Introduction
Qatar is an Arab country that draws sufficient attention to promoting cultural, social, economic, political, and environmental development. That is why Qatar National Vision 2030 appeared to explain what strategic goals the country had. The Human Development pillar is an essential part of this document, demonstrating that Qatar focuses on improving the quality of people’s lives. In particular, Qatar National Vision 2030 promotes human development by addressing workforce issues. This statement denotes that Qatari authorities invest in certification and training programs, create professional and management roles in numerous business sectors, and provide Qatari women with increased vocational support and opportunities (General Secretariat for Development Planning, 2008). This information demonstrates that Qatar is witnessing a context that welcomes initiatives to make the life of Qatari citizens better and solve the existing issues. A significant problem refers to limited employment opportunities for fresh graduates, which results in a few pain points for the nation and requires a prototype of a specific platform to improve the situation.
Defining the Problem
As has been mentioned above, the issue under consideration is associated with an insufficient number of employment opportunities for fresh graduates. The more formal problem statement is as follows: Fresh graduates need more job opportunities in the private sector because they are currently suffering from the lack of entry-level positions. It is worth admitting that a set of interrelated and complex processes and events could have contributed to the problem, and that is why they will be described in detail below.
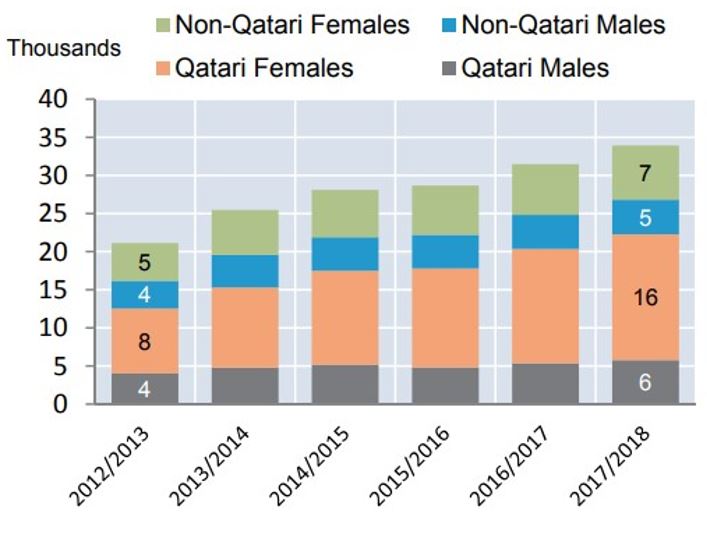
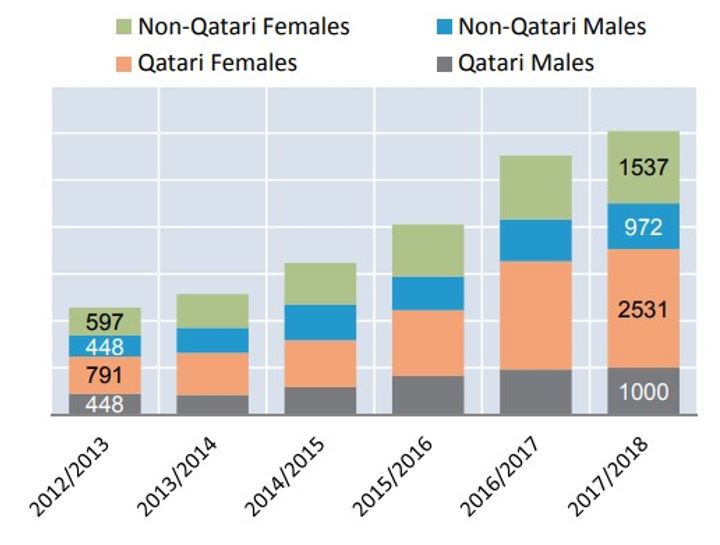
Firstly, the given problem exists because the number of Qatari graduates keeps increasing with every passing year. Figure 1 by the Planning and Statistics Authority (2019) demonstrates that there were “21,000 students in 2012/2013 and 34,000 in 2017/2018” (p. 46). This information indicates that the period of 2012-2018 saw a 3% annual growth rate regarding the number of students (Planning and Statistics Authority, 2019, p. 46). There is no doubt that this fact leads to an increased number of graduates in the country. Figure 2 proves this thought and depicts that the number of university graduates rose from 2,284 in 2013 to more than 6,000 individuals in 2018, and the portion of female graduates accounted for 42% (Planning and Statistics Authority, 2019, p. 48). Consequently, this information allows for supposing that the market has some difficulties meeting the increasing amount of labor force.
