Project Overview
Since 2020, ANR Robinson International Airport in Trinidad and Tobago has been undergoing a major expansion program to boost the country’s tourism industry. The expansion will facilitate more direct flights between the island and New York, Orlando, Houston, Miami, Newark, and Fort Lauderdale in the US. The project seeks to develop an ad marketing plan with several objectives, including attracting additional airlines (higher profile, higher paying airlines), to attract additional domestic and international passengers, selling the airport credentials (sustainability and greenness, location, and convenience), and promoting the island’s attractiveness as a destination. The project’s expected outcomes or benefits include improved tourism, direct flight to US cities, reduced environmental impact, and achieving sustainability of the airport operations.
The estimated project cost is fixed at £300,000. The costs are further broken down into four key categories: requirements elicitation and analysis at £10,000, design at £40,000, building and testing at £200,000, and salaries and labor costs at £50,000. The project assumptions revolve around the budget, timeframe, and personnel skills and competence. The project constraints are confined to the budget and timeline. It is expected to begin on November 1, 2022, and complete on Jun3 30, 2023. The main project deliverables will be delivered on December 1, 2022 (project requirements), December 31, 2022 (design), and June 1, 2023 (building and testing). The expansion program involves the construction of a new Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) certified passenger terminal building for domestic and international operations. Furthermore, the expansion of the tarmac, the construction of a new car park, and other improvements are in scope. The expansion is guided by key objectives such as minimizing environmental impact and ensuring sustainability.
Key Planning Considerations (Planning Summary)
The project planning considerations touch on the communication plan and work breakdown structure. The communication plan involves identifying the stakeholders and their role in the communication plan. They include Project Sponsor/Customer, ANR Robinson Airport Director of Sales, Delivery organization, Plane Good Agency, and The Aviation Sector. The WBS considers the key project portions. They include requirements, design, building, testing, and human resource management. The key subtasks include marketing and detailed analysis and evaluation activities. The identification of stakeholders is one of the most essential subtasks.
Other key tasks and considerations in the planning phase include the identification of key activities contained in the critical path and the creation of the risk register. The critical path encompasses sequential activities. The key activities include requirement analysis, design, constriction, and testing. Requirement analysis takes place before design. Design precedes constriction and testing. Delivery takes place after successful testing. Human resource management is parallel to all other activities. The activities must be carried out sequentially in this order: Requirements analysis->design->construction->testing->delivery. Human resource management will be carried out in parallel with all other activities. The risk register summarised the potential threats to the actualization of the project. The risk register considers the timely delivery of results, adhering to budget constraints, safety, and quality. The severity of the risks ranges from 1 (lowest) to 3 (highest). Low-priority risks may be ignored or avoided, depending on their category. High-priority risks must be addressed or avoided altogether.
Communication Plan
The communication plan details the tools and channels of communication between different stakeholders. Due to the differences in their needs, requirements, responsibilities, and deliverables, different communication tools and channels are necessary. First, online marketing complaints through Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Quora, Pinterest, Google ads, and Baidu will be used by the ANR Robinson Airport Director of Sales to reach social media and internet users. The platforms will be used on a daily basis. The aviation sector will use weekly TV and radio adverts to reach out to the general public.
The aviation sector will also use Billboards to inform individuals using particular roads or malls of the tourist destinations accessible via the airport of the services provided at the ANR Robinson Airport. Plane Good Agency will employ brochures every four months to inform potential customers of the Airport services, routes, and rates. The brochures will be provided at the airport, specific malls, and other public spaces. Email and SMS(text message) alerts will be sent to existing and new customers by the ANR Robinson Airport Director of Sales. The purpose of employing the selected communication tools and platforms is to popularize airport operations, increase traffic flows, and attain economic and environmental sustainability.
Work Breakdown Structure
The project is divided into four main tasks: requirement gathering, analysis, building, testing, and human resource management. The requirement analysis task entails gathering (research), analysis, and validation. The Main analysis task includes the analysis and validation of communication tools, risk registration, the proposition of project assumptions and constraints, and validation of project deliverables. The building task entails the incorporation of stakeholders, utilization of communication tools, platforms, and media, and the inception of marketing procedures. The testing module encompasses the assessment of marketing options and the comparison of the marketing choices. The human resource management task runs parallel to all other tasks and has the same timeframe as the entire project itself.
