Research Questions
When a firm is faced with the reality of exiting a given market, Ramady argues that it is important to choose the optimal strategy that would protect the interest of stakeholders. The primary goal is always to exit in a way that shareholders, employees, the management unit, and any other relevant stakeholders feel protected. The process must also meet the legal requirements. It was necessary to develop a research question that would inform the nature of the data in the study based on the research topic. The following are the questions that guided the process of collecting and analyzing data from various sources.
- What is the appropriate exit strategy for private businesses in Saudi Arabia?
- How can a firm choose between initial public offerings and mergers & acquisitions?
- How can a firm overcome the valuation premium issues when planning an exit strategy?
The researcher intends to use both primary and secondary data to answer the questions above.
Literature Review
The Kingdom of Saudi Arabia is one of the fastest developing economies in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region. The government has been keen on promoting business growth as a way of diversifying its economy. According to Ramady, since independence, the country has heavily been relying on the oil and gas sector to sustain its economy. Although the petroleum industry is still the main source of income for the economy, efforts have been made to ensure that there is growth in the other sectors of the economy as well. The government has been supporting the private sector through various initiatives as a way of diversifying the economy. The infrastructural development in the country has promoted the growth of various other sectors of the economy such as banking, transport, manufacturing, entertainment, and agriculture among others. Tsounta explains that despite the attractive economic growth and great support that the private sector players enjoy in this country, it is important to appreciate that sometimes it is prudent to come up with an exit strategy.
According to Tsounta, numerous factors may make it necessary for a firm to exit the market. Stiff competition is often the main reason why a firm may consider exiting the market. When competition is stiff, unfavorable market practices such as price wars may emerge. In such an environment, making profits becomes almost impossible, especially for small and medium companies that lack the financial capacity to sustain protracted price wars. Another factor may be the introduction of new government policies that that may make operations in the market unfavorable for specific firms.
Saudi American Bank (Samba) was one such firm that realized that the business environment in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia was no longer favorable because of the strained relations between the United States and Saudi Arabia. The company had to find the optimal exit strategy that would take care of the interest of its shareholders. Business owners may also be interested in pursuing different ventures locally or in other foreign countries. As such, the only option that they might have would be to exit the market in the best way possible.
Finding an optimal exit strategy in the market for corporates and start-ups is critical, as Espinasse observes. It starts by identifying the reason why the firm must exit a specific market. When it is established that exiting a given market is the only option that a firm has, then the management must find ways of protecting the interest of the shareholders. According to Espinasse, the primary aim is always to ensure that the investments made by the business owners, yield the best returns during the exit strategy. During the valuation process, it is a common business practice for a buyer to undervalue a product, while the seller would want to provide a higher value. The sale of a firm can only go through if there is an agreement between the two parties on the actual value of the product despite the conflicting interests. It means that when trying to set the highest value for the product possible, the management should ensure that the interest of the other parties is not ignored. In this section, the researcher would focus on initial public offerings, mergers, and acquisitions as some of the most preferred exit strategies for both start-ups and large corporate entities in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Initial Public Offerings
The initial public offering has become a popular way of sourcing funds among rapidly expanding companies in various parts of the world. Ramady and Mahdi argue that although an IPO may be viewed as a way of entrenching a firm’s operations in the local market, it may also be considered a market exit strategy. It would be considered an exit strategy because the few owners, which sometimes maybe the government, would relinquish their exclusive ownership of the company and invite members of the public to help in sourcing for additional revenue. According to Ramady and Mahdi, in an initial public offering, owners would sell part of their shares in the business. In other cases, they may sell all their shares in the firm, relinquish their ownership to the shareholders, and use the proceeds of their income for personal reasons. The fact that it allows business owners to sell their shares to members of the public confirms that it is one of the most effective ways of exiting a market.
The Saudi Stock Exchange, popularly known as Tadawul, is the country’s stock exchange market where firms seeking to go public often make their shares available to both local and foreign investors. According to Meglio and Park, going public is one of the best ways of exiting the market. It provides various options to the shareholders who want to leave the market. The first option is to reduce their responsibilities in the firm while remaining as the main shareholders in the firm.
