Introduction
The healthcare process is intricate and varied, involving several parties, including providers, patients, payers, and legislators. Three crucial aspects of healthcare delivery- cost, access, and quality are interconnected and greatly influence patient outcomes. Achieving the best results in healthcare requires balancing these aspects.
Addressing these problems is difficult, especially when choosing policies that affect care availability, costs, and quality (Gopal et al., 2019). The link between cost, access, and quality will be discussed, as well as essential policy concerns surrounding healthcare provision and difficulties in defining and quantifying healthcare quality. Moreover, a graphic depiction of the link between these three elements will be presented.
Take Aways
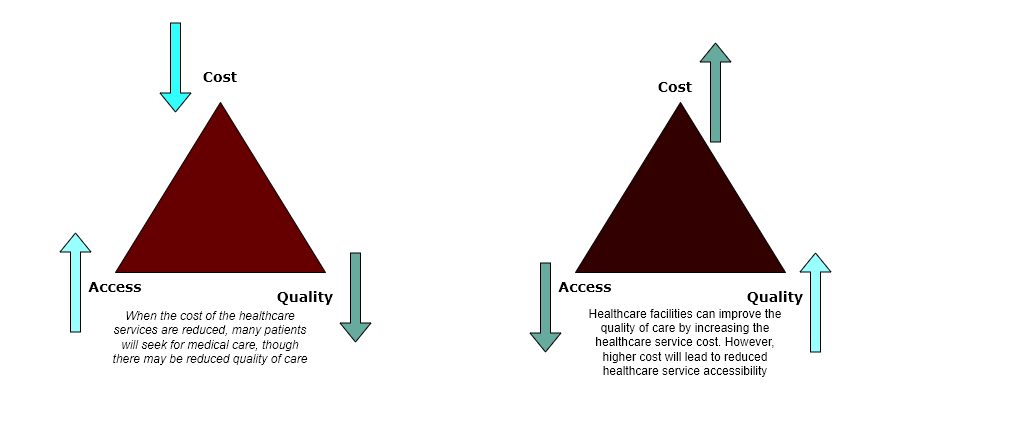
- Three key aspects of healthcare delivery are access, cost, and quality.
- Each of the three variables affects the others due to their interdependence.
- To achieve the best results in healthcare, these aspects must be balanced.
- Policy choices are essential to solving problems with cost, access, and quality.
Explanation of the Key Concept
In healthcare delivery, cost, access, and quality issues are interconnected. The cost of healthcare services impacts access and quality of care. High expenses may restrict access to healthcare services, and a lack of access may result in less effective treatment (Gopal et al., 2019). On the other hand, poor care might eventually result in higher expenses since patients might need more medical attention or hospital stays. Hence, attaining the best results in healthcare requires balancing these aspects.
Critical Policy Issues
Access to Care
Health insurance coverage is one of the most important political problems concerning access to care. Underinsurance or a lack of coverage may hamper access to healthcare services, especially for low-income individuals and families (Gopal et al., 2019). Provider shortages, geographical restrictions, and linguistic and cultural obstacles are other policy challenges that impact access to care.
Cost of Care
Healthcare spending policies aim to control costs while maintaining the standard of care. Promoting value-based care is one way to reduce high healthcare expenditures. Moreover, value-based care aims to improve patient outcomes while lowering costs by giving high-quality treatment and eliminating extraneous services (Gopal et al., 2019). Price transparency, prescription pricing, and decreased administrative expenditures are other policy concerns associated with the cost of care.
Quality of Care
Patients should receive safe, efficient, and patient-centered care according to policy decisions made regarding the quality of treatment. Patient safety is one of the most important factors affecting the standard of care. Reducing medical errors, enhancing infection control, and raising patient engagement are ways to increase patient safety (Gopal et al., 2019). The training of the healthcare personnel, performance evaluation, and accountability are further policy concerns relating to healthcare quality.
Challenges in Defining and Measuring Quality
Due to some factors, defining and assessing quality in healthcare has been challenging. The complexity of healthcare delivery systems is one factor. Healthcare systems involve a wide range of stakeholders, including payers, legislators, and providers, all of whom have unique viewpoints on what quality care entails. Moreover, elements outside of the providers’ control, such as patient behavior, socioeconomic level, and environmental factors, can impact the quality of care (Gopal et al., 2019). Finally, it can be challenging to design and execute reliable data sources and metrics necessary for accurately monitoring the quality of care.
Conclusion
The cost, access, and quality of healthcare are three aspects that are interconnected and interdependent on one another. In order to get the best possible results in healthcare, it is necessary to strike a balance between these many aspects by making decisions regarding healthcare policy and improving the healthcare system. Despite obstacles in defining and assessing the quality of care, there are still ongoing initiatives to enhance healthcare quality and outcomes.
Reference
Gopal, G., Suter-Crazzolara, C., Toldo, L., & Eberhardt, W. (2019). Digital transformation in healthcare–architectures of present and future information technologies. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 57(3), 328-335. Web.