Introduction
Research Overview
The UAE government has, over the years, rolled out strategies aimed at improving the service quality through strategic and focused touchpoints aimed at positively impacting the level of customer satisfaction. The satisfaction level is measured in terms of the happiness matrix. In the last five years, the government has been at the forefront in the introduction and institutionalization of centers of excellence across all public institutions through a policy-based customer service approach. The efforts have been expanded to include encouraging private organizations to equally integrate the centers of excellence in their customer service activities as part of the total quality management (Eman, Ayman, & El-Nahas, 2013).
The government efforts have paid off as the UAE was voted the country within the Gulf region with the highest happiness index. This means that the citizens are generally happy with the service module and strategies of the government aimed at sustaining the unique touchpoints. For instance, the UAE government has integrated the online and offline rating of the services through the suggestion boxes in most public institutions and online dating platforms at the end of every Internet-based service module. The progress in the quality of service delivery in the government offices has been positive and relatively attractive, considering the hierarchy concerns. In these offices, the quality management tools such as TQM, Lean Six-Sigma, and ISO certification has become benchmarking instruments for tracking the sustainability of the service delivery efforts. Therefore, it is important to review the effectiveness of the touchpoints within the UAE government customer service delivery strategy to establish their sustainability in terms of improving the current happiness index.
Research Problem
As already mentioned in the research overview, it is vital to review the current quality management strategies in the UAE government offices in terms of the critical success factors presented in the form of touchpoints. The study should investigate the total quality instrumentation, government policies on public service charter, and a potential barrier to a sustainable happiness index. At present, there is very little empirical evidence that has been gathered on the impacts of the UAE government’s touchpoints in customer service towards sustaining the happiness index within public institutions. The limited evidence forms the basis for this study. Through a comparative literature review and focused methodology, the proposed study will draw a conclusion in the effectiveness of the current touchpoints in improving service quality and the general country’s happiness index.
Scope
The research scope is limited to reviewing different UAE government touchpoints from a total quality management perspective to establish their existing relationship to the customer happiness index. Thus, the study is focused on the effects of total quality management strategies of the UAE government in public service and how these efforts have resulted in continuous improvement from the stakeholder perspective.
Research Question, Aim, and Objectives
The study is aimed at establishing the critical success factors in quality management of service delivery charter in the UAE government institutions. Specifically, the investigation is based on quantifying the relationship between continuous improvement touchpoints and customer happiness index. The following research question and objectives were drawn from the above aim.
Research question:
- What is the impact of the UAE government’s touchpoints in improving service quality and the general happiness index?
Research objectives:
- To investigate the current critical success factors associated with total quality management in the UAE government public service charter.
- To investigate the impacts of these critical success factors in improving the quality of public services.
- To explore how these improvements have resulted in increased happiness index in the present and foreseeable future.
Significance and Limitations of the Research
The proposed study aims at providing relevant information on the UAE government’s critical success factors in the public service charter through the implementation of total quality management. Specifically, the research focuses on the continuous service charter improvement through the unique touchpoints aimed at expanding the general customer happiness index. Therefore, the findings of this study will contribute to the existing literature on service quality as facilitating higher and sustainable happiness indices. The findings will also benefit the UAE government and public institutions on the best strategies for modifying the current touchpoints or integration of better alternatives to expand on the general customer happiness.
In addition, the results of this study will provide an insight into understanding total quality management at the government level in integrating mission, clear objectives, vision, and commitment charters in service delivery based on planning for utilization of existing resources for optimal customer satisfaction. However, since the entire study is based on secondary data, the limited information available that focuses on the UAE public service charter translates to inconclusive results. Moreover, due to the limitation of time, the researcher opted for a cross-sectional horizon approach, which can only capture the snapshot of the current events related to the topic. In addition, overreliance on the interpretivism approach by triangulation of the collected data could not give enough room for comparative analysis.