After completing the process, a board would be created responsible for the corporate management of the firm. If they aim to reduce their involvement in the business, the board will take over such roles and appoint individuals who will be responsible for the normal operations of the company. Meglio and Park explain that sometimes the interest of the original owners may be to sell all their shares and move to other businesses. In such a case, IPO offers them the best opportunity to achieve their goals. One of the main benefits of this strategy is that even if they consider exiting the market, the business model, the name and core features they created will last even after their exit. Hooke believes that the greatest challenge when using this strategy is the valuation process.
According to Hooke, it all depends on the ability of the owners to convince members of the public about the current value of the firm. Although speculative business practices are prohibited in Shariah laws, the process of valuing the price of a stock in the market is primarily based on speculation. A small company with a relatively small smaller profit may have a higher stock valuation than a larger firm that has a larger profit and revenue in the market if stock traders are convinced that the smaller company has a higher likelihood of achieving success in the market. As such, the level of success of an IPO significantly depends on the ability of the business owners to convince the public about the current and expected value of the firm.
The Saudi Stock Exchange has strict policies that have to be followed before a firm can be approved to go public. One such policy is meant to ensure that the company stock price is based on its actual and perceived value in the market. However, once the firm goes public, the company would have no control in determining the actual stock price. Forces of demand and supply and the perceived value of the company would determine the price. As such, this strategy is one of the most effective for a firm that is keen on going public in the market.
Mergers and Acquisitions
The management of a company can consider mergers and acquisitions as another optimal market exit strategy. Like initial public offering, mergers and acquisitions may be considered as an exit strategy or as a way of entrenching a firm’s operations in the market depending on the strategy that a firm takes. According to Ramady, mergers and acquisitions are often motivated by the desire to deal with stiff competition in the market. As new firms continue to emerge in the market, all struggling to capture the same customers in the market, companies are subjected to intense pressure to redefine their operational activities to remain sustainable. Some of the practices that firms may be forced to embrace to overcome stiff competition may not be feasible in long term.
As such, two or more companies may be forced to merge as a way of overcoming some of the common challenges in the market. A merger creates an environment where two large firms operate as one entity. The management of the two companies must reach an agreement on how to share in the management and revenues of the company based on their input. One such merger recently happened between Saudi British Bank and Alawwal Bank.
According to Meglio and Park merger is a common strategy among small and medium-sized companies keen on strengthening their position in the market. They merge their resources to give them the strength to compete favorably in a highly competitive business environment. However, the strategy is not exclusive to small and medium-sized companies. The merger between Saudi British Bank (SABB) Alawwal Bank was a major indication that large corporate institutions consider the strategy effective in overcoming market challenges. The Saudi financial sector is one of the most competitive industries in the country.
The booming oil and gas sector in the country has attracted financial institutions from all over the world. Firms have been keen on developing unique products as a way of overcoming stiff competition. Saudi British Bank and Alawwal Bank opted to merge as a way of overcoming the stiff competition and strengthening their position in the market. The strategy propelled the two companies to form the third-largest financial institution in the country by market capitalization. In this deal, the shareholders of Alwwal Bank would own 23% of the shares of the new company, while those of Saudi British Bank would own 73% of the shares.
The acquisition is another common strategy that a company would consider when planning to exit the market. Unlike mergers where executives of two firms agree to form one entity with shared responsibility and sharing of profits, the acquisition allows one firm to buy out another and take full control of its business operations. In normal cases, a large and financially empowered company would acquire small but ambitious companies in the market. In this case, owners of the smaller company would be exiting the market after completing the sale agreement. According to Meglio and Park, the acquisition is one of the most common ways of exiting a market. In Saudi Arabia, the competition board has rules and regulations that must be met, before one firm can acquire another. In such a scenario, the acquired firm relinquishes its ownership to the acquiring firm. After the merger, the owner of the new firm will be at liberty to retain the original name and structure of the acquired firm or to restructure it in a new way to meet specific interests. One of the most recent examples of such initiatives was Careem’s acquisition by Uber, which is discussed in chapter 4 of this paper.
