. Hot debates didn’t provide any solution to the problem, as well as small reforms. situation deteriorated which led to introduction of the next five-year plan.
As a result, the government came up with a five-year plan, which solely targets the agricultural sector. The five-year plan is aimed at reversing the disturbing trend in the sector.
The five-year plan puts emphasis on the country’s self-sufficiency and self-reliance in the food production (Vaidyanathan, 2010, p. 9; Government of India, 2013, p. 5). This paper explores the impact of the 11th five-year plan on India’s agricultural sector, particularly in promoting local food production and economy stability.
11th Five Year Plans (2007-2011)
As the country’s population keeps growing, the nation needed to enhance its food production to take care of the ever-increasing demand. Given the significance of the agricultural sector to the economy, the government introduced the 11th five-year plan to provide support and incentives to farmers and other stakeholders in order to enhance production of food (Government of India, 2013, p. 5).
There are four principal elements of this policy. The first element is enhancement of viability of agricultural operations by increasing market access, availing insurance cover, and monitoring agricultural commodity prices (IBEF, 2013, p. 7).
The second element is provision of suitable technologies through research and training. The third element is increase of budgetary allocation for agriculture and its infrastructure so as to improve efficient use of natural resources and of agricultural commodity markets functioning.
Last but not least is provision of better delivery of services, for instance, loans to farmers, veterinary services and general farm inputs. In a nutshell, the 11th five-year plan was aimed at increasing food production by providing special programs and building agricultural infrastructure (IBEF, 2013, p. 7).
The Impact of the 11th Five-Year Plan on the economy and local food production
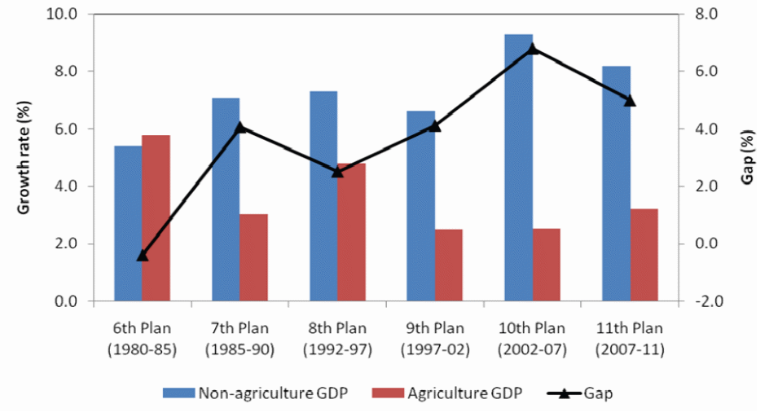
Figure 1 below shows India’s GDP growth rate over the last ten years. It is clear that between 1997 and 2007 the real agricultural output was decreasing, whereas the non-agricultural output was increasing. The ratio of agricultural GDP to the total GDP was very low during that period. This forced the government to reconsider its policy on food production, hence to introduce the 11th five-year plan (Central Statistics Office, 2011, p. 44).
The 11th five-year program introduced the National Food Security Mission (NFSM), which significantly increased production of cereals in the country. The principal goal of the National Food Security Mission was to establish scientific elements which incorporate mechanization, soil supplements and crop security measures (Government of India, 2013, p. 6).
The 11th five-year plan helped to attain 3.2 percent agricultural GDP growth. Even though the figure was below the projected value of 4 percent, it was significantly better than the figures under the previous policies (Central Statistics Office, 2011, p. 45).
Before the introduction of the 11th five-year plan, the share of acreage of agricultural lands decreased by approximately 20 million hectares. Similarly, the area under food grains shrank by 10 percent. The lowest production was recorded in 2008.
However, the introduction of new technologies under the 11th five-year plan led to 80 percent increase in acreage of agricultural lands. The production of rice, wheat and maize increased significantly, followed by pulses on the second place. Under the 11th five-year plan, food grain output increased by 2.3 percent (Central Statistics Office, 2011, p. 45).
Generally, Indian agribusiness is characterized by diminutive and divided area holdings. There are around 130 million active holdings in the country. On average, each active holding possesses approximately 1.2 hectares. Less than 1 percent own more than 10 hectares (Sharma, 2011, p. 6). Before the introduction of the 11th five-year plan, the overall productivity among the smallholder producers was exceedingly low.
Their participation in the market was poor because of such reasons as high transaction costs, low yields, inadequate information and small market consumption. In addition, increased land fragmentation led to big losses on farmlands. As a result, many farmers opted to lease their lands or seek gainful employment outside the agricultural sector (IBEF, 2013, p. 5).
The introduction of the 11th five-year plan brought some positive results. The 11th five-year plan supported the formation of cooperatives and self-help groups. The cooperatives and self-help groups not only helped farmers to access credit facilities, but also to market their products. The government increased access to loan facilities by providing interest-free loans and subsidized inputs.
For this reason, many Indians went back to farming (IBEF, 2013, p. 6). By the end of 2012, cultivation areas had increased by 8 million hectares. The government also introduced other support programs through the 11th five-year plan, such as water for canal irrigation, power for groundwater pumping, retention price subsidy scheme for fertilizers, and access to the international market (IBEF, 2013, p. 7).
According to the IBEF (2013, p. 7), the main objective of the 11th five-year plan was to increase the production of food grains by 20 million tons. The government allocated roughly 900 million U.S. dollars for the project.
