Introduction
The workplace today is in a condition of metamorphosis of workers’ motivation, customers’ satisfaction, human-resource development and customer relation management with a global mindset of penetrating every aspect of the organization. Effective workforce is a pillar in an organization as it is a great player in accomplishing the firms’ objectives and service delivery.
According to Aspatore Books, human-resource management is the organizational function that enables efficiency, innovation, creativity and flexibility of the workforce to transform them into productive assets. Therefore, many institutions have emphasized on the need to consider (HRM) human-resource management as a course.
However, it is also important to note that it is one of the demanding knowledge, especially in a workplace. An orderly managed well-organized human-resource department assists the organizations to attain the desired goals and competitiveness in the industry.
Background of the study
In the present century, the human-resource management departments are facing unlimited challenges. As paradigms have changed in various dimensions and the factors affecting human-resource management are not exceptional. The human-resource management must re-examine the organizational structure and functions in order to cope with relevance, new trends and challenges in the contemporary business setting.
In the current business context, the most affecting and challenging issue to an informed man is time’s nature of setting things in order and in place in the best and most effective way. Advanced technology, through the use of computer and smart phones, assist man to deal situations in the most effective and efficient manner.
The state of human-resource management is a system that attracts strengths, encourages, and maintains employees who are responsible for the successful operation and existence of the organization.
The main and important function of human-resource management circulates around workforce planning, recruitment and selection, job specification, dismissal, employee motivation, customer relation management (CRM), performance evaluation and employee development.
Has life changed alongside developments in technology, so, is it the human-resource management to occupy more responsibilities? These conceptual issues have established fundamental principles for the foundation of human-resource management.
Fundamental of human development
The training function of human-resource management is contemporarily termed as human-resource development. It is an orderly effort towards facilitating the workforce within the firm to acquire the required knowledge in the desire for organizational success. This revolves around three areas- employer and employee development, performance development and work environment improvement.
There are important laws that the human-resource management must equip itself with during the training. The teaching and the process must be interesting so that the trainee is motivated to grasp the important information.
In addition, the training and development must target at the performance improvement to help the organization attain stronger organizational efficiency, greater competitive practices and enhance profitability.
Objective of the study
In this paper, the primary objective is to examine and determine the value of employer’s knowledge in human-resource management. I seek to:
- Ascertain the relevance of human-resource management knowledge and skills and the workplace.
- To analyze the functions of human-resource management in an organization.
- Ascertain the relevance between motivation and job performance.
Discussion
The reorganization of the human-resource administration for “Flambo Plast Gmbh” The human-resource departments are vital players responsible for attracting, developing, motivating and maintaining best employees the human-resource management departments are required to make well-detailed organizational charts for their firms to assist the managers and executives carry their duties responsible.
In addition, the organization charts enhance the employees to understand the company strategy and structure, and their roles in delivering the organizational goals.
Organizational charts aid a company in ensuring effective and efficient communication of its objectives, employee expectations, and responsibilities. In demonstrating commitment to excellence, the company needs to develop an ideal organizational chart that is efficient in mapping the company’s communication lines.
The organizational chart is essential tool and is necessary in circumstances where management is in pursuit to identify areas through the enterprise that presents opportunities for downscaling.
The organizational structure needs to be flexible and the one that reflects the immediate requirements of the organization. The “Flambo Plast Gbhm” company must make sure the human-resource management chart allows the management and the employees to:
- existence of co-operation between the employees and the management at large.
- Perfect relation and communication among the employees and the management.
- Clear and easy understanding of the processes.
- Flexible and realistic nature.
- Clear definition of roles and responsibilities within the organization.
- The structure that allows smooth teamwork among the employees and the management.
The human-resource department organizational chart
The “Flambo Plast Gmbh” shall be organized in a manner that it constitutes the outlook of a modern human-resource department. The chart shall address the three-main sections namely:
- HR front office.
- HR back office.
- HR excellence centers.
The HR Front office
This office shall be the main interaction point for all HR team members and shall be an internal source for the employees.
