Study Objectives
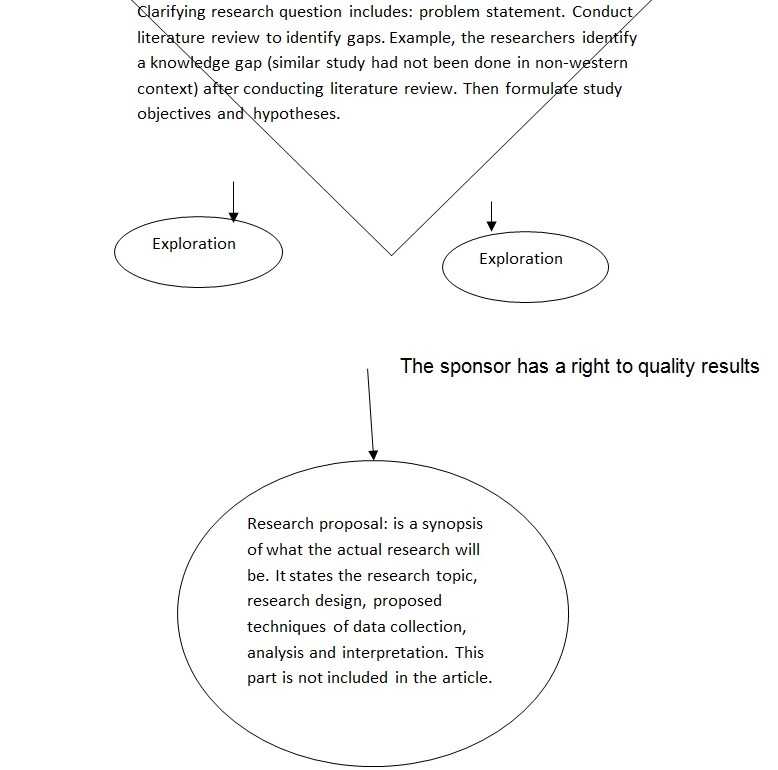
The study had two main objectives. The first objective was to investigate the influence of specific job characteristics on the attitudes as well as behaviors of workers in United Arab Emirate. The researchers focused on five job characteristics namely, “skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). The second objective was to test “the mediating effect of distributive justice on the job characteristics-work outcomes and relationships” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). The choice of these objectives was informed by the fact that the aforementioned job characteristics and their influence on workers’ attitudes have not been extensively studied in non-western countries. Consequently, it was necessary to investigate the effect of these job characteristics in a different region in order to develop new insights on their influence on workers’ attitudes and behaviors. The study adopted the JCM model which illustrates the relationship between the key job characteristics and employees’ performance.
Methodology
The researchers sampled five organizations/ firms from various industries in Dubai. A total of 350 workers were recruited from these organizations to participate in the study. Data was then collected from the participants using surveys or questionnaires with structured questions. Standards scales were used to measure the variables of interest. In order to improve the quality of the findings, the measurement scales were tested for reliability and validity (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). Using separate regression analyses, the researchers investigated the relationships between the variables under study. The hypothesized mediation effect of distributive justice was tested with the aid of the model developed by Baron and Kenny.
Findings
The study revealed that skill variety as well as feedback had significant influence on performance outcomes. They particularly affected employees’ satisfaction with their jobs, workers’ commitment to the firm and turnover levels. This finding was similar to those found in Western countries. “Task identity and task significance” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009)were also found to have significant impacts on attitudes towards work as well as employees’ behaviors. This finding, however, did not support those found in western countries. A positive relationship was found to exist between autonomy and turnover intensions. Distributive justice had full mediation effect on “the relationships between skill variety and job satisfaction and between task identity and turnover intensions” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). However, distributive justice had limited mediation effects on the remaining relationships.
Limitations
The study had the following limitations. First, the findings were negatively affected by the bias attributed to common research methods. Additionally, the reliability of the findings was limited due to the fact that the researchers used cross-sectional data. Consequently, the researchers identified future study areas that will address the limitations of their study. Despite these limitations, the study was successful in providing new insights on the variables under study. Besides, it enhanced understanding of the mediating influence associated with distributive justice.
