Introduction
It is apparent that in every organization, there are various problems which largely differ in terms of how complex they are. In current times, such complications have significantly increased leading to myriad of challenges which are being encountered especially when it comes to organizational management (Checkland, 1999 p.823). It is also imperative to note that such problems have been caused by diverse factors.
According to researchers, the complexity of most organizational problems especially at the level of management is mainly determined by social, cultural, religious, economic and political factors (Eades & Kear, 2006 p. 7). Moreover, empirical surveys have revealed that the nature of such problems determines their scale of influence in an organization.
In addition, it also influences the interconnectedness of various operations in an organization. Therefore, stakeholders in every organization must anticipate the problem and work towards minimizing them bearing in mind that it may not be an easy task to completely eradicate emerging challenges at any given time (Heiser, 2011 par. 4).
On the same note, Kahane (2007 p.37) confirms that problems in organizations are inevitable. In this case, their complexities are determined by the changing of consumers’ tastes and preferences. As such, we may not ignore the fact that change in regulations and operations in an organization also affect the complexity of problems which do arise on a daily basis.
In this case, problems emerge and grow as every individual struggle to adapt to such changes. Evidently, there is need for managers to fully embrace as well as adopt system methodologies that can be used to eliminate problematic situations in organizations (Heiser, 2011 par. 2).
Such methodologies need to be applied effectively in order to be able to track complex situations as they arise in an organization. It is on this ground that this paper examines the system methodologies that can be used to solve problems in King Feisal specialist hospital in Riyadh.
Succinct description of the organization
To begin with, king Faisal Hospital is an organization that has for a long time been able to provide relatively high quality of specialized healthcare services. In addition to this, the organization is also an integrated educational and research centre. For this reason, the organization’s vision statement is meant to make it a world leading centre of excellence and innovation in terms of healthcare service provision.
It is definite that the organization has several values that have been set to achieve the vision. For instance, it is evident that patients’ needs have been prioritized as the main point of focus. Stakeholders of the organization adhere to integrity. This has been achieved by ensuring that ethical principles are followed to the letter. Such ethics include empathy, honesty, equitability, truthfulness and responsibility.
It is against this backdrop that King Faisal specialist hospital has been able to provide patients and society at large, with excellent and high quality services. The organization has several departments that are interconnected to ensure that the mission statement is achieved.
However, it is important to focus on the department of concern. In this case, logistic services department has higher responsibilities in ensuring that patients’ care has been given the top priority. It is imperative to note that the department is accountable to the chief executive director assistant in the organization.
Therefore, this department has larger responsibilities of ensuring that the hospital has adequate supply of healthcare professionals, equipments and pharmaceuticals.
In addition to this it is also the role of the department to order, buy, ship, monitor, replenish, warehouse and distribute such items within the organization. It is thus evident that the department has diversified roles and hence has got some sub-sections that have been created to execute all the roles as mentioned above.
Description of problem situation
It is notable that problems have been inevitable within the organization and particularly in the logistic services department. It is also vivid that management procedures sometimes get to be faulty and this affects the entire operations within the organization (Wyk, 2003 p.45).
For instance, miscommunication between the top managers and the subordinate staff within the organization interferes with certain operations which are pursued by the department. In the long run, this has at times created a high level of displeasure and doubt to both patients and society. Moreover, it has been noted that the top managers are highly dominant when it comes to decision making.
In this case, the organizations operations are highly inclined to them leaving behind the subordinate workers who never get a chance to participate in making decisions (Jackson, 2003 p.12). For this reason, the subordinate workers at times get dissatisfied by some decisions made.
In this case, operational directive being filtered down from the managers are not implemented well and this in turn affect the quality of services provided to the patients. It is evident that to some extent, frictions created from such directives trigger divided loyalty among stakeholders. This has often happened in the department and thus the aftershocks have decimated the performance of the entire organization.
Justification of the choice of the methodologies based on the use of metaphor and the SoSM
As a manager of logistic services in supply cabin management department, I have identified a systematic methodology that has really been helpful in tracking down some of the complexities within the department. As such, the soft system methodology has been chosen as the most appropriate. According to research evidences, Soft Systems Methodology has been perceived to be an appropriate methodology by which people deal with problematic situations in organizations (Jackson, 2003 p.16).
From the experience gained, I perceive the methodology to be effective while dealing with problems related to political social and economic nature. Moreover, soft system methodology remains outstanding amidst other methodologies since it enables one to deal with less technical situations (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.52).
In this case, such methodology has enabled one to become creative, holistic and multi-dimensional in identifying and decimating those complications. Through the use of soft system methodology I’m ascertained to be in a position to solve high social, economic and administrative complications within the organization (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.48).
This methodology is very suitable since it is applicable while solving large or simple complications. From the previous experience, it is fundamental to note that such a methodology stands out as the best approach to all problems regardless of their nature. Research has shown that, Soft System Methodology acts as a brainwave when solving prompt complications in organizations (Checkland, 1999 p.67).