Secondly, the given problem exists because all the graduates typically have the same majors, with a few of them only having specialized degrees. For example, the Planning and Statistics Authority (2019) stipulates that 31% of male graduates have a major in the engineering sphere (p. 51). These data allow for supposing that many of them have the same specialties, meaning that employers consider them to have the same skills and expertise levels. As a result, when many graduates with identical or similar knowledge and experience enter the market, it is not a surprise that few of them can only find a job. Consequently, it is possible to conclude that the increasing number of graduates with the same degrees contributes to the fact that limited employment opportunities for fresh graduates are a problem.
When it comes to discussing the problem, it is also necessary to focus on different pain points that represent negative consequences. On the one hand, the issue under consideration adversely affects Qatari economic and business spheres. This statement refers to the fact that a knowledge transfer gap exists. Senior specialists cannot share their knowledge and expertise at full expense because fewer younger individuals enter professions. This situation can bring adverse consequences to the future of Qatari business and economy.
On the other hand, the problem can harmfully affect individuals. Firstly, a failure to find a job inevitably leads to financial difficulties. Upon graduation, a person ultimately enters adult life, meaning that they have responsibilities and should meet some obligations. Possible examples include paying for student loans, celebrating a wedding, and others. In such cases, the absence of employment creates essential barriers to dealing with the tasks above. Simultaneously, this situation can hurt graduates’ mental health and well-being. A scholarly study demonstrates that youth unemployment is associated with increased risks of mood, stress-related, depression, and bipolar disorders (Thern et al., 2017). It is challenging to underestimate the importance of this impact.
Secondly, the problem results in the fact that current students can lose motivation to end their education. When they see that graduates face significant challenges finding a job, there can arise doubt whether it is necessary to receive higher education at all. These thoughts can result in the fact that Qatar can soon face the opposite issue when the country lacks university graduates. Finally, the failure to find a job denotes that fewer graduates will start their own businesses due to the absence of experience and motivation. This scenario is negative because productive entrepreneurship is associated with economic growth (Bosma et al., 2018). This information demonstrates that it is reasonable to determine how one can solve the identified problem.
Problem Solution
A brainstorm session has revealed that it is possible to resolve the problem by creating a platform for high-school students to help them understand what employers require from them. This web-based resource should present statistical data on how many students are receiving specific majors and what specialties are underutilized. Such information can help young individuals make reasonable decisions when it comes to applying for universities. In this case, it will be possible to address most of the pain points because the platform will reduce the number of graduates with the same majors, which will improve graduates’ employment opportunities. Increased employment rates will denote that the knowledge transfer gap will shorten or disappear, graduates will face improved financial and mental conditions, and current students will not leave universities because they will see perspectives. Simultaneously, when more young individuals find a job, they will gain sufficient knowledge and experience, which will positively affect the Qatari economy.
Concluding the Pitch
The statistical data have demonstrated that limited employment opportunities for fresh graduates are a significant problem for Qatar. A few factors contribute to the issue, while its versatile adverse consequences emphasize the importance of finding an effective solution. Creating a platform for high-school students and post-graduates is a suitable option because this decision has the potential to mitigate the problem’s negative consequences. While the details of creating this resource are beyond the scope of this pitch and will be described below, it is worth admitting that the platform will collect and display relevant and real-time statistical information. Individuals will use it to identify the market demand for specialists and choose an appropriate major to satisfy it.