Implications
The researchers concluded that developing some job characteristics can help to increase performance outcomes. For instance, they concluded that task significance as well as skill variety can enhance workers’ motivation (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). Thus, managers should focus on implementing the job characteristics that enhance performance and employees’ commitment to the organization. The positive effects of the job characteristics can be improved by enhancing distributive justice at the workplace.
In conclusion, the study’s value is found in the fact that it was among the pioneer studies on the relationships between job characteristics and performance outcomes. Additionally, the study contributed to the human resources literature by being one of the first to investigate the mediation effect of distributive justice.
Type of Research
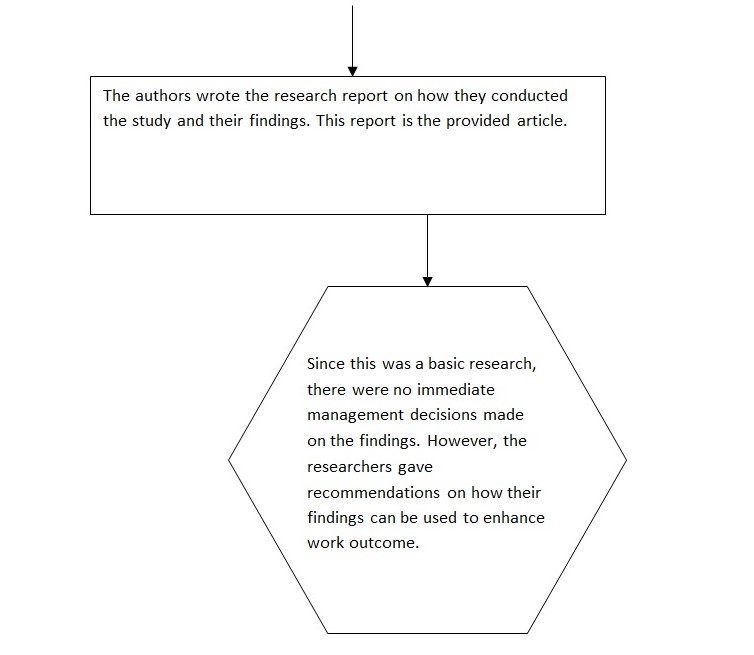
This is a basic research since its main aim was to generate new knowledge to complement existing literature. Particularly, the researchers aimed at obtaining new insights on the effect of job characteristics on employees’ performance and how such effects are enhanced by distributive justice. Thus, the focus of the study was to deepen understanding of the variables under study in order to answer the question, ‘how can performance/ work outcomes, be enhanced through job characteristics’? Consequently, the researchers used a qualitative study to investigate the variables under study.
Critique of the Research Design
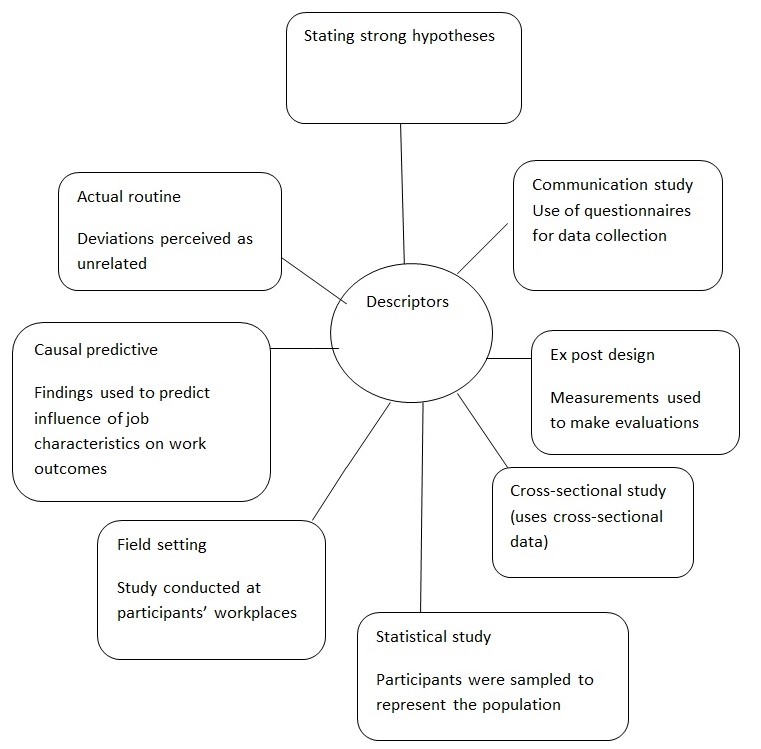
A research design is “a blue print, a guide, and a framework for fulfilling the research objectives” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The purpose of the study was to determine the causal effects between various variables. The researchers adopted a qualitative approach and utilized cross-sectional data to achieve the objectives of the study. The qualitative approach is an in-depth study. Thus, it enabled the researchers to obtain comprehensive information about their topic of study. Additionally, it enhances understanding of the phenomenon under study in a holistic manner. This is because the participants are studied in their natural setting/ environment (workplace in our case) which enables the researcher to get fast-hand information. However, cause and effect relationships cannot be easily established using cross-sectional data (McBurry & White, 2009). For example, the researchers found that skill variety enhanced workers’ motivation. However, they could not tell why skill variety led to high motivation. Besides, change in the variables under study can not be measured when a study adopts a cross-sectional approach. In this study, changes in the effect of job characteristics or workers attitude could not be measured since there was no follow up study.
