Introduction
According to various economic indicators like the Gross Domestic Products (GDP), Human Development Index and steel and energy consumption; the economy of the United Arab Emirates (UAE) is considered a diversified and highly growing economy. The UAE economy is an open economy, has 10% of the world’s oil reserves and is the world’s fifth natural gas supplier. It has consistently enjoyed an increase in the GDP that averages 6.5% per annum.
Economy
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) economy is dominantly pearl production, agriculture, mining, fishing, real estate, and herding. It is argued that the increase in oil prices in 1973 is what led to the spiraling economy of the UAE; it has a large volume of oil and gas reserves, and since then henceforth petroleum has dominated the economy and accounts for most of the UAE exports and has also been largely associated with the growth in the UAE economy since oil contributes to thirty percent of the Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Majority of the UAE imports are mostly manufactured goods and machinery which account for 70% of the imports. To spur the economy, the UAE government has created free trade zones where goods for transshipment and re-exportation are granted 100% duty exemption. Government policies are also favorable to the citizens of the UAE; an example is a mandatory requirement that any company should have a minimum of 51% local ownership which is considered a strategy to place Emiratis in management positions in all companies.
As a member of the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), the UAE is an active member of all functions that are economically oriented including investment policies and trade cooperation (UAE, 2011). Unlike the majority of the countries, the economy of the UAE is less dependent on the available natural resources as the main sources of revenue; despite relying on the exportation of gas and petroleum, the UAE economy is also driven by the flourishing construction industry and a booming services sector which has helped to diversify the economy.
The prosperous infrastructure sector confirms that every sector of the economy enjoys quick expansion; the diversification and liberalization of the economy is one way of curbing heavy reliance on oil in the transformation of the economy and has led to investments in the production of aluminum, tourism and the telecommunication sectors.
Land reclamation has also proved to be an economic force to the UAE economy; reclamation of land has enhanced food security and sufficiency. Land reclamation has facilitated the intensification of agricultural activities which accounts for 3% of the GDP and has employed the citizens.
Tourism promotion has led to the growth of the tourism sector; the opening of the Burj al-Arab has been touted as one of the most luxurious hotels and the tallest in the world. Tourism has also been promoted through the selling of holiday homes which targets the wealthiest foreigners.
The trading in shares by the companies in the UAE is through Abu Dhabi Securities Market (ADSM) and the Dubai Financial Market (DFM). These two financial markets have demonstrated a justifiable growth and are considered among the established in the world according to the analysis of the volume of shares traded (UAE Central Bank, 2011).
The real estate and construction sector has also been considered a booming sector in the UAE economy; this sector contributes to 15% of the GDP. The intensification of diversification as advocated by the government with the objective of reducing dependence on oil is what has led to the growth of the real estate sector.
The evidence of booming construction and real estate sector is due to the heavy presence of cranes and also because Dubai is the hub for the world’s best construction companies (Kumar, Agarwal & Khullar, n.d.). The currency of the UAE has been stable against the dollar, and it has constantly ranged from 2% to 3 % which is healthy for economic growth (UAE Central Bank, 2011).
Problems in the UAE economy
The economy of EAU has been significantly affected by the real estate sector. Starting from 2000, there was what has been described as a “meteoric rise” running through 2008 particularly in May of 2008 after a sharp downfall was realized. The figure below gives an illustration:
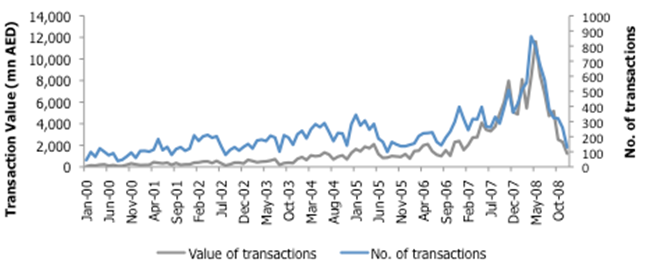
It should be noted that the above figure refers to Dubai in particular and by default, it equally applies to the UAE especially when the fact Dubai plays a very significant role in the economy of the UAE is considered. Markaz (2009) tried to analyze the real estate meltdown in the UAE. It is argued that key stakeholders in the real estate after realizing that there was no more increasing of prices in property made moves which escalated the situation.
For instance, it is pointed out that wealthy expats channeled their resources away from the real estate sector to their homes; the mortgagers took possession of the properties acting as securities, general negative sentiments followed due to rumors about possible scams in the real estates consequently driving the real estate into a meltdown.
To best explain the EUA real estate meltdown, Markaz (2009) came up with six stages of explanation:
- Stage one (healthy demand prospect): the UAE has shown above has a goal of becoming an economic hub in the Middle East region and this objective as well its strategic position catapulted the development of the construction and real estate sector.
- Stage two (supportive financing): stage one is followed by financing from local banks as well as regional and international. This ensured that financing was sufficient.
- Stage three (facilitative liquidity): stage one and two led to the growth of property prices leading to the attraction of speculators.