Research Methodology
In the previous chapter, the researcher provided a detailed review of the literature to help understand the optimal exit strategy for start-ups and corporate entities. In this chapter, the focus is to discuss the method used to conduct the study. When planning research, Brennen explains that one should have a careful plan on how to collect data from various sources. In this study, the primary aim is to determine the optimal exit strategy for corporates and start-ups. In particular, the study compares the effectiveness of initial public offerings and acquisitions as some of the most common market exit strategies. The study also focuses on how to overcome the challenge of valuation when there is a merger deal or when a firm decides to go public.
Research Approach
One of the first factors that one has to consider when conducting a study is to define the research approach. Inductive and deductive reasoning are some of the main reasoning approaches that one can choose based on the nature of the study. Based on the research question and the aim of the study, the inductive approach was considered the most appropriate. In this strategy, a researcher is expected to start by making observations or conducting tests based on the set questions or objectives. The researcher would then be required to observe patterns. In this case, the patterns would be determined by monitoring the preferred market exit strategy between initial public offering and acquisition within Saudi Arabia. The researcher would then be able to develop a theory or new knowledge based on the pattern observed. In this case, it will be possible to determine the optimal exit strategy for local firms. This approach was also considered effective when trying to explain the valuation puzzle. One needs to monitor patterns of valuations based on the past acquisitions and initial public offerings in the country over a given period. Figure 1 below shows the pattern of reasoning that this approach embraces.
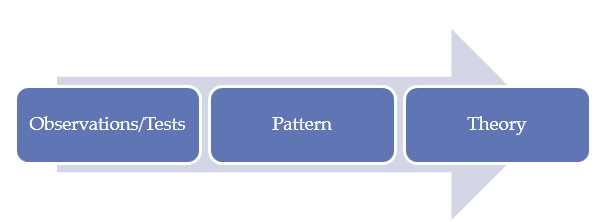
Research Strategy
When the research approach has been defined, it is important to identify the strategy that would be used to collect data, as Denscombe explains. One can consider the use of surveys, archival data, case studies, face-to-face interviews among others, based on the constraints that one is facing. The researcher opted to use face-to-face interviews, online research of reputable websites, and a case study. According to Denscombe, a face-to-face interview is one of the most effective methods of collecting data. The physical interaction between a researcher and respondents often helps in emphasizing the significance of the study. It reminds participants that their input is highly cherished and as such, the researcher had to find time to engage them.
Denscombe explains that during such an interview, a researcher can collect non-verbal cues through facial expressions and body language of those being interviewed. Non-verbal cues help to determine the perception and feelings of an individual towards a given issue. The physical interaction also reduces cases where a participant deliberately provides misleading information. One can easily request the participant to clarify an unclear issue to enhance the validity and reliability of data. However, Kara notes that such interviews are often time-consuming and require a significant amount of resources to conduct. The researcher identified a small group of respondents who helped in the collection of the needed information.
Online research also helped significantly in collecting information needed in the study. Tadawul.com.sa was an important website that was used to collect information about some of the recent initial public offerings in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia over the last ten years. The website provided information about the performance of firms, which are already listed on the Saudi Stock Exchange. The World Bank website also provided valuable information about IPOs and acquisitions in the country over the past few years. Local and international newspapers also offered information needed about the two exit strategies in the country. Information about the impending mega initial public offering of Aramco Company is widely published in the local, regional and international newspapers and magazines.
Kara explains that one of the main benefits of using newspapers is that they offer current information about a given issue, unlike books that may take a while before they are published. Important statistics used in the study were collected from these online sources. As Kara advises, when relying on online sources, one should countercheck the information by verifying facts from different sources. It helped in ensuring that the data collected were accurate.
The case study was the third strategy used to collect data. According to Kara, the use of case studies is often critical when trying to explain a given phenomenon. It makes it possible to understand factors that led to a certain event, how different parties played different roles in a given event, and the outcome. McNabb explains that case studies go beyond statistics by providing an example of a specific event that happened. In this case, the researcher provided a case study about a merger and an initial public offering that took place in Saudi Arabia. Comparing the two cases, one can easily determine the optimal exit strategy for corporates and start-ups in Saudi Arabia. They provide facts about the status of the firm before, during, and after these events. One can also determine how the initial owners of the business benefited from the exit strategy.
