Introduction
Nadler and Tushman (1980) developed a model of change describing how the components of an organization interact with each other. In essence, they established that there are several key components of an organization including, individuals, tasks, and organizational processes. In addition, it was found that these components affect each other so that a change in one of the aspects affects another one.
Importantly, it is evident that the congruence model discuss the transformation of inputs into the outputs. Inputs could include factors such as competition, finances, and human resources while the outputs include the products as well as the services provided by the organization.
This paper will focus on three critical aspects of this congruence models while analyzing the Whole Food Market as an organization. These aspects include outputs at organizational level, the groups identified by the organization during its operations, and key individual functions of the people who might be involved in the process of production.
Outputs at Organizational Level
In regard to the outputs at the organizational level, Naldler and Tushman (1980) suggested that the products and services provided by the company are the most pertinent aspects. Essentially, Whole Food Market produces food for human consumption in various geographical locations that include United Kingdom and USA among others.
In addition, the company sought to produce body care products such as lotions following the rising demand for these products in the modern society. When it comes to the classification of these products, there are three pertinent categories that include organic foods, beverages, as well as body care products in general.
The company understands that food should not only sustain physical satisfaction and tastes, but also the health of the consumers. As a result, the management sought to produce organic food since they reduce the risk of ill health among the consumers. This reduction is facilitated by the methods used during the production of the organic foods.
For example, organic farmers do not use the pesticides which have been proven to contain harmful chemical that can be taken up by the body. Some of these organic foods include frozen products, pantry staples, snacks, and supplements among others. When it comes to beverages, there are various products, including organic orange juice, rice milk, and coffee among others.
The body care products also form a crucial part of the products provided to the customers by the Whole Food Market. These products include lotions, shampoo, conditioners, and soaps used for cleaning as well as bathing.
The performance of these products is presented in terms of financial profitability in order to determine their solvency. However, it is evident that the company does not present the respective profits for each of the products.
Instead, it provides the overall profitability margins for the company. Although the margins are generalized, it is obvious that the recorded profits accrue from the sales of the foods, beverages and body care products.
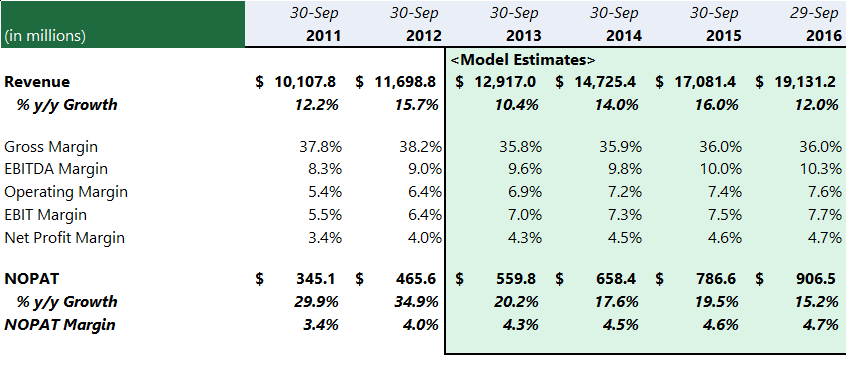
Figure 1: The Whole Food Market returns (Pollan, 2008).
From the image presented, it is evident that the pertinent aspects used to determine the performance of the products and services include gross, EBIT, operation, EBITDA and net profit margins. Further, the company makes estimates regarding the expected profits in the subsequent years using the data obtained for the previous years.
Outputs Group Level
Suppliers
In accordance to the demand for their products, Whole Food Market has identified suppliers who provide them with raw material for the production of beverages, foods and body care products. Understandably, food and beverages are the most crucial part of their production process. As a result, they have identified local farmers who provide the raw foods that are then used for the production.
When identifying the farmers, they consider the needs of the consumers’ needs in order to determine the appropriate suppliers. In this regard, the company has identified the organic farmers since they need to provide healthy food to the consumers (Mackey & Sisodia, 2013). In essence, the selection of these suppliers is based on whether the involved farmers can provide the needed quality in line with sustainable agriculture.
Employees
In relation to employees, there are both the managerial and technical employees who have been hired to oversee the running of the company and provide the required skills of production respectively. The managers have a responsibility to offer the required leadership and ensuring order in the organization.
In addition, they are mandated to recruit the technical employees whereby they are expected to ensure that each of them has the required skills in relation to the field of employment. As a result, the company is capable of maintaining high standard of production and desirable quality of the foods. The performance of these managers is measured according to the performance of their departments.
For example, the HR managers are evaluated in accordance to how they coordinate the workers and tap human skills. Failure to incorporate the necessary human resource is termed as underperformance.
For the technical employees, their performance is evaluated in accordance to how they adhere to the regulation and standards set by the management. Accordingly, employees who do not abide by these standards and regulations are underperformers.
Geographical Regions
The company recognizes the geographical groups by operating in twelve different locations. In this regard, each of the regions has a president, the administrative team and the people mandated to oversee the store. These geographical groups have been set to decentralize the services and make sure that the company is capable of reaching as many people as possible and make good financial profits.
Key Individual Functions
There are various individual functions that are identified in the entire organizational setup. The roles of the president are some of the most conspicuous individual functions within the organization’s structure.
First, the CEO has individual functions since he is the founder of the company. He offers the leadership of the entire company for all the geographical regions in which the company operates. All the presidents report to the chief executive officer regarding the performance of their respective areas. In essence, he is an executive player mandated to make critical decisions such as investments.
Second, there are presidents appointed for each of the geographical regions, and mandated to oversee the setting of the annual budget, authorize expenditure, and coordinate the administrative team.
The individual function of the president can be considered as a crucial role since the entire chain of command executes the orders and decisions made by this office. In addition, they are the mediators between the executive arms of the company and the employees in the lower levels of operation.
Chief Operating officer is another individual function which is set to oversee the daily processes of the company. These operations include the supply of raw materials and distribution among other. The officer is crucial in the chain of command due to the mandate of reporting to the president regarding any unfolding within the organizational processes of production.
The organization has incorporated a chief financial officer who advises the president concerning critical decisions. In this regard, the financial officer has the professional knowledge that enables to determine the financial implication of decisions. As a result, the president and CEO must consult with the officer before taking any step so as to evaluate the effects of their decisions before implementation.
Another individual function found within the company is executed by the Growth and Development officer. The officer is mandated to develop new products and come up with new ways of manufacturing them.
In this regard, the officer must initiate research in order to determine the changing needs to the consumers and hence provide the required products. This undertaking ensures that the company expands the market while maintaining the original customers.
Conclusion in Terms of Interacting Outputs
The individual functions of the CEO, presidents, and the various officers revolve around monitoring the operation of the mentioned groups. As a result, it is evident that there is congruence between the individual functions and the groups.
In turn, the groups provide the required raw materials and also offer the needed skills for production of the foods and beverage. Owing to the regulations and standards set by the executive arms, the groups are capable of maintaining the quality of the products. Consequently, the profitability of the products is ensured since the customers get the needed quality.
References
Mackey, J., & Sisodia, R. (2013). Conscious capitalism: liberating the heroic spirit of business. Boston, Mass.: Harvard Business Review Press.
Nadler, D., & Tushman, M. (1980). A Model for Diagnosing Organizational Behavior. Organizational Dynamics, 9(2), 35-51.
Pollan, M. (2008). In defense of Whole Food Market: an eater’s manifesto. New York: Penguin Press.