Furthermore, the methodology also acts as a device for consultancy work thereby enhancing teamwork while solving problems. This methodology entails four main basic steps that are undertaken while solving any problem in the organization (Checkland, 1999 p.34). One of the basic steps involves identifying a problem within the organization.
According to researchers, one needs to make some presumptions in regard to the nature of the problem being experienced (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.52). By taking this step, one ensures that you deal with the real complication itself and not the signs. For example, in King Faisal Specialist Hospital one might discern the in-attendance of patients has declined.
In this case, as a manager, one needs to dig deeply to know the possible cause. There are several tools that can be used in identifying the problem. For instance the notable tools include the questioning and root cause analysis methods. By doing this, one is able to uncover the root cause of the problem (Checkland, 1985 p.824).
It is imperative to note that at this step, an individual need to apply several perspectives when looking at the issue of concern. In this case, it is of use to device a problem statement that will act as a guide (Holwell, 2011 p.774). Moreover, it also acts as a checklist through which you look at several elements that could possibly be the real cause of the problem.
The other basic step involves understanding the complexity of the problem. In most cases, the problems faced in this organization vary in scale. In this case, some are simple while others are complex. Notably, simple problems need not to go through the formal process to be eliminated (Checkland, 1985 p.829). For this reason, only the complex issues are dealt with formally and particularly because they have webs if interrelated issues.
For this reason, soft system methodology has been referred to as a generic methodology. The appropriateness of the methodology in solving fuzzy problem in the organization is a clear justification that this approach should be applied to a larger extent in solving problems (Holwell, 2011 p.780).
This is due to the fact that while using the methodology, people are viewed as active subject and this allow collective participation when solving a problem. As a manager I have witnessed the assumption since the methodology purposefully allows top managers to engage workers in problem-solving activities.
For this reason this makes it easy to come up with solutions for existing problems especially where objectives are unclear (Jackson, 2003 p.22). It is thus beyond doubt to claim that soft system methodology is qualitative technique that is applicable in solving problems (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.105).
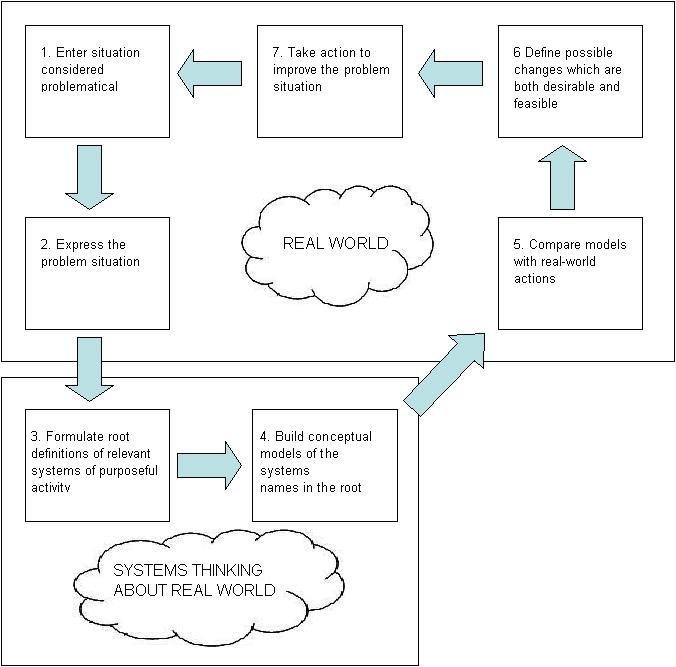
A clear description of the use in practice of the system methodology
Analysts confirm that while practicing the methodology, one needs to carefully identify some of the basic characteristics of the environment through which the problem has emerged (Gregory, 1991 p.12). For this case, it is important to understand and analyze the problems facing King Faisal Specialist Hospital. After identifying them, one needs to assess whether they are economical, social or cultural based.
This idea of defining the problem helps in simulating objectives of study (Patching, 1990 p.31)). For instance, in the logistic service department I identified a problem of miscommunication between top managers and workers. Using this methodology, I will be able to have a conceptual model that will help one to structure questions such as why, and how (Scarl, 2003 p.27).
Such simulation helps one to arrive to objectives that guide one to proceed to the next step of solving the problem. At this juncture, the approach paves way and eliminates challenges that might result due to lack of clear objectives and ill-definition of problems.
Once the problematic situation has been expressed, the next step is to identify relevant and purposeful activities that need to be done to put the system in place (Checkland, 1985 p.825). For instance, identifying activities should be undertaken in King Faisal Specialist Hospital in order to eliminate miss-communication and decision related problems.
Once the activities have been defined, it is advisable to have conceptual models through which the problem is suppressed before the actual process is over (Jackson, 2003 p.53). This practice prevents further complications that might prevent the project from being full implemented (Jackson, 2003 p.30). Finally, actions are taken to improve the situation and appropriate changes are made in the organization.
Critique of the methodology you have applied and suggestion of an alternative methodology that might complement the applied methodology
Irrespective of the advantages of soft system methodology, research has shown that its general description is highly diverse thus taking a lot of time to come up with a viable solution to any problem (Scarl, 2003 p.70). Though methodology’s descriptions are essential in ensuring greater understanding of a problematic situation, it becomes difficult for it to address unstructured complications.