Cross-sectional studies facilitate collection of data on several variables, from a large sample. In this case, it allowed the researchers to collect data on five variables. This facilitated the in-depth study associated with qualitative approach. However, the in-depth nature of qualitative approach limits the scope of the study. This is because it necessitates the use of time-consuming data collection methods (McNeil & Chapman, 2005). In this case, the researchers used questionnaires which can take a lot of time as the researcher waits the respondents to mail back the completed surveys. A wide topic can not be investigated if time is a constraint. Finally, cross-sectional design facilitates exploratory research. The study was based on the cross-sectional design since it was a pioneer study on impact of job characteristics and distributive justice.
The researchers relied on questionnaires as their main data collection technique. Since the researchers had to depend on self-reports from the employees, they could not test the reliability of the collected data. The sample size of only 350 employees is small given the large size of UAE labor force. Thus, generalization might not be very accurate.
Characteristics of a Good Research
Evaluating the quality of this study against the standards of a good research reveals the following strengths and weaknesses.
First, a good research should have a clearly defined purpose that illustrates what the researcher intends to accomplish (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The purpose of the current study is clearly specified in its objectives. These objectives include investigating the effects of “five job characteristics on work attitude and testing the mediating impact of distributive justice on job characteristic-work relationships” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009).
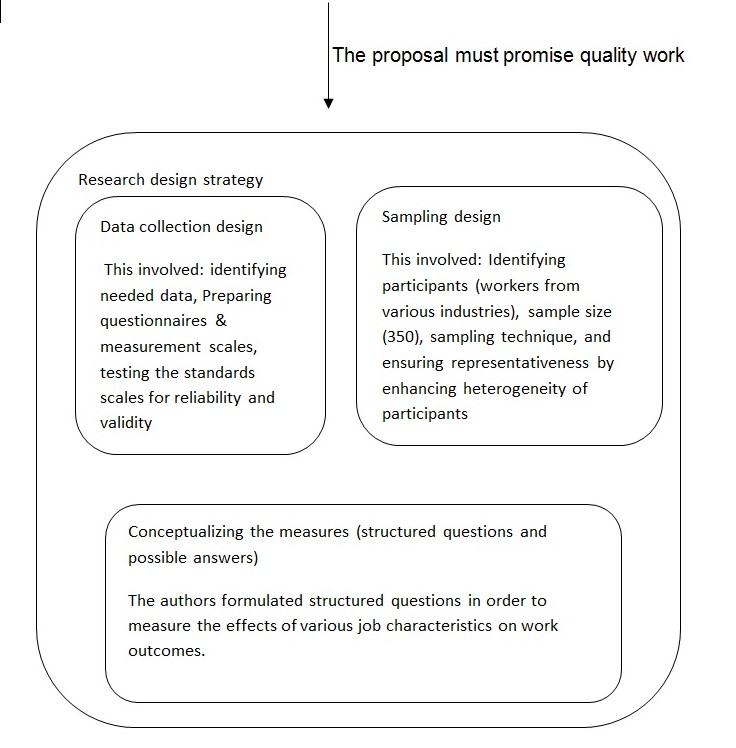
Second, the study should have a detailed research process. The researchers clearly formulated the research question in the form of six hypotheses. While such a large number of hypotheses were necessary for the scope of the study, focusing on fewer hypotheses could have resulted into better outcomes. The design strategy identifies the “type, purpose, scope and environment as well as the time dimension of the research” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The sampling design, however, fails to explain the sampling technique used to recruit the participants. Additionally, data collection design only illustrates that validity and reliability was ensured in the measurement instrument, but does to explain how it was achieved. The measurement instrument mainly consisted of structured questions. Excluding open-end questions, thus, denied the participants a chance to fully express themselves. Besides, the measurement instrument was not pilot tested as required in order to ensure reliability and validity. The data collection procedure is explained, but, the process of data preparation for analysis is not explained.