There are four main achievements of the 11th five-year plan for the first year according to the National Food Security Mission (NFSM). The first achievement was a 70 million tons to over 90 million tons increase of wheat production.
The second achievement was a 90 million tons to over 110 million tons increase of rice production. The third achievement was an 80 million tons to over 100 million tons increase of maize production. And the last was a 13 million tons to over 15 million tons increase of pulse production (IBEF, 2013, p. 7).
Figure 2 below highlights the growth rate of land, labor and capital output based on the agricultural GDP index. Even though the productivity growth rate in the agricultural sector has always been low, averaging 2 percent per year, during the 11th five-year plan it reached 5 percent. This was the highest figure recorded in the country’s history.
The closest was 3 percent, which was recorded in 1981. As a matter of fact, the Commission of Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP) estimated the growth rate of real wages in the agricultural sector at 8 percent per annum during the period (Government of India, 2013, p. 9).
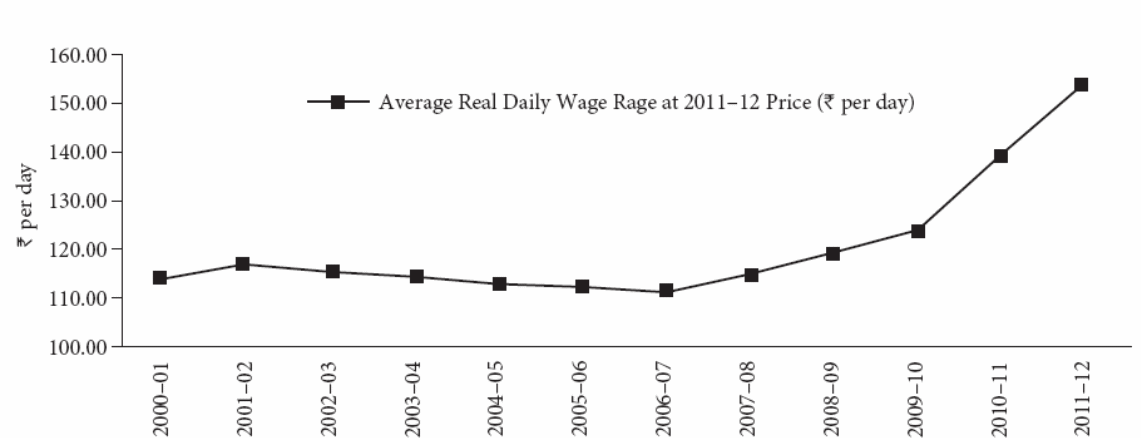
The introduction of the scientific elements, for instance, labor saving mechanization led to the rapid increase of private investment in the agricultural sector. This is attributed to the country’s rigid labor laws and the ever-increasing wages (Shiva, 2013, p. 2).
Although mechanization helped farmers to deal with labor challenges, it caused a sharp decline in capital productivity. Even though moderated by gains from trade deals and debt cancellation, long-term investment in the agricultural sector may be unsustainable due to deteriorating capital productivity (Shiva, 2013, p. 3).
The 12th five-year plan (2012-2017), which is basically a continuation of the 11th five-year plan also emphasizes increase of food grains production. The two plans (11th and 12th five-year plans) recognize the fact that self-sufficiency in food production can only be attained by increasing the production of staple foods. In India, food security is inextricably linked to food grains.
Therefore, the debates on food shortages are concentrated on rice, wheat, maize and pulses (Sharma & Dinesh, 2011, p. 30). 12th five-year plan is also expected to produce high results and solve a lot of food problems in India.
The 11th five-year plan helped substantially to make India a food sufficient country, despite the rapid growth of population. In other words, India is currently food secure due to the 11th five-year plan (IBEF, 2013, p. 9).
Conclusion
Agriculture in India is both a source of food and livelihood. In addition, the sector is very important to the country’s economy. However, the period between 1997 and 2007 was characterized by low agricultural productivity and high levels of food shortage. This forced the Indian government to spend a large amount of money on food import.
On the other hand, the ratio of agricultural imports to the aggregate imports grew by approximately 6.6 percent in the last three decades regardless of the initiated key reforms in the agricultural sector. However, the reform programs were ineffective.
This led to the introduction of the 11th five-year plan, which was aimed at making India a food-secure country through the production of food grains. The plan significantly helped reverse the situation. As a matter of fact, the 12th five-year plan, which runs up to 2017, is just a continuation of the 11th five-year plan. The 12th five-year plan also aims at increasing the production of food grains, which are staples in India.
References
Central Statistics Office 2011, Revised Estimates of Annual National Income 2010-11 and Quarterly Estimates of Gross Domestic Product, 2010-11, Central Statistics Office, New Delhi.
Government of India 2010, Agricultural Statistics at a Glance 2010. Web.
Government of India 2013, Twelfth Five Year Plan (2012-2017): Economic Sectors, Department of Economic Affairs, Ministry of Finance, New Delhi.
IBEF 2013, The Indian Agriculture Sector: Investments, Growth and Prospects, India Brand Equity Foundation, New Delhi.
Sharma, VP & Dinesh, J 2011, High Value Agriculture in India: past Trends and Future Prospects. Web.
Sharma, VP 2011, India’s Agricultural Development under the New Economic Regime: Policy Perspective and Strategy for the 12th Five Year Plan, Indian Institute of Management, Ahmedabad.
Shiva, V 2013, Agricultural Sector in India. Web.
Vaidyanathan, A 2010, Agriculture Growth in India: Role of Technology, Incentives and Institutions, Oxford University Press, New York.