The HR Back office
This office is important and responsible for HR services offered both internally and externally. This office is also in control of legal procedures, in an organization. The office will ensure that all procedures and actions are compliant with law. Indeed, all the administrative functions like payroll, bonus, and benefits are in control in this office.
The HR Excellence center
This section in human-resource management shall be responsible for maintaining policies, processes and products developed. The office will ensure and oversee the employee training, recruiting and staffing roles.
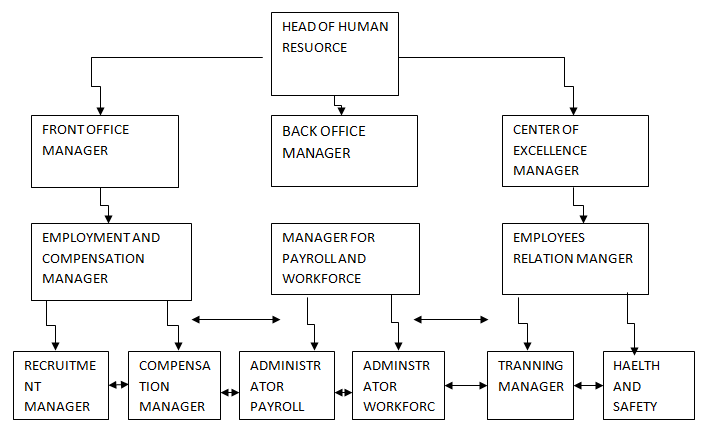
This is a hierarchical type of organizational chart. In this chart, the employees are under certain functional departments headed by a different manager. For instance, we have the front office, back office, and the excellence center headed by different managers.
The main reason for choosing this kind of chart is that it clearly explains the organizational structure in simple terms. In addition, the use of organizational charts saves an organization from problems of communication loops. These calls for another management team to assist manage the organization.
The main functions of human-resource department
The human-resource department is in control of several duties that deal with the employees of the company. Unfortunately, some managers assume HRM as a simple office with less work. The office has a lot of work and requires great attention to address these issues. However, the main duties and responsibilities of human resources management are:
- Recruitment of employees.
- Compensation and remuneration.
- Training and development.
- Planning.
Recruitment of employees
The human-resource department is vest with power to recruit and oversee the selection of employees. This involves the process of choosing few qualified candidates out from many unqualified.
The function ensures that the company under consideration selects the most skilful and competent taskforce from plenty of applicants. This function involves selection of the best individuals and evaluation of their ability in relation to the company requirements.
The recruitment can be through various processes that may include interviews, educational, psychological measurements and written interviews.
Compensation and remuneration
A capital resource is one the most important assets that the company can rely on. For efficient production, the company needs to address the issue of compensation and remuneration in details. This deals with the motivation of the employees.
The human-resource department has a task of evaluating the performance in turn rewarding those who did well or exceeded the expectation of the company. The compensation packages can be in terms of salary increment, holiday offers, awards, equities etc.
Training and development
This function is important and necessary since it adds value to the organization. Employees’ training is in relation with improvement of skills and attitudes of the employees. It is also significant in motivating the works as well as boosting their energy.
Training enables the employee to be familiar with duties that he/she supposed to work on. Some jobs require work experience or training before some can undertake the task. The can be characterized by attendance of seminars, conferences, workshops and formal talks among others.
Planning
Every manager must plan regardless of the section under his or her command. The human-resource department has the responsibility of ensuring that adequate plans are in place for the success of the organization. The department plans how the organization structure will look like, the duties and responsibilities of each employee, the chain of command and several others. The department is also bestowing with the responsibility of planning the future organizational goals in relation to people or clarifying the same goals to staff members. Planning is a useful tool in putting the organizational goals in safe basket.
Adviser
It refers to a professional or a consultant providing expert advice to his or her clients concerning a certain field.
Customer relationship management
In my own understanding, CRM is an information house or database responsible for monitoring, valuing, developing and retaining excellent relation to the customer. Simply, observing the principles of customer relationship.
Problems regarding employees’ motivation
In the turn of a century, the business setting has gone through various changes touching the style in human-resource management. Some business managers are not aware of these inventible changes. This has led to the failure of many stable businesses.
