Coca Cola Information Systems: Introduction
According to the Market Line; a Data monitor business, the global soft drinks industry consists of functional drinks, bottled water, concentrates, juices and RTD with tea and coffee included. Its market value increased by 4% to reach a value of $602.1 billion in 2011.
This is may increase by 24.6% to $749.9 billion by 2016. Of the global market value of soft drinks, the USA accounts for 41.5% and is home to the Coca-Cola Company; the leading indusry player generating 36.4% of the market’s share volume. (Market Line p. 1-38)
The scope of this paper is to evaluate the Company in terms of its business process, involvement of information systems in its process and waysn information systems could improve its process.
The Coca-Cola Company
It is an international beverage corporation founded in American with headquarters in Atlanta, Georgia. It manufacturers, distributes and markets non-alcoholic beverage solvents. The company’s history dates back to the 1886 experiment-Coca cola- of John Pemberton in Columbus, Georgia. Today it produces over 500 brands in over 200 countries, offering over 1.7 billion sales per day. The company is currently listed on the NYSE.
Business process
The company’s products, bearing the Coca-Cola Company trademark, were sold in the United States since 1886 and currently are selling in over 200 countries.
The company manufacturers solvents and syrups for beverages sells them to bottle & can operators and partially to wholesalers and some retailers. Some finished products are directly sold mainly to local distributors. The company is a large shareholder in majority of the bottle and can operations.
Its operating structure includes the following operating groups; North America, Latin America, Africa, East and south Asia, European Union, North Asia, Eurasia and Middle East and the Pacific coast line. (Aswathappa 20) see chart in the appendix. The solvents used in production of purified water and beverages are sold to bottle and can operators that have the company’s flagship.
These operators then combine the solvents and syrups with carbonated water to produce non-alcoholic drinks. The products are then packed in special containers that have the company’s trademark. The company’s brands include among others; Coca Cola, Minute Maid, Coca-Cola Zero, Sprite, Dasani Water, Diet Coke, Fanta, Powerade, Odwalla and Simply Orange.
Involvement of Coca Cola Information Systems
It uses a Transaction Processing System (TPS) whereby the company’s activities are subdivided to individual indivisible transaction processes. These processes are;
- Manufacture of beverage solvent and syrups
- Distribution of the concentrates to local and foreign bottlers
- Production of soft drinks through mixing of solvents with carbonated water by bottle and can operations
- Packaging of finished products
- Distribution to wholesalers and retailers
As a multinational company, it uses high-speed computers networked via the internet for communication in international offices. This makes communication easy, fast and cheap enabling the company to make quick decisions.
The company keeps a computerized database of its customers, suppliers and bottling & canning operations. Over ¾ of its annual marketing expenditure is IT-oriented to provide mobile connection to customers, social networking sites and loyalty programs.
The Company launched “Coca-Cola Freestyle” in 2005, a new fountain dispenser that indicated a blueprint towards a technology-driven beverage industry that would be much different from the then industry.
Previous fountains were very mechanical naturally. “Coca-Cola Freestyle” incorporates a computer in the fountain machine that calculates precisely the contents of over 100 beverage brands (Bovarnick par. 5). The company has implemented the ERP package in India where the payroll system, sales and distribution systems are already working in deports.
How Coca Cola Information Systems Could Improve Its Process
Using a computerized database helps create a paperless environment and cut costs that could otherwise go to storage of paper documents. This also helps to reduce the amount of time used to navigate through files for individual customer files thereby increasing efficiency.
The use of the internet in communication will help the management make quick decisions since meetings could be held online through teleconferencing and cut travel costs. Internet also offers vast advertising opportunities reaching out to even the most remote areas thereby increasing the customer base.
Suggestion for Coca Cola Information Systems Improvement
In 2010, SmartWater and PET Bottles were voluntarily destocked by Coca-Cola North America as these beverages failed to confine to FDA’ s standards for quality bottled water. Similarly, in 2009 Coca-Cola Israel destocked Coca-Cola and Diet Coke bottles as the drinks contained traces of poisonous elements. This was as a result of the failure of its co2 supplier (Datamonitor p. 7).
With invention of a 3D printer, such errors that could tarnish the brand image could become obsolete since this machine has surgical precision with zero chance for error. This paper suggests that the company acquires this latest development.
Summary
The Coca-Cola Company; the world’s top-brand producer and distributor of non-alcoholic solvents and syrups for beverages is a company that employs various forms of information systems in its business process, although further incorporation of the IS may further improve its process.
Conclusion
Based on the research undertaken by this paper, it surfaces that the Coca-Cola Company is a smooth-running corporation that has effectively employed Information Systems although some areas are still wanting. A few technological improvements could give the company an unmatched comparison.
Appendix
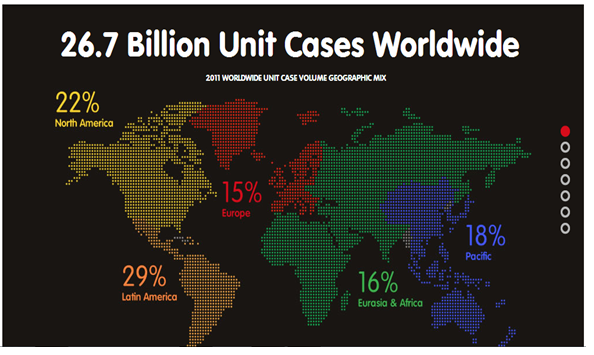
The map shows Coca-Cola Company operating segments (Operating Groups par. 1)
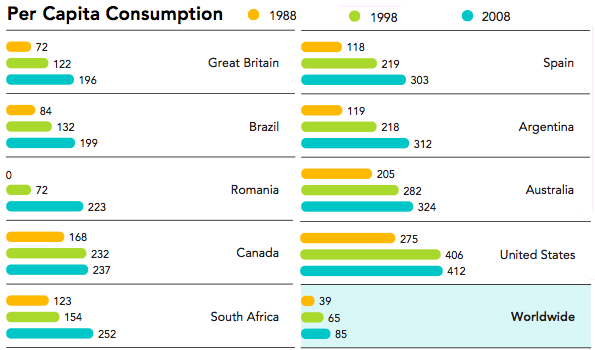
Table showing per capita consumption (Coca-Cola Consumption Per Capita par. 2)
Works Cited
Aswathappa K, Sadhna Dash. International Human Resource Management: Text and Cases. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill Pub, 2008. Print.
Bovarnick, Ellen. “VP Corporate Business Excellence.” Interview with Rod Morgan. Web.
Coca-Cola Company.Coca-Cola Consumption Per Capita. Coca-Cola, 2009. Web.
Coca-Cola Company. Operating Groups. Coca-Cola. 2012. Web.
Datamonitor. The Coca-Cola Company. Special Report. New York, London, sydney: Datamonitor, 2011. Print.
Market Line. Global Soft Drinks. Special Report. London: MarketLine, 2013. Print.