Almost all countries have experienced an increase in an urban population in recent times. A survey conducted by the United Nations (UN) shows that half of the world’s total population lives in urban centers. The current 50% is far much above the population in cities a century ago. In the past century, only 10% of the total population occupied urban areas (Hays, 2000, p. 18). According to the latest trend, the urban population is expected to shoot up to almost 75% by the year 2050. The influx of people in cities has put a lot of pressure on the available housing units. These figures are very worrying in case city planners don’t take drastic actions to solve the issue. The high population density in cities leads to high-density housing that has very serious drawbacks. A high population in the cities means that there will be a shortage in energy and other social amenities. The available green space will be a thing of the past because all the gardens will be used in constructing residential houses. This has serious environmental and social implications for the city. City designers and planners have a great challenge of ensuring that the designs are in line with the current trend in population growth. All the cities in the world face this challenge and the situation is bound to become if nothing is done to deal with the challenge. This paper will highlight the urban-ism theory and how the theory has affected modern city planning.
The problems associated with high population densities in cities are many. To begin with, the new homes are relatively small because of the ever-diminishing space in urban centers. These crowded housing units have poor standards of sound insulation leading to very noisy neighborhoods (Parker, 2004, p. 45). The crowded housing units leave very little land for development purposes. The high-density housing units do not meet most building standards and this risks the life of the inhabitants. The small housing units do not meet insulation standards leaving the residents with no insulation from the noisy city. Some cities are very crowded to the extent where the infrastructure and other social amenities are seriously strained. High-density cities have limited land for setting up new industries to meet the ever-increasing demand for jobs. High-density housing has got a lot of limitations compared to benefits and this necessitates quick action to deal with this problem before a disaster happens (Parker, 2004, p. 78). The energy demand has also been increasing as the population of people increases. Modern architectural designs that consider vertical urbanism incorporate energy production systems in the design for them to be self-sufficient in terms of energy requirements. Tall buildings consume a lot of energy in their operations and this calls for designers to develop alternati8ve means of energy for the sustainability of skyscrapers.
The ever-growing population automatically leads to an escalation in inner-city migration making it impossible to eliminate tall buildings in our cities. The theory of vertical urbanism was developed to try and demonstrate why skyscrapers are the probable solution to the ever-increasing urban population (Hays, 2000, p. 30). The theory was meant to try and solve those fundamental problems that come with tall buildings. The theory emphasizes the idea of the vertical extension of cities. The diversity found on the ground is extended to the sky like retail shops, offices, residential houses and sky gardens all in one tower. The sky gardens can also be incorporated with bars and restaurants (Hays, 2000, p. 112). The tall buildings should also have open spaces to promote social interaction and other well-being needs. The cost of constructing skyscrapers is very high because of the strict building standards that have to be observed. Tall buildings need features like lifts, ramps and other sophisticated safety facilities. Vertical urbanism advocates for the conservation of all the available natural resources. Some designs have maximized on this fact by utilizing all the available resources for the self-sustainability of the buildings. Most of the skyscrapers have natural ventilation as an energy-saving strategy. Modern designs have biogas plants incorporated in the system to help in producing alternative means of energy. Alternative energy production helps in meeting the high demand for energy by skyscrapers.
Those constructing tall buildings should consider minimizing wind pressure. Reduced wind pressure means that there are fewer loads on the building making it structurally strong (Hays, 2000, p. 115). Profiling should be done on the building to make it structurally sound. The permeability between tall buildings is very important for accessibility. The main objectives of vertical urbanism are to maximize land values, safeguard the sprawling nature of some cities and at the same time reduce ground penetration. Tall buildings help in densifying city centers and at the same time making preservation of Greenfield sites very possible (Dobbins, 2009, p. 29). Although the cost of tall building is a bit high, it is worth it considering the environmental benefits. Environmental technologies are used to ensure all the buildings have minimal damage to the environment. The materials used for constructing skyscrapers have to be certified because of the amount of load the skyscrapers carry. The building technologies have to incorporate both architectural principles and environmental conservation strategies for them to meet the required standards of vertical urbanism.