Planning for Implementation
Now, it is rational to explain how the proposed prototype can be implemented. This process consists of multiple stages that should be performed individually to ensure that the web-based platform contains all the required elements and materials. Furthermore, each of these steps implies a unique timeframe because various efforts will be needed to cope with the tasks. Thus, the details of the implementation process will be presented below.
- Step 1 involves contacting large Qatari employers to identify their demand. This stage is necessary to determine what skills and expertise levels these organizations and firms expect to obtain from hiring fresh graduates. In this case, one month will suffice to disseminate e-mail letters with questionnaires, receive the answers, and synthesize the results.
- Contacting institutions of higher education represents Step 2 of the prototype implementation. This process denotes that it is reasonable to identify how many individuals are currently studying and what their majors are. This information will demonstrate how many specialists are going to enter the labor market, which will reflect the relationship between supply and demand. One month should suffice to cope with the given task.
- Step 3 is to create a website to locate the platform. This step consists of a few smaller tasks, including plan development, information input, final review, and others. That is why the exact amount of time needed depends on what site is required. However, it is possible to suppose that approximately ten weeks will suffice to create the resource (Hendrickson, 2019). At this stage, it is necessary to insert the data identified during Step 1 and Step 2 into the website.
- As for Step 4, it refers to advertising activities aimed at increasing the public awareness of the platform. This stage implies finding the appropriate advertising channels to affect the target population. According to Benmamoun et al. (2019), Internet-based resources are the most suitable option because many social networks, including YouTube, Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook, are popular among the Qatari youth. It means that it is reasonable to distribute the platform advertisements via these sites. It is also rational to contact schools and let them invite prospective students to visit the proposed website. It is a long process, and some positive results can be obtained in two months.
- Step 5 refers to monitoring the website and ensuring its flawless operation. This process includes both updating the information and addressing all the possible technical challenges. It is a continuous task that should be performed until the platform exists.
This information demonstrates that the implementation process will consist of five separate stages. It will take approximately 4-4.5 months to create the platform and make it available for use. This timeframe includes four stages if they are completed one by one. It is worth admitting that Step 5 ensures the flawless operation of the platform, meaning that it is not reasonable to include it in counting the implementation timeframe.
Data Collection Procedures
There is no doubt that each of the steps above implies working with large volumes of data. Thus, it is necessary to ensure that the data are timely and come from reputable resources. This condition will increase the probability that the platform will provide its users with reliable and credible information that will lead to better outcomes. That is why the primary data collection procedures for each stage will be described in detail below.
Step 1 implies contacting leading Qatari employers to research the labor market and demand. It can be challenging to determine what employers to reach. However, a newspaper article by Dizon (2021) demonstrates that the list of prominent Qatari organizations includes Hamad Medical Corporation, Commercial Bank, Vodafone, Qatargas, and Qatar Fertilizer Company. There is no doubt that the nation has more reputable and trustworthy employers, but these organizations can become an excellent start to reach popular employers from various economic sectors. Thus, the data collection procedure implies sending surveys to these organizations and analyzing their answers.
When it comes to Step 2, it is necessary to contact the Qatari institutions of higher education. The country has many institutions, including public and private ones. Thus, it is ideal to reach all of them to identify the exact number of students and determine which majors are underutilized. The most popular educational establishments include Qatar University, Qatar Aeronautical Academy, Qatar Foundation Universities, University of Applied Sciences, and others (Ministry of Education and Higher Education Qatar, n.d.). It is of significance to receive data from all these establishments.
Step 3 data collection procedures are limited to studying resources to determine what website structure perfectly meets the goal. At this stage, it is possible to hire IT specialists who will help cope with the task. However, another suitable strategy is to study multiple structures and layouts to identify which of them allows for the most effective information presentation. This data collection procedure implies working with appropriate Internet resources.