Literature Review
Theoretical Literature Review
The concept of quality management integrates quality control, assurance, inspection, and TQM (Daft & Marcic, 2016). The elements of quality inspection and control are “retrospective in such a way that their function is to identify and detect any problems or defects before they happen” (Daft & Marcic, 2016, p. 44). On the other hand, TQM and quality assurance instruments seek to improve and avoid future defects or problems. The quality assurance instrument is designed in a service delivery charter to prevent potential defects or foreseeable problems that are associated with quality through proactive and self-sustaining planning methodologies. For instance, the ISO certification is carried to institutionalize confidence levels through unique activities or service charters laden with problem identification and rectification tools (see figure 1).
The impact of quality assurance in facilitating touchpoints in service delivery is a proactive focus to achieve a stable quality management system. Quality control instrument details methodologies and procedures involved in developing, planning, and scheduling to guarantee quality assurance (Daft & Marcic, 2016). For instance, the Hoyle PDCA framework in integrates the elements of requirement, plan, do, check, conform, remedial actions, and corrective action (see figure 2 and 3). This theory proposes the use of quality management tools such as quality control, assurance, and Pareto charts among others to manage the requirement and feedback channels. This Plan, Do, Check, and Act cycle encourages controlled and continuous improvement in the quality management processes from a holistic and subjective perspectives. When the PDCA framework is not properly integrated, the potential challenges that might grapple an organization include inconsistency, overconcentration on short-term, unpredictable level of commitment in process management, and overdependence on accounting numbers or figures at the expense of quality problems (Bryman & Bell, 2015).
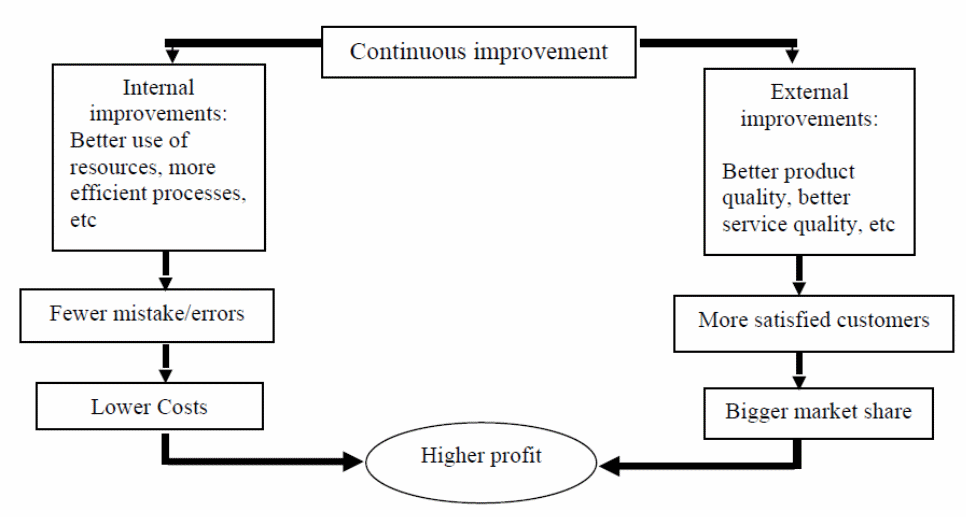
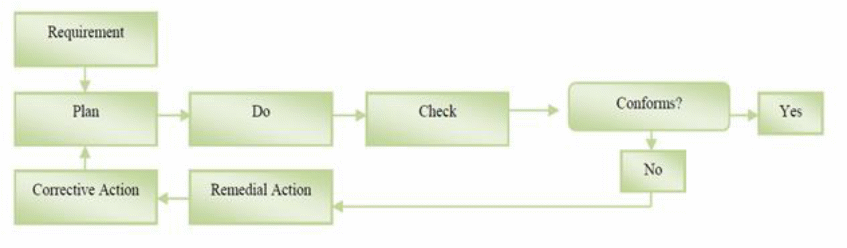
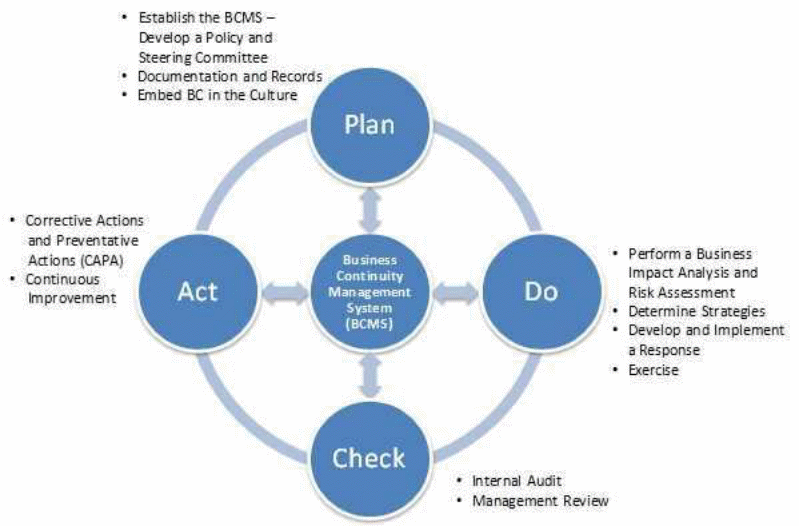
The theoretical modeling of quality management in the form of touch points indicates that the process is dynamic and multifaceted. This means that an effective service charter should integrate the PDCA elements for continuous, effective, sustainable, and self-sustaining customer satisfaction.