Vertical land use is one of the major aspects of the vertical urbanism theory. The high population density in cities puts a lot of pressure on the already limited pieces of land. The vertical urbanism theory suggests maximum utilization of the space in the sky by investing in tall buildings. If some of the social facilities on the ground can be transferred to the sky then there will be enough space on the ground that eventually minimizes the problem of overcrowding (Yeang, 2002, p. 74). The ratio of open space to built up area should be considerable enough to provide enough space for social interaction and movement. The same ratio applies in the sky and the major challenge is in quantifying movements. The pedestrian flow in tall buildings should be properly quantified for the sky scrapers to completely fulfill their purpose (O’Connor, 1983, p.56). Pavements, streets and parks should be considered by city planners as part of the public realm. The city should provide enough space for the public.
Vertical urbanism aims to bring the ground feeling to the sky. The various architectural schemes put in place aims at creating enough space when walking through tall buildings that is a representative of the space on the ground. The ratio of open space should be legislated to ensure all developers meet the conditions before constructing tall buildings (Mayhew, 2009, p.123). Effective utilization of the vertical space helps a great deal in reducing ground congestion and improves the wellbeing of city residents. The central theme of tall buildings should be space and not just a stand alone object. The typology of tall buildings should be a clear demonstration of vertical urbanism. The mixed use of tall buildings is the only way vertical space can be effectively utilized. A new tall building architecture incorporates desperate vertical use of land (Evans, 2004, p. 54). The buildings must have ramps top connect the top floors of the building to shops and other retail facilities.
The increasing population has actually left less open space for the natural environment. The environmental impact of urbanity calls for green landscape architecture for both commercial and residential buildings. There is a great need for landscape strategies that promote an increase in green space in the cities. Sustainable landscaping emphasizes the availability of open spaces and vegetation. Vertical landscaping aims at integrating architecture and nature without undermining either of the two (Evans, 2004, p. 113). A vertical landscape strategy has come up with a wall system that sustains all kinds of vegetation regardless of their thriving conditions. The vegetation becomes an integral part of the wall and not just hanging garden. There should be sufficient open space on buildings with green gardens for recreation purposes. The rooftop gardens provide a good environment for social interaction (Kibert, 2008, p. 27). The living walls have got a lot of benefits to the building. To begin with, the vegetation gives the building a good scenic view that has a good appeal to the eye. The wall insulates the building from the usual city noise. The vegetation is also a source of fresh air that facilitates the natural ventilation system in the building. The vegetation has to be well maintained by frequent watering.
Vertical urbanism also puts into consideration the issue of neighborhoods. Since the main objective of vertical urbanism is to replicate all the ground elements on the ground, the issue of neighborhood is not an exemption. The tall residential buildings should provide a conducive atmosphere that allows all the residents to feel part of the community (Kibert, 2008, p.72). The availability of retail facilities and other social amenities makes the sky a good neighborhood just like the ground. Safety facilities like evacuation channels should be properly laid out to ensure safety of residents incase of any danger. The open spaces allow easy movement of people through the buildings without overcrowding. All the qualities of a good neighborhood should be comprehensively reflected in vertical urbanism. The mixed skyscrapers are very tricky to design of the complex requirements that they are supposed to meet. It is always a challenge to meet all the requirements of a good neighborhood in the sky compared to the ground.
The Singapore Editt Tower in Singapore and the Bahrain World Trade Centre are perfect examples of buildings that portray vertical landscaping strategies. The Editt Tower design emphasizes biodiversity and local eco-system rehabilitation. The Editt tower is 26-storey tall specifically to promote vertical land use. Photovoltaic panels and a plant that generates biogas are incorporated in the design as alternative sources of energy. Half of the wall surface is covered with a living wall that offers insulation and gives the building a good scenic look. The designers showcase one of the best examples of vertical landscaping in the world with very beautiful walls of colorful plants. The design of this building is based on ecological factors and environmental conservation (Kibert, 2008, p. 118). The building was designed by TR Hamzah and Yeang. The building is one of the best examples of vertical urbanism in the world. The tower is designed to allow natural ventilation in all the rooms. The design includes publicly accessible ramps that allow a connection between the top floors of the building and the available shops on the ground (Kibert, 2008, p. 59). This kind of design promotes a good neighborhood. There are sufficient open spaces at the top of the building that allow natural ventilation. The open spaces have designed into sky gardens fro relaxation. There is enough public space between the Editt tower and other buildings that meets the public realm conditions.