Data Collection
Data used in this study were collected from both primary and secondary sources. Secondary data was collected from books, journal articles, and reliable online sources. Information from books and journals formed the basis of the literature review provided in the previous chapter. McNabb argues that a researcher should review the works of other scholars to find out the existing knowledge and address gaps and contradictions that exist. Information that was obtained from reliable websites provided critical data used in the analysis section of the paper. Using keywords and phrases such as mergers, acquisitions, and initial public offerings in Saudi Arabia, the researcher was able to access critical data that helped to inform the study.
Primary data was collected from a sample of respondents who know the issue under investigation. The researcher was interested in interviewing industry experts, individuals working in Saudi Stock Exchange, and business executives who have been involved in mergers or initial public offerings in the country. Given the small number of respondents needed for the interview, the complex nature of identifying and convincing them to be part of the study, and the broad nature of their specialty, purposive sampling was considered appropriate for the study. It is a judgmental sampling where a researcher selects specific individuals based on whether they meet specific criteria needed in the study. Those who were selected for the study had to meet the criteria explained above.
A simple questionnaire was developed to help collect data from the participants in a standardized format. McNabb explains that a questionnaire is critical whether one is conducting qualitative or quantitative research. Developing a set of questions before the actual interview helps a researcher to prepare adequately for the process. It eliminates cases where one gets confused or forgets about critical questions during an interview. It also ensures that a researcher asks the same questions in a similar format to help develop a pattern. The questionnaire had two sections. The first section focused on the demographics of the participants to determine the level of their authority in this topic based on their level of education and experience. The second section focused on issues relating to the optimal exit strategy in the country.
Data Analysis
When data has been collected, the final stage is to conduct an analysis that would help in answering specific research questions. The researcher chose mixed-method research because of the nature of the topic and research questions. Using both qualitative and quantitative research methods made it possible to provide a detailed understanding of the issue. Regression analysis made it possible to compare variables in the study. Comparing the number of acquisitions and IPOs in the country through statistical analysis makes it possible to establish the optimal exit strategy between the two options. On the other hand, the qualitative analysis explained the data. Through this method, it was possible to understand from the industry experts and players why business executives preferred a specific exit strategy. The information was crucial when making a conclusion and recommendation about the optimal exit strategy in Saudi Arabia.
Ethical Considerations
When conducting this investigation, the researcher was keen on observing various ethical considerations. According to McNabb, one of the most important ethical concerns that should be considered when conducting such a study is the protection of subjects. It is possible that one can be intimidated or discriminated against by colleagues or those in authority if they have a conflicting opinion from that of the majority. To avoid such undesirable occurrences, the researcher made sure that the identity of those who took part in the interview remained anonymous. Instead of using their real names, the researcher opted to assign each one of the codes to help in their identification. Before starting each interview, participants were informed about the use of codes instead of their actual names. They were also told that participation was voluntary and that if they felt there were compelling reasons to withdraw, they had the liberty to do so. As an academic study, the researcher had to observe rules and regulations set by the school. The research had to be completed in time. Any form of plagiarism was avoided when writing the paper.
Statistical Analysis
In the previous chapter, the researcher provided a detailed explanation of the method that was used to collect and analyze data. In this chapter, a researcher focused on the analysis of data collected from sampled respondents and statistical information collected from various sources. The primary aim of this chapter was to conduct statistical analysis to confirm or refute information obtained from secondary sources. The researcher used both qualitative and quantitative analysis to determine the optimal exit strategy for start-ups and large corporate entities operating within the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The analysis focused on comparing initial public offering and mergers & acquisitions based on the recent trends in the country.
