Introduction
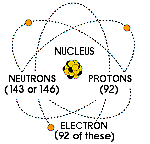
Uranium (U) is normally used in nuclear reactors where it helps in producing energy. The element naturally occurs in rocks with a concentration of 4 ppm. In the earth’s crust, it normally occurs as tin, tungsten, or molybdenum. It can also be recovered from the ocean as well as in sea water. Uranium was first discovered in 1789 by a German chemist called Martin Klaproth. Uranium has a high density and this characteristic makes it suitable for use in the keels of yatch and in radiation shielding. In addition, it is the heaviest naturally occurring element. In fact, it is 18.7 times denser than water. Uranium has isotopes that differ from each other in terms of the number of uncharged particles called neutrons in the nucleus. Naturally occurring uranium is a mixture of two isotopes namely uranium-238 and uranium-235. Uranium-235 is economically important because it can readily be split to release a lot of energy. This isotope is also fissile. Both U-238 and U-235 are capable of decaying. However, U-238 decays so slowly and its half-life is the same as the age of earth. This implies that it is less radioactive. U-235 decays faster relative to U-238. The nucleus of U-235 has 92 protons and 143 neutrons. When its nucleus captures a moving neutron, it splits into two and in the process releases energy in form of heat. In the process, two or three additional neutrons may be thrown off. A fission chain reaction can result when the expelled neutrons cause nuclei of other U-235 atoms to split (World Nuclear Association, 2011).
Uranium Mining
Uranium mining in the United States is basically done in all the states. These include Alabama, Alaska, Arizona, California, Colorado, Florida, Idaho, Nebraska, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, North Dakota, Oklahoma, to mention but a few. Despite the fact that Uranium has been found in Coosa Block and metamorphic Uranium found in Higgins Ferry Group, deposits of economic value have not been found in Alabama. Using airborne gamma radiation, scientists discovered Uranium in Ross-Adams in Alaska. Its deposits are found in the Prince of Wales Islands. Here, its principal ore mineral was uranothorite that were found in veinlets in granite.
Societal issues tied to mining, distribution, and use of uranium
Places where uranium is mined are often destroyed by rigorous mining activities. Besides, mining areas close to the earth’s surface are normally covered by mine dumps and it is a common site to find numerous individual veins of deposits mined up to the surface with no safety pillars put in place. This often leads to subsidence of up to 10m. The mine dumps may have serious radiation hazards. The miners are also exposed to the health effects of the mineral. Exposure to Radon leads to lung cancer deaths (Roscoe, Steenland, Halperin, Beaumont, and Waxweiler, 1989). Radon is a product of radioactive decay of uranium and is high in concentrations in underground mines. In fact, a number of miners in the Four Corners succumbed to lung cancer in the mid-50. This happened because during this time, the mines did not have adequate ventilation, this situation is still observed in a number of Uranium mining areas (OECD, 2001).
Because of the harmful effects of Uranium mining on the communities around such locations, there is need for the industries that carry out the mining activities to come up with remedial activities to counter the hazards. Uranium mining has scientific-technical, political and socio-economic challenges that accompany it. Workers, community around the mines, and other stakeholders should be highly involved in mitigating the radiological challenges that accompany uranium mining. In the scientific-technical context, there should be a national and international guidance on intervention and on protection against natural radiation. This enhances flexibility in decision-making. The national and international guidelines can be counterproductive in the sense that they can impact, albeit negatively, the credibility of expert judgments hence protracted uncertainty. Radiation protection legislation should be put in place while its flexibility is prioritized. Because the effects of radiation can be far reaching on the health of the workers and the people living in close proximity to areas where uranium is mined authorities should ensure that they provide information on radiological and other impacts of uranium mining and milling. Authorities have to ensure that they set aside funds meant for countering the effects of uranium mining. On the socio-economic perspective, the proprietors of uranium mining company should ensure that as part of their Corporate Social Responsibility, they absorb into their labor force the neighboring communities. The workers in these plants and the neighboring communities have to be involved in the decision process. A culture of openness and willingness to take part in these debates should be cultivated. The management should show the affected populations that their concerns are being treated with the seriousness that is deserved (OECD, 2001).
Economic issues
How the cost of mining uranium compares to that of mining coal
The costs incurred in mining of uranium include costs of procuring leases, costs of exploration and discovery of the ore body, the front end costs of setting up an underground mine, mining costs, environmental costs and cost of milling Uranium ore. Because of difficulties in acquiring land, the only option that exists is buying a lock of land from another leaseholder. For potential success, it is imperative that a block of up to 10 000 acres is acquired. Other than front end costs there are other costs related to legal fees, abstracts, and geological research. On the higher side, the cost of procuring leases adds up to $ 1.5 million. The costs of exploration and discovery of ore factors in the geological staff, contract drilling of the exploration holes, logging of holes, assaying, surveying, mapping, clean-up environmental work, and the consultants fees. Contract drilling, logging, assaying, geological report, and location clean up incurs cost of a total of $ 11000 per drilled hole. When a 3000 feet and below drilling depth is done, exploration costs will be nearly $10 million. The front-end costs incurred in setting up an underground mine costs up to $50 million depending on condition and size of operation. The cost of mining when labour, supplies, equipment and other factors are factored in varies depending on whether the mine is new or old. Front-end cost of setting up mines keep changing due to inflation in equipment and engineering costs. The cost of milling uranium ore and environment costs are low relative to other costs (New Mexico Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources n.d.).
