Executive Summary
The efficiency and functionality of an organisation depend on the management science, resources available, and the nature of the market sector. Efficiency and performance of an organisation are determined by the performance ratios such as the gearing ratio and equity ratio among others. The performance of the Wm Morrison Supermarket has been stable over the years, despite the serious economic downturn in the year 2009. The company has survived economic turbulences as a result of the series of management strategies aimed at stratifying the market and surviving competition from companies offering the same services. The supermarket is well positioned to expand within the UK market due to its dynamic approach towards provision of quality products. As a sustainability strategy, the supermarket is committed to creating strong product brands that appeal to different market segments. For instance, the marketing department within the Wm Morrison Supermarket has been consistent in creating attractive and persuasive product brands. Despite the successful operations over the years, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has not fully developed its online business platform since majority of its customers are the traditional buyers. The Balanced Scorecard will bridge the gap between the current business strategies and future action plans. Besides, the paper will present a strategy map for the Wm Morrison Supermarket to survive competition and achieve its business goals. It is apparent that the Wm Morrison Supermarket has a sustainable business model which functions within the parameters of customised services, proactive promotions, and quality services.
Introduction
The Wm Morrison Supermarket has its headquarters in the city of London and has more than 500 stores within and without the UK. The Wm Morrison Supermarket operates on the business pillars such as persuasive merchandise, balanced business channels, uninterrupted business growth, and establishment of assessment in service delivery. The company targets shoppers from across the UK and has popularised the ‘all under one roof’ service provision model. The company has a well functioning supply chain management system which supports its short and long term goals of quality service delivery. This paper will present a comprehensive Balanced Scorecard and long term strategic plan for the Wm Morrison Supermarket’s business strategy of expanding its scope and growing the online business platform.
Business vision and strategy
Vision
The business vision for the Wm Morrison Supermarket is designed to continually build sustainable business with customers through quality service provision and offering competitive prices. The vision promotes a proactive relationship with the customers, suppliers, and employees of the Wm Morrison Supermarket. The vision supports the Business to Customer (B2C) business strategy for sustainable business (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014).
Business strategy
As one of the largest supermarkets in the UK, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has created a sustainable business through its dynamic style of management and strategic planning. The Wm Morrison Supermarket operates on the business pillars such as persuasive merchandise, balanced business channels, uninterrupted business growth, and establishment of assessment in service delivery (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014). These strategies are aimed at ensuring continuous expansion and customer satisfaction. As reported in the 2013/2014 financial year preliminary report of the Wm Morrison Supermarket, the supermarket experienced a physical expansion by opening eighteen new supermarkets and increasing the office space from 37,300 to 45,120 square feet. Besides, the company was in a position to instigate more than six thousand product brands that target different market segments (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014). As a long term strategy, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has put in place mechanisms that will support its long term market expansion for the next five years. Besides, the company has long term plans of improving the delivery channels and its online business portal (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014).
As a market leader and the third largest supermarket brand in the UK, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has initiated several support services to customers and communities surrounding its branches. As indicated in the preliminary report for the 2013/2014 financial year, the supermarket initiated 25 different support services to the community (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014). Besides, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has been in the forefront of promoting wellness through its healthy customer initiative. These initiatives have enabled the Wm Morrison Supermarket to expand rapidly due to improved customer loyalty. Moreover, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has managed to penetrate the traditional markets as the suppliers always perform the function of marketing the supermarket to potential customers (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014).
In the Wm Morrison Supermarket, the management is keen on ensuring that its suppliers meet the standards outlined in the suppliers’ code of conduct. This practice has a number of benefits for the organisation. First, it ensures that the supermarket receives quality goods since the supply chain is monitored and managed at all levels. This in turn leads to quality output of the Wm Morrison Supermarket as the aspects of efficiency and optimal operations form the basis of operations within acceptable factors of production (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014). Also, vetting enables the Wm Morrison Supermarket to comply with various regulatory requirements that ensures that the company and its clients are protected at legal and ethical levels (Pearce and Robinson, 2009). The Wm Morrison Supermarket has a long term strategic goal of improving the supermarket’s visibility by expanding the market coverage. The Wm Morrison Supermarket intends to achieve this goal by initiating different physical expansion plans for the supermarket within and without the UK in the next decade. The Wm Morrison Supermarket plans to open at least 20 new branches every year for the next ten years to benefit from the expanding UK retail sector (WM Morrison Supermarkets plc, 2014).
