The US automobile market has received a severe blow due to the economic recession (Feroli, 2009). The recession especially hit the annual auto sales in the country, which caused dire problems for the large automakers of the country. US companies filed for bankruptcy, asked for financial bail out, and underwent structural changes in order to be function efficiently. The new auto market in the US shrank by 22.4% in 2009 and is expected to reduce further by 1.1% by 2014 (Datamonitor, 2009a). The US new car market generated total revenue of $151.6 billion in 2009, which presented a growth rate of -8.7% (Datamonitor, 2009a). The market reduced by 10.2 percent in the US from 2005 through 2009. Figure 1 shows that the sales of automobiles that is new cars and light trucks in the US from 2005 to 2009. The figure shows that the sales of automobiles in the US market i.e. new cars and trucks had increased in 2006, but since then have been going down. The market has hit the lowest sales in 2009 as car sales dropped below $150 billion and truck sales below $200 billion. This has badly hit the US automakers like GM, Ford, and Chrysler. These big-three automakers of US Given this condition, as they face bankruptcy and the US based foreign automakers are still able to maintain growth it is important to understand the state of the US automakers is in the present downturn in the auto market (Feroli, 2009). This paper will discuss General Motors and the way it has been affected by the economic recession.
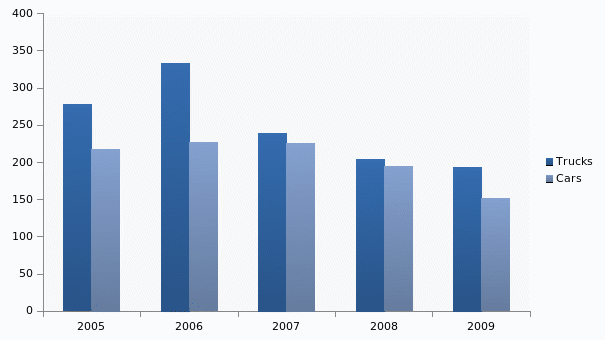
The recession has led General Motors (GM) through bankruptcy and eventual public bail out of the company, which has led the control of the company with the government and the unions owning majority of the company shares. The present strategy that the company undertakes is to undergo massive restructuring endeavours that will result in leaner and more efficient organization. A revenue analysis of the company shows that the revenue recorded by the company in FY2008 is $148,979 million which declined by 17.2% since FY 2007 (Datamonitor, 2009c). The largest fall in sales revenue was faced in North America, which was the company’s largest geographic market, where sales fell by 59.3% (Datamonitor, 2009c). a SWOT analysis done of the company shows that the main strengths of the company are its brand portfolio which has got names like Buick, Cadillac, Chevrolet, GMC, Hummer, Pontiac, Saab and Saturn (GM, 2010). The company has a very strong dealer network in the US. The marketing of the GM vehicles are done through independent dealers’ network and had 6,375 dealers in the US in 2008 (Datamonitor, 2009c). One of the main weaknesses of GM is inadequate liquidity through 2005 to 2008 that led to their eventual bankruptcy (Datamonitor, 2009c). The company had gathered a negative operating cash flow in 2008 of $12.2 billion (GM, 2010). In 2008, the company faced a negative earning before tax of $447 billion (GM, 2009). This greatly restricted the company’s innovation and R&D expenditure in order to develop new technology for their products. Performance of the company had been very weak in one of its key business segments i.e. North America and Europe. GM had its presence mainly in North America and its sales volume declined heavily in the region. North America accounted for more than 55% of their total revenue and Europe comprise of 21% of their total sales. Thus, a decline in the sales in these geographical segments crippled sales of the company considerably (Datamonitor, 2009c; GM, 2010). The opportunities that the company has are in its expansion in other geographical areas yet unexploited by the company i.e. the emerging economies. Emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil hold many opportunities for a growth for automobile companies. New car market in India grew by 15% in 2008 and that in China by 14.2% in 2008 (Datamonitor, 2009c). These markets hold immense potential for growth and increase in consumption of automobiles. Further, there is an increased demand fro hybrid cars and electrically drives vehicles due to the increasing concern regarding global warming, pollution, and depleting oil resources (Freeman, 2003). The company faces threats from global competitors like Toyota and Honda and the recession, which has made the functioning of the company difficult.
The present state of the company makes it important for the company to undergo organizational changes in order to make its operations more efficient (Tell & Kleiner, 2009). GM has already begun to look into the complexities of its operations and has “undertaken efforts to improve fuel emissions as well as fuel economy” of its vehicles (Tell & Kleiner, 2009, p. 23). For this, the company must undertake efforts to make hybrid and electric vehicles, which will have higher demand in the future. Further expansion of its geographic operations in the emerging economies will provide the company better opportunities to gain higher sales as the sales in these countries are expected to rise further in future. Further one other reason for depleting market share of GM in the US has been an increasing demand for smaller and more fuel-efficient cars which foreign carmakers like Toyota have provided, but GM has failed. Thus, increasing the range of smaller cars will be effecting in retaining customer loyalty (Sharp, 2009). Thus, the main aim of GM should be to restructure its operations in order to have a leaner company as well as more fuel-efficient products.
References
Datamonitor. (2009c). General Motors – Company Profile. New York: Datamonitor.
Datamonitor. (2009a). New Cars in the United States. New York: Datamonitor.
Datamonitor. (2009b). Trucks in the United States. New York: Datamonitor.
Feroli, M. (2009). U.S. automakers still spinning their wheels. ABA Banking Journal , 44.
Freeman, S. (2003). High Pump Prices Are Fueling Spike in Sales for Hybrid Cars. Web.
GM. (2010). Web.
GM. (2009). General Motors Company. Web.
Sharp, B. (2009). Detroit’s Real Problem. Marketing Research , pp. 26-27.
Tell, R., & Kleiner, B. (2009). Organizational Change Can Rescue Industry. Industrial Management , pp. 20-24.