The research had a well planned design. However, as discussed earlier, the design has several limitations. The limitations are mainly attributed to the use of cross-sectional data and the qualitative approach.
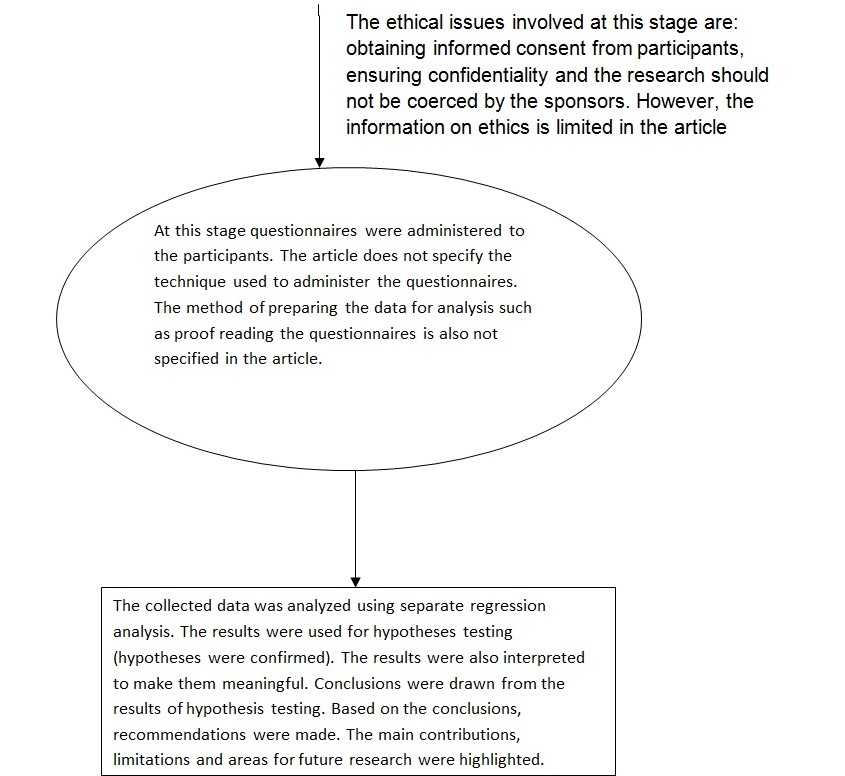
Information about the ethical standards of the research is limited, and this makes it hard to judge its ethical position. For example, we can not tell whether informed consent was obtained from the participants. We can not tell whether or not the questionnaires were anonymous to ensure privacy. However, given the robust findings of the study we can conclude that it had value to the society. In this context, it can be considered ethical (Kother, 2008).
The limitations of the research have been identified. Besides, the researchers recommend further studies in order to address the identified weaknesses. The study adopted a qualitative approach, but, used statistical (quantitative) approach for its analyses. However, the process of converting the data from qualitative to quantitative, such as coding, is not addressed by the researchers. The findings have been presented in the form of a report. This has helped to eliminate ambiguity. Finally, the conclusions are justified since they are drawn from the findings and results of hypothesis testing. For example, they conclude that managers should implement skill variety to enhance workers’ motivation. This draws from the findings that skill variety and motivation have a positive and significant relationship.