However, motivation has both positive and negative effects to the business. Therefore, it is important they learn, understand and are familiarized with factors that promote positive motivation at the workplace.
The objective of this paper is to assist the manager to understand the need for motivation at the workplace. This can be through identifying factors that may occur because of lack of motivation in the workplace.
According to Fredrick Herzberg, motivation is the force that makes us do things: this is a result of our individual needs being satisfied so that we are inspired to accomplish our tasks. Motivation is essential in achieving the best from human capital.
Motivation has a great impact on the output of the business in terms of quality and quantity. Production staff is the pivot that the business relies heavily regarding the output. When motivation is not satisfied, the company suffers a huge loss hence there is the failure of business to perform effectively.
A de-motivated workforce ultimately results in high absenteeism and employee turnover rates always accompanied by poor customer service. Fredrick Herzberg came up with two main divisions that deal with motivation.
- Those factors that motivated work staff at the workplace and,
- Hygiene Factors.
The motivators enhanced excellent performance in an organization leading high output and works’ friendly working environment. However, the hygiene factors, if not met, has a negative impact on employee’s efficiency and immeasurable loss to business. There are a number of problems regarding the employees’ motivation. These may include:
- Poor pay.
- Work conditions.
- Supervision.
- Inadequate recognition.
Poor pay
Many companies have failed to demonstrate excellent efforts towards workers’ remuneration. Though money is not the only reason why employees cause unrest at the workplace, in most cases, it is the main reason. In the recent world, most of havoc caused at the workplace results from poor pay. If the workers’ effort is unappreciated, they feel low sometimes boycotting the work or bringing unrest in the company.
Worker’ salary must be revised regulated according to ensure the equity. Employees are equally motivated to achieve the organizational objectives when salary is perceived as enough. The output of the employees must match the salary. Poor pay of workers to some extend causes sick leave and inefficient works.
Work condition
The prevailing working environment of an employee is very critical issue in the contemporary business context. Though motivation is something that comes from the inner force of a person, management has a big role in creating an environment that encourages employee motivation.
The employer must eliminate risks that de-motivate the workers at the workplace. Workplace safety must be the point of concern to management and shareholders as a whole. Most of the workforces consider this as a motivator.
Supervision
Supervision direction is wrong in certain organization leading qualified employees quitting their jobs. According to the recent research, it reveals that some managers have poor leadership and management styles in stabilizing the work of an efficient employee. It is certain that some workers quit the managers but not the job. Supervision should give direction but not cause disharmony at the workplace.
Recognition failure
Recognition failure is one of the main reasons why employees get hurt. Recognition is one of the important factors that fuels personal motives. Recognizing employees for the efforts made towards achieving the organizational goals not only make them proud but also promote self-esteem and cultivate spirits of more innovations. Motivation can be through promotions, pay increase, comments and many unlisted.
Theories on connection between motivation and job performance
Several psychologists have come with theories supported by empirical evidence to show the relationship between motivation and job performance. The world known psychologists like Fredrick Herzberg, Abraham Maslow, Elton Mayo, Douglas McGregor, among unlisted through different researches have tried to show the relation that exists between motivation and job performance.
This paper will examine through the two theories the relationship prevalence between the job performance and motivation. It is going to focus on a two-factor theory by Herzberg and the theory by Maslow.
Two-factor theory
According to Herzberg, motivation is in two motives. He also refers to this theory as “the dual structure theory.” From his theory, Herzberg believed that two sets factors influence people. He classified these two sets into motivator and hygiene.
The hygiene referred to as dissatisfied, as their absence causes dissatisfaction while their presence does not motivate. The hygiene included pay and benefit, supervision, job security, personal life working conditions, status and relationship with co-workers.
However, on the motivator side, he includes recognition, promotion, achievements and growth. According to him, hygiene factors operate separately or independently from the motivators. He argued that the hygiene factors were of short-term effects and that a little improvement would be to their removal. According to him, motivation was important and necessary for achievements.