Bearing in mind that both Uranium and coal are used in production of electricity, the environmental costs incurred as a result of using coal in generation of electricity outweighs that of uranium which is considered green source of energy because it produces less carbon that leads to environmental degradation. Annual compliance costs in coal mining that includes monitoring costs and additional BMP efforts add up to $758,500. Surface mine operators do incur additional costs of $50,000 to comply with watershed modeling requirements (EPA, 2000).
Labor and uranium mining
The mining industry is generally facing an acute shortage of skilled manpower. This shortage impacts the mining industry negatively and this has made potential investors to be very skeptical about investing in Uranium mining. This greatly interferes with the production of already established mines. The supply of uranium to the market is impeded by shortage of skilled manpower leading to instability in world Uranium prices. Uranium has been in the bear market for the last 30 years during which there has been attrition of skilled mining manpower. Young people in pursuit of new careers avoid the no-go areas of geology and mining engineering. Consequently, universities have been forced to close down geology and mining departments because of declining student numbers. Because companies prospecting uranium have kept increasing in numbers, the demand for skilled manpower has risen correspondingly. Labor and infrastructure shortages have contributed to the decline in labour. Labor shortage can also be attributed to delays in preparation of feasibility studies. Retirement is worsening labor shortage in uranium mining because there are few skilled personnel joining the sector while retirement takes away experienced and expert personnel (Field, 2007).
Environmental issues with uranium mining
Despite the fact that Uranium is radioactive, it is not very rare. It occurs naturally in the environment in very small quantities in rock, soil, air, and water. Because of human activities, uranium is added to the environment in various ways, for instance, when metals and compounds are disposed especially during milling and mining processes. The concentration of Uranium in the air is very low. However, even at higher concentration in the air, there is very little Uranium present per cubic meter, that is, less than one atom transfers everyday. In water, it is normally derived from rocks that water erodes or weathers. Quantities of uranium in drinking water are generally low. Exposure to the mineral can occur through water, air, or soil. Root vegetables normally have small amounts of natural uranium. Uranium is also breathed in minimal concentrations in the air.
Individuals living next to hazardous waste sites, uranium mines, are highly exposed to the effects of uranium. Natural uranium has no harmful radiation effects. However, after large intake occasioned by exposure, diseases like kidney disease and even lung cancer may result due to the process of bioaccumulation. Radionuclides formed during the process of radioactive decay may cause cancer after longer exposure. In fact, chances of getting cancer in this case are higher than when somebody is exposed to enriched uranium. Radioactive Uranium emits dangerous radiation that can facilitate growth of cancerous cells in individuals within a very short period of time. Because Uranium is very reactive, it cannot be found in the environment in elemental form. Compounds of the element easily dissolve in water and this increases the mobility and toxicity of environment. Radon, a decay product of uranium, builds up in confined places. Radon was associated with lung cancer fatalities exhibited in the U.S. mines with no or poor ventilations (Roscoe et al, 1989).
Conclusion
Uranium naturally occurs in air, water, and soil in quantities that are not detrimental to human life. The element has two isotopes: U-235 and U-238. U-235 is more radioactive than Uranim-238 that has half-life equal to the age of the earth. Uranium mining in the United States takes place in virtually every state. The US uses Uranium in production of electricity. When the element undergoes fission, it is capable of producing copious amounts of heat that is used in turning turbines in nuclear reactors. Uranium mining elicits societal concerns with regard to the safety of people who work in these mines, effects of the activities that take place in these mines on the people who live in the immediate neighborhood, and the remedial measures that are supposed to be taken in areas where uranium mining have turned out to be catastrophic.
Some of the economic issues that characterize uranium mining entail availability of labour, the costs incurred in its mining relative to mining substitute energy sources like coal. Uranium mining also raises environmental concerns especially with regard to emission of radiation that is dangerous to human health.
Reference List
EPA. (2000). Economic and Environmental Impact Assessment of Proposed Effluent Limitations Guidelines and Standards for the Coal Mining Industry: Re-mining and Western Alkaline Subcategories. Web.
al_impact.pdf Field, A. (2007). Mining Manpower Crisis. Web.
New Mexico Bureau of Mines and Mineral Resources. (n.d.). Open File Report 77. Web.
OECD. (2001). Radiation Protection: Better Radiation Protection in Modern Society. Geneva: Nuclear Energy Agency.
Roscoe, R. J. Steenland, K. Halperin, W. E. Beaumont, J. J. and Waxweiler, R. J. (1989). Lung cancer Mortality among nonsmoking uranium miners exposed to radon daughters. Journal of the American Medical Association, 262 (5), 629.
World Nuclear Association (2011). What is uranium? How does it work? Web.