It is also definite that this methodology is not suitable to deal with highly complicated problems. Instead, the methodology is only applicable to problems that are only put in a detailed order. However, analysts confirm that there is no single methodology that is best appropriate in solving problems (Checkland, 1985 p. 823).
For this reason, it is always challenging to apply soft system methodology to problems that are ill-defined. Moreover, research done reveals that the method might be tricky to used especially when there lack fine details of the contemporary working systems (Gregory, 1991 p.12).
From my own perspective, it can turn problematic when applying such a methodology on certain systems in the organization without evaluating the nature of complications. The other critique of this methodology is that it is multifaceted. For this reason, it becomes complicated particularly when there emerge myriad aspects to be considered while solving a problem.
To some extent, one might get stuck due to the presence of multi-dimensional objectives (Gregory, 1991 p.14). This implies that managers need to set the objectives clear to avoid confusion from multidimensional solutions identified. Besides this, the methodology have definite steps that are followed ton ensure that solutions to problems are obtained.
On the other hand, application of the methodology in every situation may become monotonous and to some extent inappropriate to problems with different characteristics (Scarl, 2003 p.37). It is also possible to generate myriad of results when this type of methodology is used bearing in mind that diverse views are incorporated in the problem situation.
For this reason, the problem might merely fade away as the result of such consensus (Jackson, 2003 p.36). There is also a higher likelihood of resorting to unstructured solutions. For instance, unique organizational roles might be adopted. While such a move may be applauded at some point, it may lack the required efficiency and effectiveness.
There is also a possibility that the problem might become structured in the process though it requires high and extensive strategies that might consume a lot of time before a consensus is made. With that said, research has shown that there is a need to have several methodologies reinforcing each other while solving problematic situations (Gregory, 1991 p.22).
In addition, analysts have argued that there are limited number of methodologies that can be suitably applied and thus the available ones should be made use of with adequate experience and familiarity to achieve good results (Scarl, 2003 p.77). Needless to say, it is made easier when one chooses an alternative methodology which is relatively compatible with the nature of the problem situation.
For my case, soft system methodology should be reinforced with a more comprehensive methodology such as simplex or appreciative inquiry. Simplex is a methodology that has eight definite stages (Holwell, 2011 p.784). These stages involve finding the problem, facts, problem definition, selection and evaluations, planning, selling and acting the idea.
It is apparent that this methodology builds on the earlier discussed methodology (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.99). However, it is more applicable to hard problematic situations and thus emerges as a suitable alternative for SSM (McKenzie & Kotecki, 2011 p.2).
A combination of the two methodologies stands a position for one to understand the problems better and thus build a team that will act against the existing problems (Ketola, & Kathy, 2003 p.44). Nevertheless, analysts lament that even with a combination of the set methodologies the task may not always be that clear-cut (Rosenhead & Mingers, 2000 p.102).
For this reason, there is need for organizational managers to choose appropriate methodologies that are likely to merit the situation. From their counter-argument, one needs to understand that all problematic situations are unique and thus it is essential to apply all experience gained to decimate the limitations associated with this type of methodology (Jackson, 2003 p.56).
References
Checkland, P. 1985. Achieving ‘Desirable and Feasible’ Change: An Application of Soft Systems Methodology. The Journal of the Operational Research Society. 36, 821 – 831.
Checkland, P.1999. Systems Thinking, Systems Practice: a 30 year retrospective. Chichester: Wiley Publishing, Inc.
Eades, M. & Kear, E. 2006. The solution: Centric Organization. Canada: McGraw-Hill Companies.
Gregory, F. 1991. Causation and Soft Systems Models. Systemist. 13 (3), 105-112.
Heiser, R. 2011. Problem Solving. Web.
Holwell, S. 2011. Soft Systems Methodology: Other Voices 13(6), 773-797.
Jackson, C. 2003. Systems Thinking: Creative Holism for Managers. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Kahane, A. 2007. Solving tough problems: an open way of talking Listening and Creating New Realities. California: Barrett-Koehler Publisher, Inc.
Ketola, J. &Kathy, R. 2003. Correct! Prevent! Improve!: Driving Improvement Through Problem Solving and Corrective and Preventive Action. Milwaukee: ASQ Quality Press.
McKenzie, R. & Kotecki, E. 2011. An Introduction to Community Health. Toronto: Jones& Barrett.
Mingers, J. &Taylor, S. 1992. The Use of Soft Systems Methodology in Practice, The Journal of the Operational Research Society. 43(4), 321-332.
Patching, D. 1990. Practical soft systems analysis. London: Pitman, Inc.
Rosenhead, J. & Mingers J. 2000. Rational Analysis for a Problematic World Revisited. Chichester: Wiley Publishing, Inc.
Scarl, D. 2003. How to Solve Problems: For Success in Freshman Physics, Engineering and Beyond. New York: Dosoris Press.
Wyk, V. 2003. A Systems Approach To social And Organizational Planning. Toronto: Trafford Publishing , Inc.