The walls and floors of the building are designed in such a way that they can be removed incase of any future modifications. Since the city is widely known for heavy downpours, the design has incorporated a rainwater collection system for harvesting rain water. The water is channeled for irrigation and flushing of toilets. This system makes the building to be self-sufficient in terms of water supply. The photovoltaic panels generate almost 40% of the total energy consumption with future plans being put in place to put up a biogas plant for production of extra energy from the sewage system. Most of the materials to be used to construct the tower will be recyclable ones with each floor having a centre of collecting recyclable materials (Kibert, 2008, p. 61).
Bahrain World Trade Centre building is 50-storey high with the concept design incorporating a renewable energy production project that utilizes the onshore breeze from the gulf. The tower has a total of three wind turbines. The twin towers are 240 meters high and follow the vertical land use policy. The building doubles as a hotel and a shopping mall. This calls for organized and adequate public real facilities. The basement of the building is a shopping mall that accommodates a variety of businesses with a spacious car park for the public. The wind turbines are approximately 25 meters long (Evans, 2004, p. 32). The concept design was inspired by the traditional Arabic design. The energy production system is one of the major successes of this design with the wind energy plant supplying almost 15 % of the total energy consumption in the building. The location of the building is very strategic and provides a conducive environment for tourists who visit the city. The cool breeze from the sea provides natural ventilation to the building that saves the cost of using the artificial ventilation. The design has got good environmental considerations because of the various measures put in place. Carbon emissions to the atmosphere are very dangerous to the survival of human beings and other living species and this call for special consideration when designing.
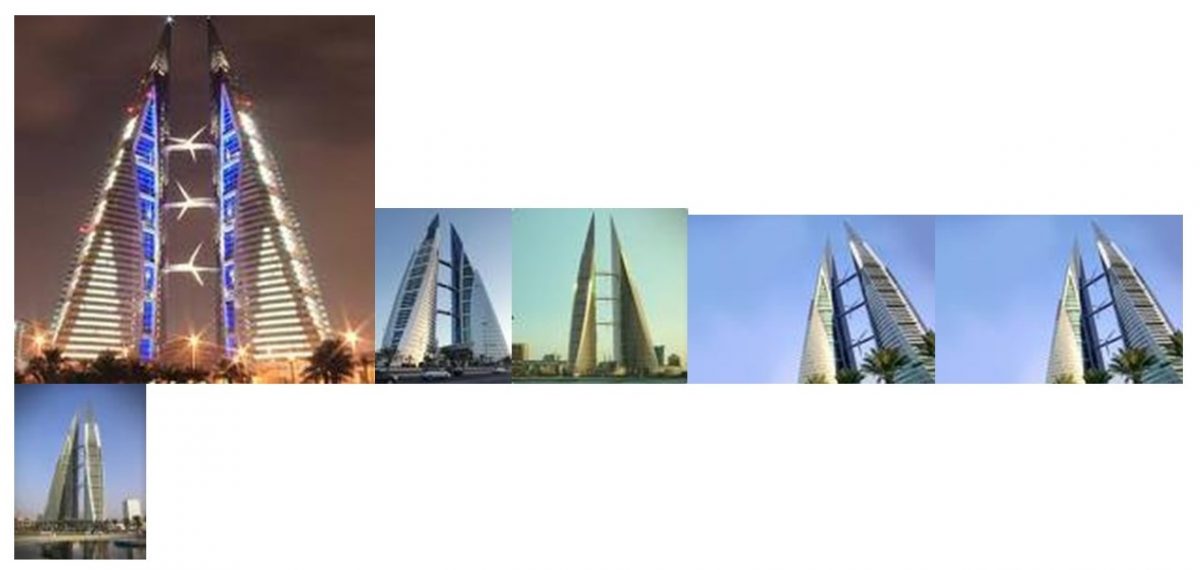

The wind energy project has been of great help to the general operations in the Tower. Being a mixed tower, the electricity consumption is very high because of the businesses and hotel facilities in the building. The thought of incorporating the renewable energy project in the design was inspired by the vertical urbanism theory that emphasizes energy conservation and production for sustainability of high density living. The building has got strategic open spaces that benefit immensely from the gulf breeze. The building also has enough water supplies because of its nearness to the sea. The open roof top gardens and balconies provide a perfect view of the city and the sea especially at night (Evans, 2004, p. 67). The 50-storey design put into consideration the large amount of space needed to accommodate a shopping mall and a hotel. The building also has a good vertical landscape that has helped a great deal in reducing the carbon emissions to the atmosphere. The vertical landscape provides a shade for car parks. Like other designs that advocate for vertical urbanism, the Bahrain World Trade Centre has got a biogas production plant and other recycling systems that ensure that there is minimal waste. The use of biogas energy ensures that there is less carbon emission to the atmosphere (Evans, 2004, p. 67). The building has got numerous ramps and various overhead connections as facilities for the public realm. The public space facilitates smooth a pedestrian flow in and out of the building. The building has got high traffic due to the large number of people coming in for shopping and hotel services. This calls for elaborate safety mechanism in the neighborhood to be put in place because the high chances of emergency cases.