Critique of the Literature and Quality of the Article
According to Cooper and Schindler (2000), a good research article or report should have four main parts. These four parts include the “executive summary, overview of the research, implementation strategy section and a technical appendix” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). Thus, following Cooper and Schindler (2000), the quality of the article can be descried as follows. The executive summary has been conceptualized as abstract. The abstract has given the main details of the research. In particular, it has summarized the research’s findings, purpose, methodology, limitations, and implications/ recommendations. Thus, the summary section is complete since it captures all the details of the research.
The overview of the research has been done as follows. The introduction part gives adequate background information about the problem and the justification for the study. The literature review part explains the “exploratory findings from secondary data” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The research’s design as well as its procedures has been explained under the methods and analysis section. Finally, the conclusion is explained under the discussion section. Thus, the article has given a complete overview of the research.
The implementation strategy has been explained under the implications section. This section has explained how the research findings should be used to enhance work outcome. However, the article lacks a technical appendix section. Consequently, it lacks information that can be used to replicate it.
The researchers fail to distinguish empirical literature and theoretical literature or conceptual framework. The two have been discussed as one and the same thing, thereby causing confusion. The theoretical literature review or conceptual framework should be discussed separately since it is a general view that guides the study. The empirical literature review is an analysis of past research findings on the topic of study. Thus, it helps in making comparisons with findings of the current research.
The empirical literature on job characteristics identifies the researchers and their findings. However, the methodology adopted by these studies; the countries in which they were conducted as well as the participants are not explained. Thus, it is difficult to compare their findings with those of the current study. The same flaw is repeated in the literature on “characteristics, distributive justice and work outcome” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009).
The empirical literature on work attitude has clearly specified the country in which the studies were done (UAE). Similarly, the time when the studies were done and the main findings are clearly defined. However, most of the empirical literature from UAE is based on studies done by one researcher, Yousef. Consequently, the possibility of a biased view is high in the literature. Besides, reliability of the findings can not be determined since the studies were done by the same person.
Finally, the researchers did not criticize or evaluate the literature review. Best practice in business research requires the researcher to evaluate the literature review in order to find knowledge gaps and possible flaws that might exist in previous studies.
Evaluation of the Research Question or Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an informed guess about something. The role of a research is to investigate a phenomenon with the aim of testing the hypothesis or answering the research questions. The current study has developed six hypotheses. Three of these hypotheses are related to the “impact of job characteristics on work outcome” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009) while the remaining three are related to the effect of distributive effect on job characteristics. The characteristics and quality of the developed hypothesis can be explained as follows.
The researchers developed causal relationship hypotheses. This is because their hypotheses suggest that a change in one variable causes either a positive or a negative change in another variable. For example, they hypothesis that, “each job characteristics has a positive relationship with job satisfaction” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). Thus, in terms of the role of a hypothesis, the research’s hypotheses are effective due to the following reasons. First, the hypotheses helped the researchers to establish relevant facts. Since the hypotheses suggest causal relationships, the researchers focused on finding out whether changes in work outcomes were caused by changes in job characteristics. For example, the researchers found that enhancing task significance led to high levels of job satisfaction among employees.
Secondly, the hypotheses did a good job in guiding the study. Stating the hypotheses enable the researchers to develop the big picture of the expected results. Consequently, the study focused on a particular methodology in order to realize the expected results.
Third, the hypotheses formed the basis of the research design. From the hypotheses it is clear that qualitative data was needed to realize the objectives of the research. Consequently, they acted as a guide in choosing the data collection method. Even though qualitative data was used in the study, testing the hypotheses required statistical (quantitative) techniques. For example, regression analysis was used to test the statistical relationships between the dependent and independent variables. This led to the transformation of the qualitative data into quantitative data. Thus, the hypotheses also guided the analysis process.
Finally, the hypotheses provided a framework for making conclusions (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). As stated earlier, hypotheses are guesses which are either accepted or rejected through empirical studies. The researchers used their findings to test the hypotheses of the study. The results of the hypothesis testing process formed the basis of making conclusions. For example, the research found a significant and positive relationship between “skill variety and motivation” (Hossman & Elanain, 2009). This finding led to the conclusion that enhancing skill variety will translate into high motivation among workers.