Empirical Literature Review
A study by Talib, Ali, and Adris (2014) acknowledged that TQM is a multidimensional process integrating a holistic view of an organization from top management to the lowest rank when developing processes and service charters. The findings concluded that TQM is a philosophical and management style created to manage customer needs, expectations, and satisfaction. According to Singh and Singh (2014), the concept of TQM consists of three distinctive elements that are dependent on each other. The first element is Total, which integrates all the stakeholders involves in the service delivery charter. The second element is Quality, which defines and manages the customer requirements that should be met. The last element is Management, which defines the level of executive management commitment in managing the service delivery process (Guiso, Sapienza, & Zingales, 2015).
Another study by Eman, Ayman, and El-Nahas (2013) established that quality leadership is a significant ingredient for creating a culture of customer satisfaction. These findings were confirmed by a study by Battor and Battour (2013), which stated that total quality management in public service may only succeed when it is categorized as a top priority by the executive management team. These results are consistent with a study by Abusa and Gibson (2013) confirming that management commitment level is a prerequisite for creation of goals, value, and alignment of the customer satisfaction systems. The empirical literature indicate that effective quality management contributes to effective communication in the service delivery charter, creation of a strong system for effectiveness in management commitment, and empowerment of the entire channel for tracking or managing customer feedback.
Significance of Literature Review and Gap
The empirical and theoretical literature review indicates that the concept of quality management is laden with a myriad of instruments aimed at improving services and customer satisfaction. The PDCA and continuous improvement models have highlighted the steps and procedures used in tracking and managing the quality service charter in general. In a similar way, the empirical studies focus on the application of different quality management tools to institutionalize the touch points for customer satisfaction, which translated to higher happiness index. However, very little research has been focused in the UAE government’s public service charter. Therefore, this study aims to fill this gap by concentrating the research on touch points of the UAE government as quality management inputs aimed at improving customer satisfaction levels.
Methodology
Since the study was focused and systematic, the researcher opted for secondary survey of journal articles focusing on quality management from customer satisfaction perspective. Specifically, the researcher opted for qualitative research design to establish the insights presented in each article and their associated with the current UAE government touch points (see figure 4). The research then related these touch points are quality assurance and control instruments for improving and sustaining thee high happiness index the UAE.
Findings and Analysis
The first theme investigated from the secondary sources was the current critical success factors associated with total quality management in the UAE government public service charter. The findings revealed that the UAE government has put in place stringent measures in place to ensure that management commitment through quality leadership is part of the public service charter. The existing pool of experienced manager in the government institutions have ensured that the touch points are implemented to the later as part of the annual government service delivery charter. For instance, the instruments of TQM, lean Six Sigma, and continuous improvement have been integrated in the public service charter towards quality performance the service process. The executive and regional governments in the UAE have a unique quality motto angled on meeting preset performance objectives in serving customers.