The Bahrain World Trade Center architecture is a combination of the traditional Arabic design and the contemporary vertical urbanism design. Its design clearly fits its location. The building is highly profiled for it to withstand the pressure brought about by the sea breeze. The buildings has an almost pyramid shape that makes it structurally strong. This gives the building a strong base that makes it strong and a curving top as a profiling strategy. The design makes good use of the vertical space. The building has helped in reducing congestion in the city because hotel and accommodation facilities together with retail services can now be found in one building (Yeang, 2002, p. 91). This has left enough open space for the public. The public real facilities and other social centers in the building represent a good urban neighborhood.
In conclusion, the high population density in cities has forced many city planners to apply the vertical urbanism theory in solving the problem of congestion in cities. Vertical urbanism advocates for tall buildings with the aim of utilizing the unlimited space in the sky to offer residential, recreational, office and retail facilities all in one building. Vertical space utilization helps in environmental conservation. Modern architecture employs vertical landscaping that combines architecture and vegetation conservation. Tall buildings must have adequate open spaces to facilitate good social interaction and movement through buildings without overcrowding. The ratio of built up space to open space in skyscrapers should be a representation of the ground ratio. With a continued increase in urban population, tall building architecture is becoming popular allover the world. The Editt tower in Singapore and the Bahrain World Trade Centre are good examples of buildings that have observed the theory of vertical urbanism in their designs. The two buildings have elaborate vertical landscaping with alternative energy production facilities incorporated in their designs. The buildings represent a modern skyscraper that is flexible to any future modification. Good designers design for the future and these two buildings represent that. The modern architectural design put much emphasis on the reinvention of the skyscraper so it that it meets environmental conservation standards. Vertical urbanism is actually the only solution to the high density living in the cities (Yeang, 2002, p. 97). Cities continue to attract a lot of visitors and planners have a huge responsibility of ensuring that all the people are well accommodated without environmental degradation and a strain on the available resources. Vertical landscaping and open spaces has helped in conserving the vegetation by incorporating vegetation in the walls of buildings. The green space is created by this strategy making the city look beautiful despite the large population. Vertical urbanism has facilitated social interaction by emphasizing the setting up sky gardens in all skyscrapers. The major challenge facing vertical urbanism is the creation of good neighborhoods in the sky. Designers are trying their level best to ensure that there is a good neighborhood in the sky.
References
Dobbins, M., 2009. Urban design and people. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Evans, A. W., 2004. Economics and land use planning. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Hays, K. M., 2000. Architecture theory since 1968. New York, NY: MIT Press.
Kibert, C. J., 2008. Sustainable construction: Area building design and delivery. New York, NY: John Wiley and Sons.
Mayhew, S., 2009. A dictionary of Geography. New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
O’Connor, R. A., 1983. A theory of Southeast Asian urbanism. New York, NY: Routledge.
Parker, S., 2004. Urban theory and urban experience: Encountering the city. New York, NY: Routledge.
Yeang, K., 2002. Reinventing the skyscraper: A vertical theory of urban design. New York, NY: Academy Press.