In light of the characteristics of a strong hypothesis, the study’s hypotheses can be explained as follows. All the hypotheses are short, “easy to read and understandable” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). Additionally, the hypotheses are direct while still remaining powerful. They clearly illustrate the relationships between variables. Consequently, they are better than potential hypotheses that could have been used in the study.
The hypotheses used in the study were adequate. They were developed from the findings of previous studies. Besides, they followed the most likely results. This point is illustrated by the fact that the researchers had already known the relationships between the variables by conducting literature review. Thus, they guessed that the same findings could be found in non-western countries.
Finally, a good hypothesis should be testable, given the data that is available to the researcher. The hypotheses enabled the researchers to identify the participants, the required data and the expected results. Using the available data, all the hypotheses were tested. The test revealed that some of the findings confirmed the studies conducted in western countries while others rejected the findings of previous studies. We can conclude that the researchers stated strong hypotheses. Besides, the hypotheses served the intended purpose as discussed above.
Evaluation of the Appropriateness of the Data used
The data used in the study was adequate for the scope of the research. The researchers used a large number of articles as sources of their information. The sources of information included journals, textbooks and publications of past research findings. These sources were published at different points in time. Consequently, the researchers had the opportunity of analyzing the evolution of the research topic or the effects of the variables over time. The sources contained information or data collected through studies conducted in different areas. Most of these studies were done in western countries. Using data collected from different geographical areas, such as different countries, enhanced the reliability of the findings (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). This means that we can comfortably make generalizations on the population if consistent results are found in different geographical areas. Thus, using a variety of sources enhanced a deep understanding of the topic under study since they presented different or diverse views.
The data can be described as ‘authoritative’ since they are from trusted sources (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). Most of the sources are articles published in peer reviewed journals which not only give emphasis to a balanced view, but also have fewer errors. This is because information in such journals is verified for reliability prior to its publication. Journal articles are also suitable since their findings are based on empirical studies.
The relevance of the used articles is demonstrated by the fact that they are directly linked to the research topic. Most of the sources presented information about the topic of study. This is illustrated by the fact that some of the journal articles had research topics that are similar to that of the current study. Besides, in-text citations, especially quotes, from some of the used sources reveal that their contents are applicable to the study at hand.
The main weakness of the used sources is that most of them are not up to date. Most of them were published in 1970s, 1980s, and 1990s. Even though this was a business research, it focused on the socio-psychological attributes of the participants. Such attributes include job satisfaction, work attitude and motivation. These attributes evolve over time, depending on the work environment. This has two implications for research. First, the findings of past studies are needed in order to trace the evolution of the variables (socio-psychological attributes) over time. Second, the findings of past studies might be less useful (irrelevant) as people change their attitudes and perceptions. The current study, however, can not be easily used to trace variables of socio-psychological nature since most of them were published in the same period, 1970s and 1980s). Additionally, some of the sources may not present the current view about the research topic. We can conclude that the sources and the data contained in them are not reliable.
Data Collection
The researchers used the communication method to collect data. In particular, questionnaires were used to gather the required information. The questionnaires had structured questions and standards scales for each measure. The reliability of each scale was tested for reliability before being used. This means that the scales were able to consistently measure what they were designed to measure.
The use of questionnaires is probably justified by the fact that it had the potential of enabling the researchers to reach many responds within a relatively short period of time. The response rate of 70% is encouraging since it indicates that majority of the participants were willing to participate. Besides, collecting data from as many participants as possible enhanced the quality of the findings (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). However, a follow up was not done on the questionnaires that were not returned. Consequently, the researchers missed the chance to determine or to find out why some participants failed to complete the questionnaires. Besides, the opinions of such participants were left out of the study.
The use of structured questions might be justified by the fact that it enabled the researchers to ensure objectivity in the study. This is because the questions had to be answered only in a particular way. For example, the answer to a structured question can be a yes or no. However, failing to include open end questions denied the researchers the opportunity to gather more information.