Initial Public Offering Versus Mergers and Acquisition
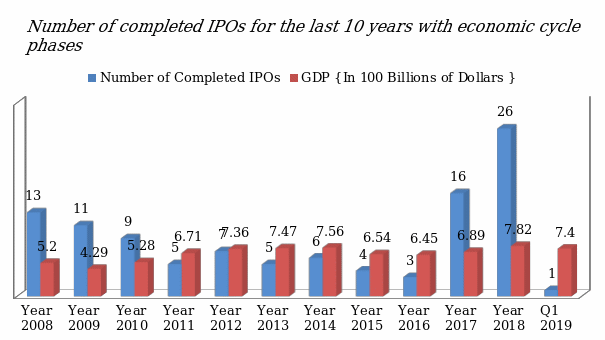
In the literature review, an initial public offering was identified as one of the most popular exit strategies among companies in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. In this section, the researcher analyzed primary data to compare the number of completed IPOs, as a dependent variable, against economic cycle phases as the independent variable. The analysis focused on determining the popularity of this strategy in different phases of the economy (peak, recession, and growth).
Number of completed IPOs (dependent variable) for last 10 years in Saudi with the economic cycle phases (peak, recession, and growth) as an independent variable
The researcher conducted a regression analysis of the two variables over the last ten years and figure 2 below shows the outcome. The economy of the country has been going through different phases over the last ten years. During an economic boom (peak), the number of completed IPOs is likely to be high. Saudi Arabian GDP was at its highest in 2018. In that year, the country had the highest number of completed IPOs, at 26. During the recession of 2008/2009, the number of completed IPOs dropped from 13 to 11. It is important to note that a few rare cases exist where a drop in GDP does not directly translate to a drop in the number of completed initial public offerings.
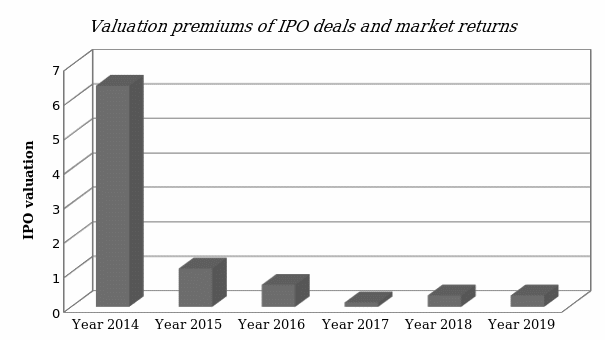
In the review of literature, it was established that mergers and acquisitions are some of the most effective means of exiting the market. The researcher collected data from various sources to determine the effectiveness of the strategy in the Saudi Arabian market. It is also evident that the value of completed IPOs is directly proportional to the number of initial public offerings made within a year and market returns as shown in figure 3 below.
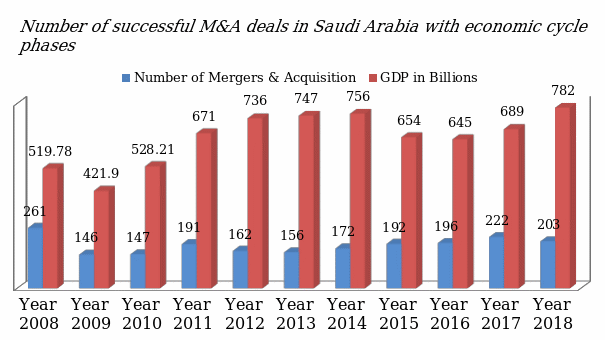
Number of successful M&A deals in Saudi for last ten years as Dependent V and the economic cycle phases (peak, recession, and growth)
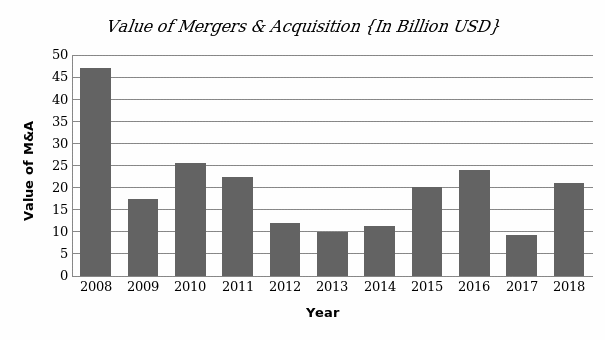
As shown in figure 4 below, there is a directly proportionate relationship between the number of completed mergers and acquisitions (dependent variable) and economic phases (independent variable). During the recession, such as that of 2008/2009, the number of completed mergers and acquisitions dropped. When the economy started to grow from 2009 to 2011, the number of IPOs also started to increase. When the country’s gross domestic product peaked in 2018, the country registered the highest number of mergers and acquisitions, at 782. It means that during the period when the economy is performing well, a high number of firms consider mergers and acquisitions as a way of exiting the market or strengthening their position in the country.
