Introduction
This assignment focuses on steps of needs assessment and provides a visual representation. Needs assessment is regarded a thorough process of collecting information necessary, appropriate and adequate to create an operative educational program that aims to account to the existing needs and gaps of a selected nursing issue. Thus, some gaps are noted during nursing practice for a needs assessment to be initiated. As such, a gap analysis, which refers to the identification of the variation between current knowledge or practices and current evidence based practices, is necessary.
Various methods can be used to conduct a needs assessment in nursing. They include the following learning needs survey; community health needs assessment; patient care needs; assessment of prior practices; assessment of healthcare trend; and focus groups among others. In addition, available data may also be reviewed during a needs assessment exercise.
A needs assessment, for instance in community health, helps nurses to plan, develop and provide the most effective care to patients most in need. They ensure that limited nursing resources are allocated in specific areas where maximum benefits would be achieved while working collaboratively with all stakeholders to deliver quality care (World Health Organization, 2001).
Nurses may experience gaps in current knowledge, practices and skills. Consequently, they must find the need by performing a needs assessment. The gap can be identified from knowledge, skill or practice areas while nurses determine the importance of the assessment to develop an effective solution to close the gap.
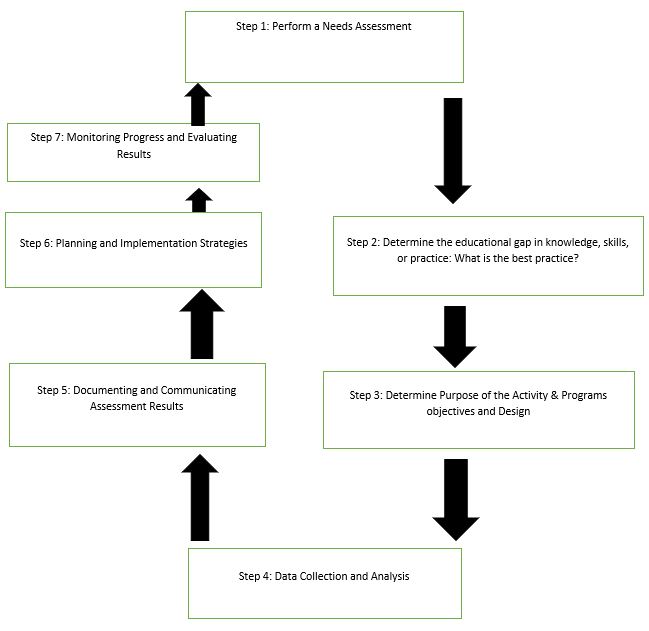
The steps of a needs assessment
Step 1: Perform a needs assessment
This step, essentially, entails gathering of information pertinent to current nursing practices and establishing probable gaps. Researchers carry out studies to establish existing nursing practice, knowledge, and skills. Correspondingly, stakeholders must identify prerequisites for the best nursing practice. The comparison of current practice and the desired practice will ultimately exemplify likely needs.
The nursing field is dynamic and, thus, changes occur from time to time. Reviewing and careful implementation of changes in nursing will result in what can be considered the best practice in nursing. First, nursing legislative and regulatory frameworks keep changing. Therefore, up-to-date legislation and regulations must be sought for best nursing practices. Second, researchers get new findings. As such, the most current research findings should be used. Third, for best nursing practices, nurses should use new technologies in carrying out diagnosis and treatment. Lastly, nurses must use reliable nursing literature and clinical guidelines for care to comprehend the requirements for best nursing practices.
Further, performing need assessment must distinguish real from exaggerated needs and consequently give appropriate importance to each category. As such, data collection processes must uphold optimal objectivity.
Step 2: Determining gaps in knowledge, skills or practice
Shortage in knowledge, for example, has been observed in the US healthcare system. Generally, a lack of knowledge of how the US healthcare system operates affects many stakeholders. As such, nurses may lack the relevant knowledge to address concerns of patients (Anthony J. Jannetti, Inc, 2012).
Nurses also require procedural knowledge or skills to address concerns of patients. However, when a gap exists, then they are unable to address concerns of the stakeholders.
Effective nurse practice reflects the ability to demonstrate nurse knowledge or skills during care provision successfully. Inadequate practice in the healthcare system affects outcomes in healthcare.
Step 3: Needs Assessment Purpose, Objectives, and Design
It is imperative to determine the purpose of needs assessment based on knowledge, skills, or practice gap. The purpose of needs assessment may be to identify the status of the patient, specific areas for improving health, determine health determinants, and resources that may be required to meet patients’ needs. Consequently, nurses can then formulate appropriate objectives and design specific tools to gather the necessary data.
Step 4: Data Collection and Analysis
Nurses may collect data as supporting evidence from diverse sources, including patients and employee interviews, literature reviews, surveys, and focus groups. It is imperative to use a combination of closed-ended and open-ended questions to collect both qualitative and quantitative data. This approach would ensure that data needed for needs assessment are collected. The design process must ensure that questions are formulated in a manner that would result in the collection of relevant, meaningful data.
After data collection, nurses should analyze data collected to learn more and gain insights about a needs assessment issues, including skills, knowledge and practice. It is imperative to recognize that data analysis largely relies on the nature of data collected i.e., quantitative or qualitative data.
Step 5: Documenting and Communicating Assessment Results
After data analysis, critical messages should be identified. A needs assessment report must show specific areas of knowledge, skills and practice gap. Besides, other factors that are considered health determinants such as poverty, education, environments and access should also be considered.
This step should also account for the written report, a communication plan, and publication of findings.
Step 6: Planning and Implementation Strategies
A critical use of a needs assessment finding on practice, knowledge and skills is to formulate an effective program that can address all the gaps identified to address nursing and health issues (Connecticut Hospital Association, 2013). Nurses must identify specific areas of health priorities to develop the most effective implementation plan based on preferred objectives, evidence-based practices, feasible activities and realistic implementation and evaluation.
The needs assessment findings should be implemented using the most effective strategies and including all stakeholders to ensure positive outcomes.
Step 7: Monitoring Progress and Evaluating Results
Monitoring and evaluation of needs assessment activity implementation would assist stakeholders to address issues related to project accountability, systematic methods of gauging progress against goals and objectives, and implementation approaches. In addition, they also provide any required reports on mid-course progress, activity improvement, and show outcomes of the deployed resources.
A visual that represents a needs assessment
Conclusion
A needs assessment is critical for nurses and nursing practice. All nurses and other healthcare practitioners should maintain and improve their knowledge, skills and practices by identifying disparities between current practices and what ought to be. Hence, understanding needs assessment steps is relevant for nurses. Besides, nurses should demonstrate competency in knowledge, skills and practices as they improve through evidence-based practices. Ongoing needs assessment is therefore critical to ensure that nurses offer safe, effective healthcare (Dyson, Hedgecock, Tomkins, & Cooke, 2009).
References
Anthony J. Jannetti, Inc. (2012). A Representation: Incorporating a needs assessment and gap analysis into the educational design. Pitman, NJ: Anthony J. Jannetti, Inc.
Connecticut Hospital Association. (2013). Guidelines for Conducting a Community Health Needs Assessment. Web.
Dyson, L., Hedgecock, B., Tomkins, S., & Cooke, G. (2009). Learning needs assessment for registered nurses in two large acute care hospitals in Urban New Zealand.Nurse Education Today, 29, 821–828. Web.
World Health Organization. (2001). Community Health Needs Assessment. Copenhagen: World Health Organization.