As a result, there are key performance indicators institutionalized through the touch points from the top management to the lowest ranking public service employees (Eman, Ayman, & El-Nahas, 2013). In application, the leadership commitment has introduced the aspect of balancing the UAE government mission, vision, and service objectives with regards to quality in the public service charter. Through a proactive and integral management of the vision and mission, it is relatively easy for the government agencies to benchmark their performance against preset key performance indicators in public service delivery. In addition, there are short and long-term goals developed by the different public service management levels in the UAE. These short and long-term strategies are aimed at ensuring that the continuous improvement goals contribute to positive happiness index. The public service employees are also empowered through competitive remuneration and healthy work environment to encourage optimal performance and individual and organizational levels.
The second these investigated was the impacts of these critical success factors in improving the quality of the public services. The findings indicated that the critical success factors have created a holistic service delivery environment within the UAE public service institutions. Since each performance indicator is laden with specific, replicable, and self-regulating quality matrices, it is possible to track the feedback of the general public and organizational functionality in the service charter (Talib, Ali, &Adris, 2014). For instance, the key performance indicators are organized around strategy, leadership, empowerment, and responsibility to minimize mistakes associated with poor service quality. As a result, the UAE government institutions have institutionalized trust, coordination, interdependency, communication, and overall satisfaction in customer service points by observing the ‘touch points’. Among the notable touch points include quick service delivery (15-20 minutes), online service portal, effective customer relationship management, and follow-ups at the end of each service cycle. These touch points have generally improved the service environment in line with the preset key performance indicators.
The last theme explored was how these improvements have resulted in increased happiness index at present and foreseeable future. The findings indicated that the current happiness index is actually the highest in the region. The general public has a high satisfaction rate with government services at 70%. The high positive review could be associated with the continuous improvements in the service charter and integration of a formalized, dynamic, and customer friendly service platforms. At present, in any government office, a citizen of the UAE is assured of a quick and insightful service. Moreover, at the end of each service cycle, the general public is encouraged to objectively rate the assistance and provide recommendations. These ratings are integrated into the future service charter planning strategies to guarantee continuous, effective, and optimal satisfaction level, thus, the high customer happiness index. These findings confirm that the UAE government touch points have been effective in facilitating quality service delivery and are associated with the high happiness index.
Recommendations and Conclusion
The UAE government should consider formalizing the current continuous improvement at internal and external levels to create policies that will guarantee sustainability of the current high quality service charter. In application, the mission and vision should be clearly defined by the management team and institutionalized at organizational level. There should be specific improvements in the opportunities on the basis of impacts and criticality as perceived by customers. Moreover, it is imperative for the UAE government to integrate different quality management tools such as lean Six-Sigma, TQM, and continuous process improvement to ensure that deployment of quality functioning and process analysis are positively aligned to the sustainability goals. The UAE government should also consider using the proposed quality management tools as the primary baseline for creating annual vision and mission in the service charter to improve on the current happiness index. This process should be done on the background of customer concerns, recommendations, and criticism since the end product aims at satisfying the general public. In application, these recommendations should be executed in a cycle to ensure continuity and adjustments in the improvement strategies aimed at sustaining the high happiness index. These suggestions will ensure that the touch points facilitate the achievement of the national agenda and the UAE 2021 vision.
References
Abusa, F., & Gibson, P. (2013). TQM implementation in developing countries: A case study of the Libyan industrial sector. An International Journal, 20(5), 693-711.
Battor, M., & Battour, M. (2013). Can organizational learning foster customer relationships? Implications for performance. The Learning Organization, 20(5), 279-290.
Bryman, A., & Bell, E. (2015). Business research methods (4th ed.). Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Daft, R., & Marcic, D. (2016). Understanding management (10th ed.). London, UK: Cengage Learning.
Eman, M., Ayman, Y., & El-Nahas, T. (2013). The impact of corporate image and reputation on service quality, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty: Testing the mediating role: Case Analysis in an international service company. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 8(1), 12-33.
Guiso, L., Sapienza, P., & Zingales, L. (2015). The value of corporate culture. Journal of Financial Economics, 117(1), 60-76.
Singh, H., & Singh, B. (2014). Total quality management: Today’s business excellence strategy. International Letters of Social and Humanistic Sciences, 12(32), 188-196.
Talib, A., Ali, K., & Idris, F. (2014). Critical success factors of quality management practices among SMEs in the food processing industry in Malaysia. Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 21(1), 152-176.