A comparative analysis of IPOs and M&A in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia shows that most firms often consider mergers and acquisitions as the easiest way of exiting the market. In 2008 when the economy peaked, the number of IPOs in the country was 26, against the number of M&A, which stood at 782. It was established that on average, there are 20 mergers and acquisitions for every initial public offering in Saudi Arabia. Hooke explains that the exit strategy is more popular because it is simple and only needs the two parties involved to reach an agreement. Initial public offerings are strictly controlled by the Saudi Stock Exchange, making it a little more complex way of entering the market. Figure 5 below shows that the value of mergers and acquisitions directly depends on the number of M&A irrespective of the growth of the economy. The market returns depend on the negotiated value for the M&A.
Aramco IPO and Its Impact
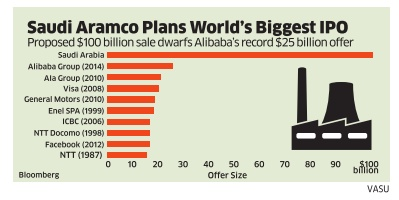
Saudi Aramco is an oil and gas company that operates in the global market and has its headquarters in Dhahran in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Founded in 1933, the company has registered impressive growth in the market over the past decades to become the most profitable company in the world. It is also reported that it has the second-largest daily oil production and second-largest known oil reserves in the world. The company is valued at between 1.2 to 2 billion dollars and it has networks in North and South America, Europe, Asia, and Africa to facilitate its export activities. The government announced the initial public offerings of the company, which is yet to take place. Given the strategic significance of the company, its huge market value, and the number of investors that it has attracted, Saudi Aramco is set to register the largest IPO in history. In case the IPO is completed based on the government plan and projected figures, it will become the largest initial public offering in the world, almost three times larger than that of Alibaba Group, which is currently holding the top spot. The statistics are shown in figure 6 below.
Careem’s Acquisition by Uber
Careem Inc. is an Emirati transport company that was founded in March 2012. The company has its headquarters in Dubai and operates in 100 cities across the Middle East, South Asia, and parts of Africa. According to Tsounta, Mudassir Sheikha and Magnus Olsson founded this company while they were still working for McKinsey & Company. They borrowed the concept from Uber and realized that the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region has a huge potential because of the popularity of taxis. The company started its operations in Dubai and expanded rapidly to major regional cities such as Abu Dhabi, Riyadh, Cairo, Baghdad, Tehran, Mecca, and Istanbul among others.
When it started its operations in 2012, the company did not face stiff competition in the market from local players. Its managers were able to understand the local needs of its clients and develop mechanisms for meeting them. As it expanded its operations, the management decided to expand its line of products. In 2015, it acquired a Saudi Arabian home-delivery service company as it sought to reduce competition and increase its market share in the region. In February 2018, the company announced that it had acquired RoundMenu, a fast food outlet that was operating in different countries in the Arab world. The firm also went ahead to acquire Cycle, a Dubai-based bike-sharing company, and rebranded it as Careem Bike.
When Uber made an entry into the Middle East and North African market, Careem started facing a new challenge in the market. The competition was getting stiff as the new firm started taking part in Careem’s market share. The shareholders decided to embrace the optimal exit strategy to ensure that they protect their investment. According to Meglio and Park, the management of Careem agreed with Uber, in a deal that allowed the American firm to wholly own the start-up App Company. The Emirati firm was acquired for $ 3.1 billion under certain specific terms of the agreement. The two companies agreed that after the merger, Careem would continue to operate under its original brand name and logo.
It was also agreed that the firm would retain its management unit to ensure continuity and maintain an innovative team of employees who were responsible for the rapid growth of the company. Meglio and Park note that Careem has remained an innovative firm even after the acquisition, coming up with unique products that meet the various needs of its customers. Its ability to understand the needs of its local customers has enabled it to expand its market share beyond the Middle East region.