- Stage four (excess in leverage): there was seemingly much excitement in stage three above which lead to excessive leverage. This is said to have occurred between 2005 and 2007.
- Stage five (excessive speculation and scams): this stage was witnessed between July 2007 and April 2008. At stage five scams touching on the real estate business was unearthed leading a sharp change in the number of transactions in this area.
- Stage six (failed demand expectations): the value of the property became too high as compared to the income which was likely to be generated from such property. This was aggravated by the recessionary paths in the USA and western world in general. The net effect was reduced demand as compared to the supply hence the meltdown.
Political Unrest
Political unrest in the region: this is considered to adversely affect the economy of the UAE. The political unrests being experienced in Syria, Bahrain, Jordan, and the Maghreb region has led to deteriorating market conditions and consequently a dive in equity markets.
The recent international sanctions placed on Iran are also a major problem that is likely to affect the economy of the UAE. This is because Iran is among the largest trading partners of the UAE and therefore sanctions against Iran will weaken the economy of UAE.
Another problem that will heavily impact on the economy of UAE is the ever increasing population. This population may be due to a large number of immigrants who have gone to seek green pastures in the UAE. Lack of strong immigration policies is the greatest challenge that emerges from this issue of immigration.
Also, the absence of a democratically elected government casts doubt into the stability and continuity of the union; it is feared that suspicion among the various emirates on resource distribution may threaten the ability of the Emirates to hold on together.
Furthermore, the volatility of oil prices in the international market poses a great threat to the stability of the economy. This is because oil revenues account for 30% of the GDP and the fall in the global oil prices may weaken the economy.
Prospects of the UAE Economy
The base of the UAE economy is the macroeconomic fundamentals and good policies that concern infrastructure and competitive advantage. The step towards diversification has made the UAE a strategic trading partner for other countries outside the GCC, and this has the potential of driving the economic growth of the UAE forward.
Consequently, the UAE is pursuing a globalized, open and a technologically driven economic system and this has been instrumental in facilitating its bilateral trading agreements with EU and China just like in the context of GCC. The open door policy, in particular, has enhanced its industrial restructuring.
Despite the geographical location of the UAE, its politically stable government makes it a favorable place to work and invest in. The UAE is considered an entry point into the GCC which is a strategic economic bloc with a population of 300 million people.
Also, the continued political riots in the Gulf, that is in Bahrain, Syria and the Maghreb region is considered a prospect in the UAE economy; this is due to the fact that the protracted riots increase the bid for the UAE’s enhanced financial, tourism and aviation sectors and the economic hub of the Middle East.
Global oil companies and banks that earlier operated in these countries hit by crises have relocated from Alexandria, Cairo, Damascus, Tripoli to Dubai and Abu Dhabi in the UAE. This situation also attracted regional capital flows since investments cannot operate favorably in an environment characterized by political strife.
The laissez-faire policy that is applied by the government of the UAE is also a considerable force in the economy of the UAE. This creates the tendency of transforming the UAE into a regional industrial and services hub. The government of the UAE provides an enabling regulatory environment, and this has driven the UAE into the path of economic development.
My Opinion of the UAE Economy
UAE is a haven for investment in the globe: the policy of free trade increases competitiveness in any investment environment. The fact that the UAE government does not impose protectionist tendencies like tariff barriers make the UAE economy a competitive environment.
The UAE is a favorable investment hub; this is due to its ability to provide a wide variety of investment opportunities. The diversified economy widens the scope of investment; also the creation of special economic zones or more referred to as the free trade zones facilitate international trade and investment.
The UAE is a country of huge potential: the country has vast resources; it is the fourth largest supplier of oil, the country has the best political and economic climate characterized with free-market policies, abundant financial resources, zero income tax and free movement of goods and capital. The fact that the UAE is China’s biggest trading partner implies that the UAE will greatly benefit from China’s economic growth and the large population of China will provide a ready market for the UAE’s goods.
The UAE also has a potential for economic growth and development; this is due to its transshipment ability. The UAE has excellent port facilities; it houses the world’s largest artificial port and the third largest re-export center after Hong Kong and Singapore which is a sign of perspective and prosperous economic growth (UAE, 2011).
My Recommendations
Having accomplished a strong growth in development, the UAE should move away from reliance on oil revenues by intensifying developments in infrastructure and other alternative growth sectors like financial, manufacturing and service. The overreliance on the oil sector makes the economy volatile since oil prices are determined by the forces of the international market; these forces are dynamic.
Despite the flourishing economy of the UAE, it is imperative to understand that a stable economy only prevails when there is strong monetary policy, government regulation, financial openness and institutional environment (Parkin, 2004).
References
Kumar, R., Agarwal, A & Khullar, R. (n.d.). Real Estate and Construction Sector in the UAE: Growth Strategies. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Markaz, A. (2009). Dubai Real Estate Meltdown. Kuwait Financial Centre MArkaz. Web.
Parkin, M. (2004). Economics. Ontario, Canada: University of Western Ontario.
UAE Central Bank. (2011). UAE Central Bank. Central Bank. Web.
UAE. (2011). Ministry of economy of United Arab Emirates. Economy. Web.