The Proposed Balanced Scorecard
By definition, a Balanced Scorecard is a business management process that functions within the premise of balancing the different elements of strategic plans. The Balanced Scorecard operates as a planning regulator within a multi-user interface for micromanaging short term and long term goals of a company (Peng, 2004). In the case of the Wm Morrison Supermarket, the proposed Balanced Scorecard will function as an evaluation tool to check the progress and report any feedback for the long term goals of business sustainability and physical expansion.
Wm Morrison Supermarket’s Balanced Scorecard
The Wm Morrison Supermarket requires a Balanced Scorecard to evaluate the effectiveness of the long term business strategy. The proposed Balanced Scorecard will capture the perspectives such as learning and innovation, internal business process, customers, and financial management. The different components of the Balanced Scorecard are presented below.
Perspective: Learning and innovation.
Perspective: Internal business process.
Perspective: Customer.
Perspective: Financial.
How to apply the Balanced Scorecard within the Wm Morrison Supermarket
Sustainability is required for the placement of a business strategy. Several key preconditions such a long-term commitment to the brand strategy, advertisement campaigns, adequate budget allocation, response to societal changes, and the need for specific objectives determine the success and sustainability of a business when applying the Balanced Scorecard. Thus, the revenues of the Wm Morrison Supermarket should be embedded in a number of strategic strengths such as effective advertisements, diversity of products, and consistency in the organisational culture. When the Balanced Scorecard is properly implemented, the long term goals of the Wm Morrison Supermarket will become a reality since the implementation process will be appropriate (Pearce and Robinson, 2009).
The management of the Wm Morrison Supermarket will also be in a position to micromanage the tracking system which checks the effectiveness of the implementation approach. The scorecard will become part of the decision making process since it will empower scientific rationalisation of any implementation strategy (Peng, 2004). The line managers will have the ability to balance the vision of the Wm Morrison Supermarket within the action plans proposed in the Balanced Scorecard.
Building a strategic map
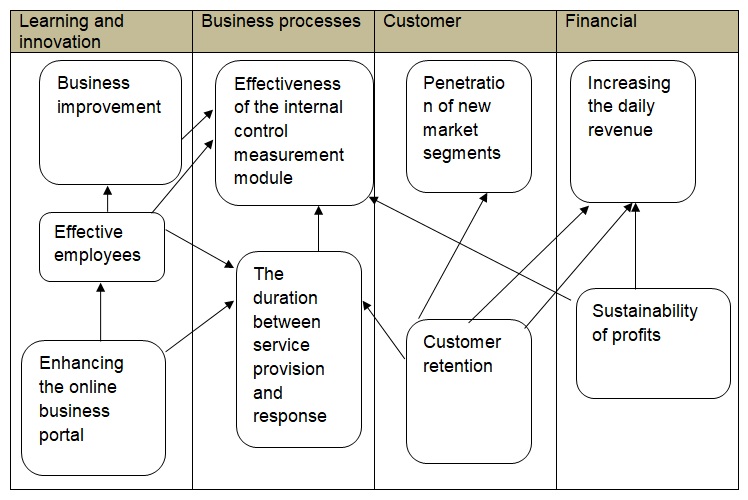
Quality improvement
Customer satisfaction is the focal point of the company in attaining a competitive advantage in the market above other players. Specifically, operations systems are employed in the Wm Morrison Supermarket to monitor and increase productivity at minimal error and poor quality. The system is currently not satisfactory since the Wm Morrison Supermarket has very little activities aimed at customer satisfaction assurance. This has not been possible because its model of running overseas customer assurance strategies does not allow for the customer preference tracking process. Besides, it does not monitor the wrongful use of resources or misappropriation within the after sales services in the local market segment. Besides, the company’s customer overseas service strategy is not based on people and their values, rather, it functions on the assumptions of the cultural dynamics of the local market in the UK. The success of the strategy is made through investing in the communities and its stakeholders (Samson and Singh, 2008).
In order to improve on quality to overcome the above challenges, it is important for the management to adopt a proactive role in balancing the strategic plan and current business dynamics as presented in the table below.
Proposed Strategic Plan
Planning of the proposed strategic map
For the management of the Wm Morrison Supermarket to successfully implement the quality improvement system as part of the strategic plan, it is important to carry out planning (Williams, 2007). The planning process is summarised in the table below.
Wm Morrison Supermarket’s existing forms of system monitoring should be periodically upgraded to introduce multiple operating system models such as ratio analysis in operation management, that is compatible with tracking and analysis within and without the company across the three major segments. Currently, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has a centralised monitoring system controlled by a few managers despite having a workforce of more than ten thousand employees. The current system is inclusive of the scientific aspects such as a technical process of understanding the operations involved in operations management, their application, and evaluation criteria which is monitored by the support department. The Wm Morrison Supermarket has not fully established a mechanism of monitoring progress at micro level and depends on macro auditing in decision making and still has to deal with the risk of changing customer preference (MacKay and McKiernan, 2004).