Given the qualitative nature of the research, a questionnaire was not an adequate technique of data collection. A questionnaire, for instance, can not enable the researcher to obtain certain information such as changes in feelings or emotions. A method such as interview could have helped the researchers to understand the attitudes of the employees in a better way.
Reliability of questionnaires is also limited due to the fact that it is difficult to verify “how truthful the respondent is being” (Kother, 2008). The respondent can give false information if he misinterprets the questions or if he fails to give enough thought to the questions. When this happens, the conclusions based on the collected data will be unreliable.
Data collection through questionnaires enhanced the analysis process. The structured nature of the questions made it easy to transform the data from qualitative to quantitative. Consequently, it was possible to use quantitative techniques to analyze the data.
Evaluation of the Data Analysis
Data analysis was done with the aid of statistical (quantitative) techniques. In particular, regression analysis was used to separately investigate the effect of each job characteristic on performance outcomes. Testing for mediation effect was done using the approach proposed by Baron and Kenny.
Regression was suitable for the analysis since the statistical significance of the outcome formed the basis for either rejecting or accepting the research hypotheses. The regression analysis was, however, not comprehensive (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). A long regression that includes all the variables was not developed to investigate the overall effect of the independent variables on the dependent variables. The results are likely to have been different if a long regression was used alongside the separate regressions. Consequently, it could have been possible to verify the reliability of the findings.
The researchers attempted to control for various variables in order to improve the reliability of the results. However, only demographic variables were controlled for. Important variables such as staff training and development, organizational policies and relationships among workers were not controlled for. Thus, it is not possible to conclude with certainty that the found results were purely attributed to the effects of the included variables.
The researchers failed to address the problem of reverse causality. Reverse causality is a situation whereby the independent variable causes the dependent variable and vice versa. For example, a negative relationship was found between skill variety and turnover intentions. This means that an organization with low skill variety among its workers is also associated with high turnover intentions. While this can be true, we can not rule out the fact that the presence of high turnover intensions can induce the management to enhance skill variety. In this case, it is turnover intensions that cause skill variety.
Despite the weaknesses of the analysis process, the results enabled the researchers to effectively test all the hypotheses. The adoption of Baron and Kenny’s procedure improved the outcome of mediation testing. This is because the recommendations of the procedure were followed as required.
Evaluation of the Discussion Part
The discussion part explains the main conclusions of the researchers. A high quality discussion part not only explains the conclusions of the study, but also explains how the conclusions were reached. Thus, it should answer the research question. In order to achieve this objective, the researchers began by restating the purpose or the main objectives of their study with the aim of demonstrating the extent to which they were achieved.
The researchers have clearly stated the main findings of their study. They have also interpreted their findings by offering intuitive explanations on the possible causes of the results. For example, the regression analysis showed a positive relationship between task variety and commitment to an organization. However, this statistical outcome does not explain the cause of the relationship. Thus, the researchers used their knowledge of human resources management to offer explanations for the causes of the results. In this example, the researchers asserted that task variety helps to reduce role conflict which in turn stimulates the workers’ satisfaction and commitment to the organization. The interpretation and explanation of the causal relationship has two advantages. First, not all users of the research findings have knowledge of statistical procedures (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). Thus, they might not correctly interpret the coefficients of predictors. In this case, offering interpretation enhances understanding of the findings. Second, offering explanations on the causes of the results enhances the implementation of the findings.
The findings have been used to test the research hypotheses. All the hypotheses have been supported by the results as expected by the researchers. The conclusions of the study have been drawn from the results of hypothesis testing. In order to enhance the usefulness of the conclusions, the researchers have explained the importance of their findings. For example, they explain that feedback helps workers facing role conflict by enhancing job satisfaction. This further enhances the implementation of the findings.
The discussion part has been used to generate new knowledge that complements the existing literature in regard to the research topic (Kother, 2008). The findings of the research have been compared with those found by previous studies. For instance, the study supports the widely held view that job characteristics enhance performance outcomes. This finding reinforces the confidence in the literature about job characteristics and its influence on performance outcome. The researchers further give explanations for the differences that exist between their findings and those of previous studies. For instance, in western countries task significance was found to rarely enhance performance outcomes. However, in UAE, task significance was found to have significant positive effect on performance outcome. This difference has been attributed to the fact that the culture in UAE associates task significance with status in the society. Thus, the significance of a given task is likely to lead to high job satisfaction in UAE, than in western countries. The researchers have, thus, generated new knowledge by justifying the difference between their findings and those of other researchers.