Advertising activities can be successful if they are supported by background information. It means that Step 3 emphasizes the importance of collecting data to analyze students’ behavior. As has been mentioned, numerous social media platforms are requested among the Qatari youth (Benmamoun et al., 2019). That is why it is rational to rely on these Internet-based resources to popularize the proposed platform among the target audience.
Finally, Step 5 denotes that it is necessary to keep collecting technical data regarding how the platform works. This information is required to determine whether its capacity is sufficient to meet the influx of users. Simultaneously, this stage implies collecting feedback and feedforward to identify what the customers think of the platform. This process is significant in the long run since it will help make the necessary adjustments to ensure that the resource meets the people’s expectations.
Feedback and Feedforward
It is challenging to overestimate the importance of feedback and feedforward because the two allow for identifying what users think of a product a service. This approach can also help find moments of pain and joy. As a rule, many people take feedback personally, which makes it challenging for them to control emotions and focus on the message. That is why it is reasonable to draw sufficient attention to feedforward that refers to recommendations and suggestions on how to overcome upcoming issues.
Feedback Loops
It seems a suitable option to create a specific questionnaire and asks platform visitors to answer the questions after they have used the resource. This information is significant because it can demonstrate the platform’s advantages and disadvantages. The moments of pay can relate to complicated navigation through the website, inappropriate colors used, small font size, and many others. It is necessary to know these inefficiencies to eliminate them. As for the moments of joy, they can include the availability of exhaustive and timely information, the usefulness of the resource, and others. It is not reasonable to take these positive features for granted. Their analysis can reveal what is preferable for users, and this finding can contribute to some improvements in other aspects.
Feedforward Loops
It is reasonable to ask the users to provide their feedforward to predict future challenges and their possible solutions. For example, it is rational to ask the individuals to ask some questions regarding what additional information they would like to find on the platform. This answer will help address the future potential problem that the user can lose interest in using the resource. Thus, the obtained feedforward will demonstrate how it will be possible to address the issue. Consequently, it is not reasonable to undermine the importance of feedforward since it can help make the platform better.
Conclusion
In Qatar, an increasing number of graduates is a significant problem because few of them manage to find jobs. This situation occurs because many individuals have similar knowledge and skills, and employers cannot hire many of them. As a result, it is reasonable to find an effective solution to this issue, and creating a web-based platform is a suitable option. This resource will collect and display information for high-school students to understand what skills are requested by employers and what majors to choose to face less competition in finding a job. Thus, the proposed prototype offers five steps with specific data collection procedures that will help create the platform. In this process, it is necessary to draw sufficient attention to collecting feedback and feedforward to solve the current and future challenges and ensure that the platform is beneficial and convenient for its users.
References
Benmamoun, M., Singh, N., & Sobh, R. (2019). How advertisers can target Arab e-consumers more effectively: A framework for localizing digital advertising and marketing content to Arab e-consumers.Journal of Advertising Research, 59(2), 171-184. Web.
Bosma, N., Content, J., Sanders, M., & Stam, E. (2018). Institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth in Europe.Small Business Economics, 51, 483-499. Web.
Dizon, L. R. R. (2021). QP tops LinkedIn’s ’10 best workplaces in Qatar for 2021’ list.The Peninsula. Web.
General Secretariat for Development Planning. (2008). Qatar national vision 2030.Web.
Hendrickson, M. (2019). How long does it take to build a website?DreamHost. Web.
Ministry of Education and Higher Education Qatar. (n.d.). Higher education in Qatar.Web.
Planning and Statistics Authority. (2019). Education in Qatar statistical profile 2019.Web.
Thern, E., de Munter, J., Hemmingsson, T., & Rasmussen, F. (2017). Long-term effects of youth unemployment on mental health: Does an economic crisis make a difference.Journal of Epidemiology & Community Health, 71(4), 344-349. Web.