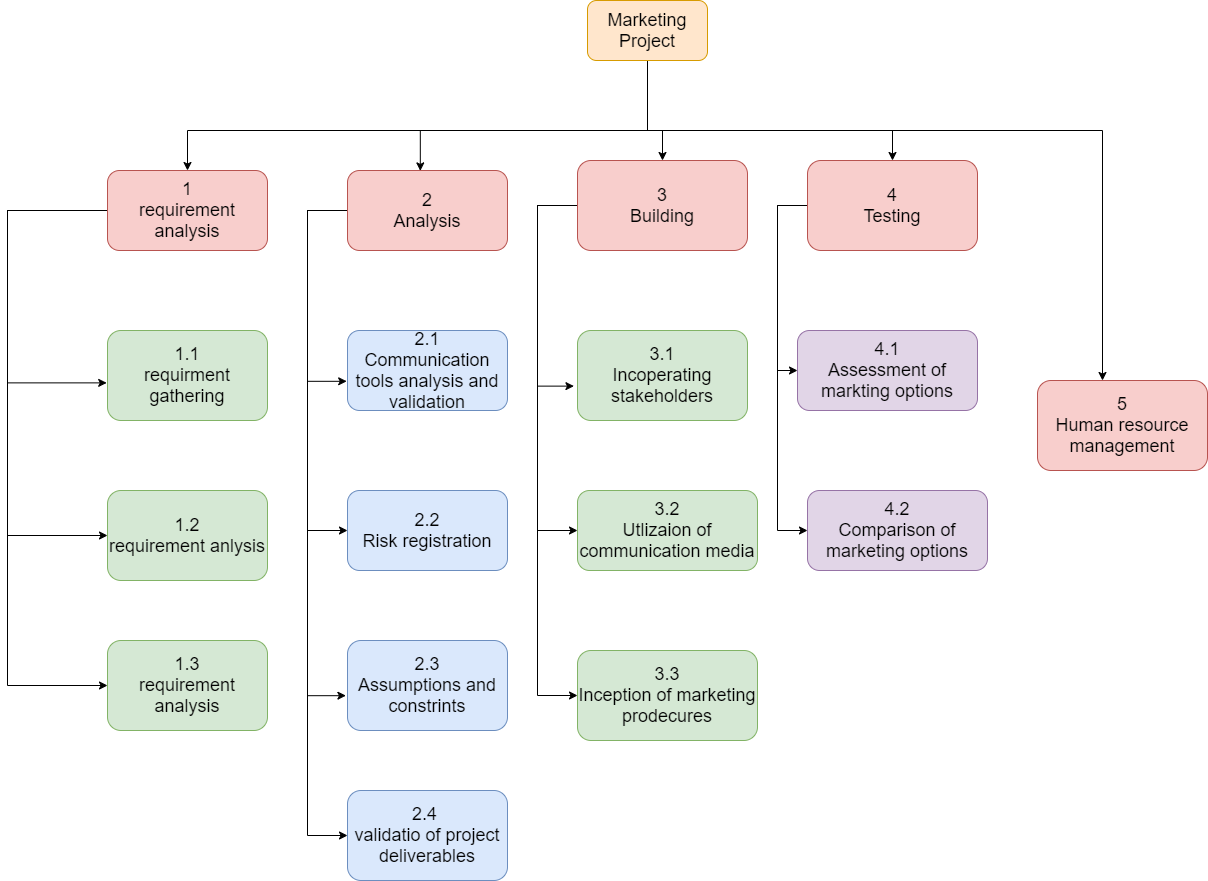
Activity List
The main activities include requirement gathering and analysis. The requirements tasks include gathering, analysis, and validation. The requirement gathering lasts ten days and involves identifying stakeholders, deliverables, and requirements. The analysis process also takes ten days and establishes the project needs. The main agenda of requirement validation is to validate the project requirements. The analysis task is scheduled to last 25 days and incorporates four main tasks: analysis and validation of communication tools and platforms, risk registration, formulation of constraints and assumptions, and the validation of project deliverables. The chosen communication tools are evaluated for applicability in the validation phase of the analysis task. The potential risks associated with the project are established and ranked during the risk registration. The project assumptions and constraints are established during the formulation stage. Finally, all project deliverables are validated to ensure they qualify for the allocated time, financial, and human resources.