Conclusion and Recommendations
The economy of Saudi Arabia is growing rapidly over the past three decades following deliberate attempts by the government to reduce overreliance on the oil and gas industry. The service industry, construction, real estate, communication, transport, and automotive sectors have developed rapidly in the country. As shown in the review of the literature and analysis of primary data, massive infrastructural development, improved security and the decision by the government to open the economy for both local and foreign investors have contributed immensely to the growth of different sectors of the country’s economy. Despite these positive changes, the study has shown that sometimes it may be necessary for a firm to exit this market. Choosing an appropriate market strategy is critical for the management of a firm to ensure that the interest of all its shareholders, especially the employees and stockholders, is protected.
The study has conducted a detailed analysis of both primary and secondary data to determine the appropriate exit strategy for a firm operating in the Saudi Arabian market. The analysis focused on two popular methods of exiting the market. On the one end, a firm can opt to use an initial public offering as a way of exiting the market. The strategy allows a firm to invite the public to help in generating more capital for the firm. In return, the original owners would relinquish ownership of the firm to the board of directors and major shareholders of the firm. The strategy was considered effective for a rapidly expanding firm where owners are keen on expanding its capital base by inviting members of the public to be part of the ownership of the firm.
Mergers and acquisition is another strategy that owners of a firm can use to exit the market. In this strategy, owners of the business can opt to use two approaches based on what is more optimal for the shareholders. The first strategy is to have a merger with one or more firms in the same industry. In a merger, two firms sharing interest enter a deal to operate as a single entity. It eliminates competition and gives the merging firms greater bargaining power in the market. The second option is the acquisition of one firm by another. In cases of acquisition, a larger and financially empowered firm would acquire a smaller firm in the market to expand market coverage, eliminate competition in the market. Owners of the acquired business would have to relinquish all their interest in the firm. The acquiring company will have the liberty to decide on the fate of the firm that has been bought out.
Initial public offering, mergers, and acquisition all have their strengths and weaknesses that have to be considered. However, mergers and acquisitions are more popular in the country than initial public offerings. When choosing the optimal exit strategy in Saudi Arabia, numerous factors should be considered. As shown in the review of the literature and analysis of primary data, no single strategy is optimal for all firms considering exiting this market. Each firm will encounter different market forces that must be considered before deciding on the strategy that should be used. The critical factor that should be considered is to protect the interest of shareholders, employees, and any other relevant shareholder. The deal offered must provide maximum value for the owners without jeopardizing the ability to exit the market within the desired period. The following recommendations should be considered:
- Exit strategy in Saudi Arabia should be chosen based on the current factors that a firm is facing and external forces in the market.
- When planning an exit strategy, the team should protect the interest of all stakeholders, especially during the valuation of the firm.
- Both corporates and small start-ups should understand that some of these strategies such as mergers and initial public offerings create growth opportunities.
Bibliography
Brennen, B., Qualitative Research Methods for Media Studies. London, UK, Taylor & Francis Group, 2017.
Bryman, A., and Bell, E., Business Research Methods. Oxford, UK, Oxford University Press, 2015.
Denscombe, M., The Good Research Guide: For Small-Scale Social Research Projects. New York, NY, Open University Press, 2014.
Espinasse, P., Ipo: A Global Guide. Hong Kong, HKU Press, 2014.
Hooke, J., M & A: A Practical Guide to Doing the Deal. Hoboken, NY, Wiley, 2015.
Kara, H., Creative Research Methods in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide. New York, NY, Cengage Learning, 2015.
McNabb, D., Research Methods for Political Science: Quantitative and Qualitative Methods. New York. NY, Routledge, 2015.
Meglio, O., and Park, K., Strategic Decisions and Sustainability Choices: Mergers, Acquisitions, and Corporate Social Responsibility from a Global Perspective. Boston, MA, McMillan, 2019.
Ramady, M., Saudi Aramco 2030: Post Ipo Challenges. Cham, Springer, 2018.
Ramady, M., and Mahdi, W., Opec in a Shale Oil World: Where to Next? Dhahran, Springer, 2015.
Tsounta, E., Slowdown in Emerging Markets. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, 2014.