Introduction
The Oxoid Streptococcal Grouping Kit is a latex agglutination test that is used to identify streptococci of A, B, C, D, F, and G groups. Researchers and clinicians state that this kit is appropriate and important to be used for identifying beta-haemolytic streptococcal infections. Thus, the timely identification of beta-haemolytic streptococci and appropriate treatment can prevent subsequent severe respiratory diseases.
According to Cunningham, group A beta-haemolytic streptococci often cause acute pharyngitis and scarlet fever, and if these bacteria are not identified, they can lead to rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, and reactive arthritis. Rheumatic heart disease often leads to myocarditis and problems with the heart valve requiring the valve replacement, and rheumatic fever leads to heart diseases in children as the sequel of pharyngitis and scarlet fever. Therefore, it is important to research how the use of the proposed kit can influence diagnosing respiratory diseases.
Aim
To research advantages and disadvantages of the Oxoid Streptococcal Grouping Kit and conclude whether or not this kit can be useful for diagnosing respiratory infections.
Methods
The following principles determine the work of the test used in the kit:
- Different streptococci have specific carbohydrates (Lancefield antigens) on their cell wall.
- These antigens are extracted with the extraction reagent.
- Latex particles are coated with antibodies against the specific antigen.
- If the homologous antigen is present, the process of agglutination can be observed when latex particles are added.
- A lattice is observed as a result of agglutination (a positive result).
- If the homologous antigen is absent, there is no agglutination (smooth suspension, a negative result).
Figure 1 demonstrates steps to conduct while analyzing the positive reaction on the slide.
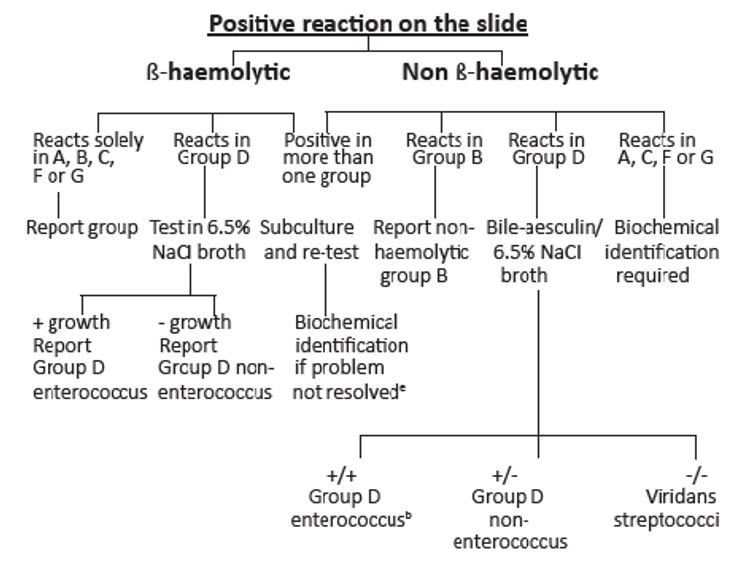
Therefore, to use the kit for identifying streptococci, it is necessary to test the reaction of beta-haemolytic colonies. First, colonies are incubated with the help of the extraction reagent. After incubation, the specific carbohydrate on the cell wall can be identified due to reacting with latex particles. Then, the latex particles are coated with antibodies against the specific carbohydrates. As a result, it is possible to conclude regarding the presence of beta-haemolytic streptococci.
Results
The results of using the kit for identifying beta-haemolytic streptococci that provoke the development of respiratory diseases allow for speaking about advantages and disadvantages of the test. First, accurate results can be received due to the high specificity of the test. In addition, all the necessary materials are provided in the kit, and it includes the guidelines for conducting the test. Furthermore, the kit is not expensive because the average price for 50 tests in the kit is about $500, and the average price for one test is about $10.
However, in some cases, the test can take up to 20 minutes (including 10 minutes of incubation). Moreover, the test can indicate false negatives if the amount of culture is not enough for extraction, and it can be used only with beta-haemolytic streptococci. Still, the kit should be included in the manual to support the work in the laboratory because it is easy to use, accurate, and inexpensive.
Discussion
The main reason to include the Oxoid Streptococcal Grouping Kit in the laboratory manual and use the test in practice is that the provided latex agglutination test is sensitive and effective to identify and classify different groups of streptococci. There are many tests that can be used to identify streptococcal groups and respiratory infections, but beta-haemolytic streptococci cannot be determined with the help of other tests at the same level of accuracy. Furthermore, the test can be conducted quickly and with the help of the minimum resources.
Conclusion
The results and analysis of the test’s advantages and disadvantages indicate that the Oxoid Streptococcal Grouping Kit is characterized by high levels of sensitivity and specificity important for identifying beta-haemolytic streptococci. Therefore, this kit is efficient to be used for diagnosing respiratory infections, and it should be included in the laboratory manual.
References
Oxoid: Streptococcal Grouping Kit. n.d. Web.
Davies S. Streptococcus grouping latex kits: evaluation of five commercially available examples. Br J Biomed Sci. 2003; 60(3):136- 142.
Cunningham M. Pathogenesis of Group A streptococcal infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2000; 13(3):470-511.
Ghaddar N, Alfouzan W, Anastasiadis E, Al Jiser T. Evaluation of chromogenic medium and direct latex agglutination test for detection of Group B streptococcus in vaginal specimens from pregnant women in Lebanon and Kuwait. J Med Microbiol. 2014; 63(10):1395-9.
Hassan IA, Onon TS, Weston D, Isalska B, Wall K. A quantitative descriptive study of the prevalence of carriage (colonisation) of haemolytic streptococci groups A, B, C and G in pregnancy. J Obst Gyn. 2011; 31(3):207-9.
Parks T, Barrett L, Jones N. Invasive streptococcal disease: a review for clinicians. Br Med Bul. 2015; 115(1):77-89.