The building task includes three main subtasks: incorporating stakeholders, utilization of communication media, and inception of marketing procedures. The building task is the longest, lasting five moths. The incorporation of stakeholders is concerned with identifying all stakeholders and establishing their roles and is scheduled to last two weeks. The utilization of communication media exploits the available tools and platforms that are required. The inception of marketing procedures will employ the tools and procedures required to popularize and expand airport operations within a four-month time frame. The testing task must follow the building phase. It is scheduled to last for a month, completing two main subtasks. First, the assessment of marketing options is preceded by the inception of the corresponding procedures. The comparison of the marketing options follows the assessment subtasks and is scheduled to last two weeks. The management of human resources is essential throughout the project activities and endeavors.
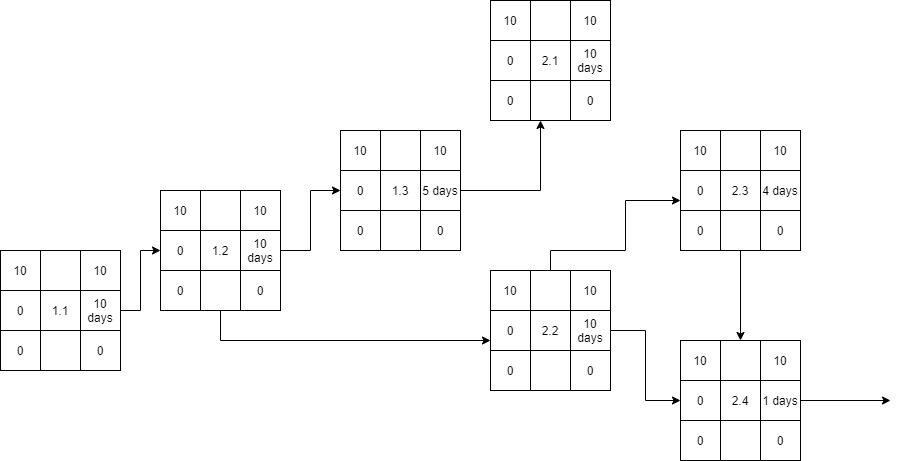
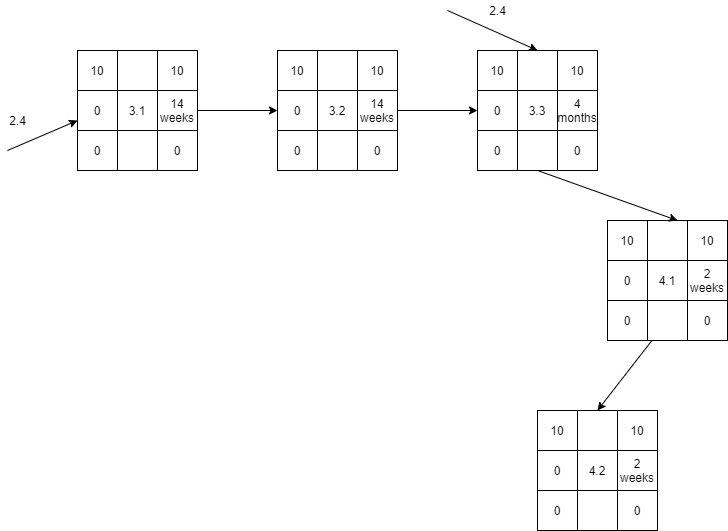
Network Analysis and Critical Path
The project activities are summarized in the partial representation of the project network graph. All activities of the requirement gathering and analysis (with the activity code 1.*) are sequential. However, the activities of the second task (with activity number 2.*) are not sequential but are presented by earlier activities as illustrated in the figure. For instance, activity 2.4 is preceded by 2.2 and 2.3, while activity 2.2 is preceded by activity 1.2.
Activity 3.1 is precedent by 2.4. All other activities are sequential, following each other as suggested by their codes (3.1->3.2->3.3->4.1->4.2). However, activity 3.3 required the prior completion of 2.4.
Risk Register
The project risk register contains a set of threats established after the project’s onset. The first risk concerning a possible budget overdraft was established on November 10, 2022. A resolution was established to adjust the expenditures on all subtasks to ensure the set budget is not exceeded. The risk was reviewed on November 30, as indicated in the risk register. Other key risks documented include delayed completion of project deliverables and delays in budgetary allocations. The probability and impacts of each risk, as well as the calculated rating, indicate their potential impact on the success of the project.
Limited skills among the project personnel, poor quality results, bad choice of communication tools and platforms, and poor choice of marketing platforms are the other documented risks. The quality of the project deliverables is essential in attaining sustainability. The impact of the risk of obtaining poor quality results is at maximum (3 * 3= 9) and hence requires effective intervention measures. The incorporation of a quality assurance department to oversee approved standards was resolved to eliminate the risk.