The other strength of the discussion part is that the researchers have criticized their work in an honest manner (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The limitations of the study have been clearly discussed alongside their possible effects on the findings. Additionally, several areas for further research have been identified. Further research has been recommended as a solution to the limitations of the study. The self-criticism, thus, offers a framework for developing hypotheses for future studies. It also enables the users of the research to determine the extent to which they can apply the findings.
We can conclude that the discussion part is adequate due to the following reasons. First, it answers the research questions or hypotheses. Second, it clearly interprets the findings. Finally, it states the limitations of the study and how such limitations can e addressed.
Evaluation of Contribution Strength, Limitation and Future Research
A good research should achieve its objectives despite its limitations. As stated earlier, the limitations of the study have been clearly discussed. The causes of the limitations and their potential impact on the results have been discussed too. Future studies have been recommended to overcome the identified limitations. For example, since the study used cross-sectional data, the researchers suggest that the study should be replicated in future to enhance the applicability of its findings.
The main contributions of the study have also been identified. Particularly, the research deepened understanding of the impact of job characteristics on work outcomes.
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Article
The article has the following strengths. First, the findings have contributed to the body of knowledge regarding the relationships between various job characteristics and specific work outcomes. Second, it meets most of the characteristics of a good research. In particular, it has a clearly defined purpose, a detailed research process, and a thoroughly planned design. The ethical implications of the study, however, could not be easily evaluated due to lack of adequate information. Third, trusted sources of data were used in the article. Besides, a large number of sources were used to explain the research topic. Finally, the methodology used in the article is adequate. The hypotheses were not only clear, but also “adequate, better than others as well as measurable” (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). The response rate in data collection was very high. Besides, heterogeneity of respondents was ensured with the aim of enhancing representativeness. This indicates that sampling design was adequate.
The weaknesses of the article include the following. The literature review is not adequate. This is because the sources used were not up to date. Besides, information such as the place in which previous studies were done is also not mentioned in the review. Second, cross-sectional data was used, thereby reducing the usefulness of the findings for generalization. Finally, the analysis was inadequate due to the following reasons. The problem of reverse causality was not addressed. Only demographic variables were controlled for, while other important variables such the relationships among workers were ignored.
Recommendations on how to Improve the Paper
The paper should conform to all the characteristics of a good research. Consequently, the ethical issues such as ensuring confidentiality over information, obtaining informed consent and respect for subjects should be addressed. The analysis method should be improved by employing additional statistical methods of analysis. For instance using an instrumental variable model could help to eliminate the problem of reverse causality (Kother, 2008). Besides, representativeness of the sample could have been improved by recruiting respondents from more industries in Dubai.
The literature review should be improved by using more of up to date sources of data. This will improve the reliability of the review (Cooper & Schindler, 2000). Besides, a good literature review should have key features such as date of publication, names of researchers, place in which the study was done, methodology used and the findings.
A longitudinal approach should be adopted to enhance the reliability of the findings. It will help to determine the consistency of the findings and the reliability of the measurement instrument, thereby enhancing the use of the findings for generalization.
Finally, data collection strategy should be improved. This can be achieved by including open end questions in the questionnaires. Besides, additional data collection methods such as focus group discussions will help in gathering more accurate and adequate data.
Model 1: Research Process
Model 2: Descriptors of research
References
Cooper, D., & Schindler, P. (2000). Business Research Method. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hossman, M., & Elanain, A. (2009). Jb Characteristics, Work Attitudes and Behaviors in a Non-Western Context. Journal of Management Development 28(5) , 457-477.
Kother, R. (2008). Reserach Methodology. New York: McGraw-Hill.
McBurry, D., & White, T. (2009). Reserach Methods. New York: McGraw-Hill.
McNeil, P., & Chapman, S. (2005). Reserach Methods. New York: Cengage Learning.