Measuring the success of the Balanced Scorecard
In order to present an alternative but flexible change plan, the process should be able to allow the supermarket to plan for future desirability and be able to achieve them while responding to the rising circumstances (Pearce and Robinson, 2009). Being cyclic in nature, it operates on the perception that management of change in an organisation is an interactive process (Bowden, 2009).
Implementing the strategic map
Analysis of the Wm Morrison Supermarket’s strategic plan
The Wm Morrison Supermarket has a localisation strategy which involves giving more monotony on distribution and marketing units operating in different markets. Through localisation, the elements of creativity, customer loyalty, and meeting specific needs in different regions are met by the company. In the recent past, in order to diversify market operations, the company has created multiple products from the same product with different coloration, sizes, packaging, prices, and the difference in quality in the localisation strategy to meet these varying demands (Michael, 2008).
Recommendation
In order to move the Wm Morrison Supermarket brand forward, it is critical to adopt the localisation strategy that directly appeals to different target markets. The Wm Morrison Supermarket should remain the organisation that has localised its means of production and marketing to appeal to different customer bases. The localisation strategy will help in triangulation of the “how”, “where”, and “what” of management strategies since it focuses on a specific market (Bowman, 2003). It involves the identification of the customer needs, examining and deploying potential enablers in new converging innovative technologies, and identifying capabilities to ensure that the needs are met within the expectation of the local markets. The company’s advertisements should remain specific to different geographical regions that appeal directly to the target consumers (Bustin, 2004). In achieving these objectives, the strategic blend should map possible competition, positioning strategy, consumer and market analysis, and geographical regions of operation to minimise the risk of product rejection. Generally, the localisation strategy should be redesigned to be flexible to market dynamics and embrace alterations where necessary for each target market (Bowden, 2009).
In response to the strong competitive advantage of its competitors, the Wm Morrison Supermarket should resort to developing a good brand positioning as a marketing strategy that guides the strategic plan and illustrates their brand’s essence. Specifically, the branding strategies should be accompanied by a reorganisation of market segmentation to introduce a direct interaction between the company and the clients when selling products. The Wm Morrison Supermarket can fortify this relationship by offering free customer online support services (Bloom, 2004).
Conclusion
The proper use of the localisation strategy will determine the success and sustainability of the Wm Morrison Supermarket in penetrating the global market. To increase credibility and maintain professionalism, the localisation strategy will flawlessly facilitate a healthy and a lifetime relationship between the company and its clients in different regions. The Wm Morrison Supermarket functions on the strategies such as compelling merchandise, complimentary services and channels, continuous business development, and creation of value in services. The company targets shoppers from across the UK and has popularised the ‘all under one roof’ service provision model. The company has a well functioning supply chain management system which supports its short and long term goals of quality service delivery and physically expansion. Generally, the Wm Morrison Supermarket has a sustainable business model which will support the proposed Balanced Scorecard and strategy map. However, the localisation strategy should be redesigned to be flexible to market dynamics and embrace alterations where necessary for each target market. In achieving these objectives, the strategic blend should map possible competition, positioning strategy, consumer and market analysis, and geographical regions of operation to minimise the risk of product rejection.
Reference List
Bloom, P 2004, Circle of influence: Implementing shared decision making and participative management, Lake Forest, IL, New Horizons.
Bowden, J 2009, “The Process of Customer Engagement: A Conceptual Framework.” Journal of Marketing Theory & Practice, vol. 17 no 1, pp. 63-74.
Bowman, S 2003, “Corporate restructuring: Reconfiguring the firm”, Strategic Management Journal, vol.1 no 4, pp. 5–14.
Bustin, G 2004, Take charge: How leaders profit from change, Tapestry Press, Irving, Texas.
MacKay, B., & McKiernan, P 2004, “The role of hindsight in foresight: refining strategic reasoning”, Futures, vol. 36 no 3, pp. 161-179.
Michael, S 2008, ‘Investments to create bargaining power: The case of franchising’, Strategic Management Journal, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 497-514.
Pearce, J., & Robinson 2009, Strategic management: Formulation, implementation, and control, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Peng, M 2004, ‘Identifying the big question in international business research’, Journal of International Business Studies, vol. 35, no. 2, pp. 99-108.
Samson, D., & Singh, P 2008, Operations management: An integrated approach, Cambridge University Press, London.
Williams, C 2007, Re-thinking the future of work: directions and visions, Palgrave, New York.
WM Morrison Supermarkets plc 2014, Preliminary results for the year ended 2 February 2014 and strategic update, Web.