The theory Z
Abraham Maslow developed another important theory to link relationship between motivation and job performance. Maslow (1971), named his final theory “Theory Z.” Maslow tried to relate motivation and job performance by using theory z, to explain the self-actualization.
In his study, Maslow said less than 1%of the adult population was self-actualizing. Abraham Maslow focused his life’s work on the study of human potential, development and motivation. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, visible deference was given to people who had a value focused.
He reveals that the level of unhealthiness exists in all areas of development. He refers to being self-actualized as becoming more fully human who responds to the inner forces for development. Most recent authors with the present leadership style concur with him.
According to him, before one becomes self-actualized, he must first meet the physiological needs. He demonstrated his ideas using the hierarchy of needs. Theory Z was clearly an indication of unhealthy people in unhealthy organization.
Critical review of the theories
The two theories developed by the two psychologists ultimately relate job performance to motivation. From the dual research, it is evidently that motivation is ideal in improving work efficiency. Motivation leads to high output and works that motivate results in high production.
For example, in the work of Herzberg, he believes that when hygiene is not satisfied, they cause dissatisfaction. This is actual true because when employees’ hygiene is not met, they cause underproduction.
On the other hand, Maslow work supports the connection between the job performance and motivation. In his work, “Those serving customers must be longer range in time and longer range in space and wider thinking in terms of causes and effects and holistic relationships. Why is this? It’s because the relationships…are very different when these customers are supposed to be kept for a century or two.”
Recommendations
First, I recommend the manager to enroll for the MBA course in human-resource management. This course will assist the manager in acquiring managerial skills and knowledge that will enable him or her to demonstrate quality leadership style in management.
Secondly, I recommend the management to revise and uphold the importance of motivation and strongly put it in practice. This would motivate the workforce leading to efficiency production. It will also create a good rapport between the customers and the business. Finally, the human-resource organizational chart requires another structure with well-defined duties of the concern.
Conclusion
Human-resource management is an important resource to any organization set up. The current managers require to be trained in this field to ensure they utilize this capital. This will have a positive impact on the output of the business. For any milestone development, this pillar department of the organization must be vested with responsible and knowledgeable persons.
Bibliography
Ahmad, Shoeb. Human Resources Management and Technical Changes. New Delhi: Gyan Publishing House, 2004.
Anderson, Charles. Tool Kit for Human Resources. Lincoln: iUniverse, 2004.
Anderson, Kristin and Carol Kerr. Customer relationship management. McGraw-Hill Professional, 2002.
Armstrong, Michael. Strategic Human Resource Management: A Guide to Action. London: Kogan Page Publishers, 2008.
Aspatore Books. The Role of Human Resources: Top Executives on Using HR to Drive Business Results and Add Value to a Company (Inside the Minds). London: Aspatore Books, Incorporated, 2005.
Green, Jerry W. Exploring the needs of teleworkers using Herzberg’s two-factor theory. New York: ProQuest, 2009.
Ionazzi, Daniel A. The stage management handbook. New York: Writer’s Digest Books, 1992.
Knox, Simon. Customer relationship management: perspectives from the marketplace Butterworth-Heinemann, 2003.
Koontz, Harold and Heinz Weihrich. Essentials of Management. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2006.
Lawler, Edward and John Boudreau. Achieving excellence in human resource management: an assessment of human resource functions. Stanford University: Stanford University Press, 2009.
Rothwell, William J and Kazanas Hanze. Planning and managing human resources: strategic planning for human resources management. New York: Human Resource Development, 2003.
Saiyadain, Mirza. Human Resources Management. New York: Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2009.
Mathis, Robert and John Jackson H. Human Resource Management. New York: Cengage Learning, 2010.
Ulrich, David. Human resource champions: the next agenda for adding value and delivering results. New York: Harvard Business Press, 1996.
University of Nebraska (Lincoln campus). Dept. of Psychology. Current theory and research in motivation. University of Nebraska: University of Nebraska Press, 2003.
Wilson, John P. Human resource development: learning & training for individuals & organizations. London: Kogan Page Publishers, 2005.