Vaccines are regarded as one of the twentieth century’s most significant public health accomplishments. Vaccination aims to produce a protective immune reaction against a specific pathogen without the danger of contracting the illness and its potential sequelae. The capacity of governments to convey the advantages of vaccination and administer the vaccinations in a secure and convenient way is essential for preserving public confidence in vaccines. The power of the government should be reassessed regarding its ability to force its’ citizens to receive medication.
It should be a personal decision to receive medications and treatments. Shared decision-making is a collective approach in which caregivers and patients pick tests, treatments, or management based on clinical evidence and patient choices. It is particularly crucial to promote patient involvement in regard to medications since the patient must comprehend, approve, and administer the therapy for it to be effective. Physicians foster patient autonomy when involved in talks about their treatment (Olejarczyk and Young). Patients expect their doctors to interpret the information and provide suggestions based on the medical facts and objectives. Clients do not want their doctors to make decisions for them, though. The most prevalent reason why people forgo suggested therapy is a lack of knowledge. In these situations, a physician’s ethical role is to assure that patients fully comprehend what they are refusing. Physicians must respect competent patients’ right to refuse suggested therapies.
A number of medication-related concerns remain unknown to patients and the wider population. The findings of over half of the medical studies conducted on the drugs used today have never been published (Lane). Most individuals believe that all officially authorized, prescribed, and marketed medications are effective and safe. With outcomes from merely half of the experiments, policymakers lack the necessary data to make intelligent decisions. In the 1980s, a medication named lorcainide was studied in clinical tests in the United States and the United Kingdom (Lane). Patients who received the medicine were much more inclined to die during the experiment than those who did not. These findings were released more than a decade after the company’s release of the drug. During this period, it is believed that over 100,000 individuals died after taking the ineffective medicine.
Additionally, some researchers are investigating the outcomes that are published and those that are not. Unsurprisingly, more data from studies demonstrating a medicine’s efficacy are published than those demonstrating its ineffectiveness. In fact, positive-result studies are twice as probable as negative-result trials to have had their results published. In addition to the issue of insufficient information, the details that the public always get is often skewed.
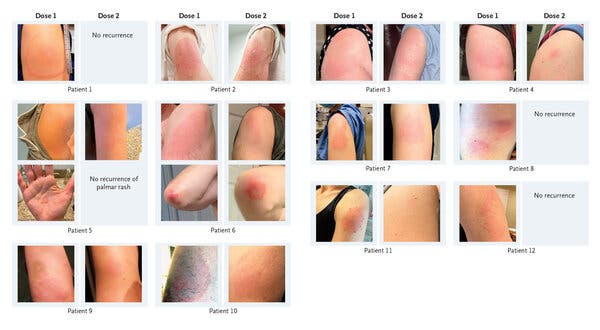
Several medications and vaccines have risks and may affect individuals differently. No vaccination provides 100 percent immunity, and vaccine effectiveness, or how effectively a vaccine prevents disease in vaccinated individuals, varies by vaccine type. Vaccines and drugs can have a risk of unpleasant responses, with redness and pain at the site of injection or fever and hypersensitivity responses being the most prevalent (Wongtaweepkij et al. 1141). Epilepsy and the neurologic disorder Guillain-Barre are also recorded, although they are very uncommon and occur significantly less often than complications and fatalities from vaccine-preventable infections.
Most patients have limited knowledge regarding the side effects of the medications or vaccines administered to them. Although most patients are aware of the indications and possible advantages of medications, they are often less educated about their hazards. Educating patients on the advantages and hazards of pharmaceuticals might increase their understanding of medications and their safe usage and help them achieve a balance between benefit and risk perception (Wongtaweepkij et al. 1141). Previous research has indicated that information about the safe utilization of medicine favorably influences attitudes and behaviors about medication.
People have to be saved from themselves due to lack of knowledge regarding the medications and vaccines administered to them. The public needs to be aware through campaigns to increase knowledge of medications and vaccines. It is common to employ mass media campaigns to introduce huge numbers of people to messages via the normal usage of current media, like radio, television, and newspapers. Vast numbers are susceptible to favorable or negative changes in their health-related behaviors due to media campaigns. In addition, it is vital to recruit volunteers and professionals to go to areas with low vaccination numbers to speak with them about immunizations and clarify their concerns about vaccines.
The science of developing vaccines and other treatments cannot be effective if people do not have sufficient faith in it to get immunized. The creation of COVID vaccinations has been lauded as a spectacular scientific success. There is universal agreement among government officials and scientific professionals that mass immunization is the key to reducing the disease’s mortality rate. However, more than a year following the licensing of the first COVID–19 vaccination, a considerable fraction of the populace eligible for the vaccine has opted not to do so (Chevallier et al. 331). One of the primary goals was to determine the relationship between vaccination acceptance or reluctance and confidence in organizations that would play a crucial role in persuading the public to be immunized.
Faith in science, notably the capacity of biomedical science to generate an effective and safe vaccine, has the greatest influence on the choice to get immunized. According to the researchers, the confidence gap in science has numerous plausible causes. Scientific literacy is essential since it is susceptible to conspiracy beliefs and misrepresentations due to its reliance on time, its propensity to produce various results, and the many methodological and scope restrictions of scientific investigations. The science-based policy is also susceptible to politicization, and there is a long-standing distrust of science in many communities owing to previous abuses.
Vaccines may aid in the prevention of some illnesses by simulating an infection. This form of simulated illness trains the immune system to combat future infections. Occasionally, the simulated illness might induce modest side effects, like fever after receiving a vaccination. Such mild symptoms are typical and should be anticipated as the immune system develops. Once the body has been immunized, B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes will recognize the antigen and defend against the illness. Nevertheless, it normally takes a couple of weeks for the body to create B- and T- lymphocytes after immunization (Centers for Disease Control and Prevention). Since the immunization has not had sufficient time to give protection, it is conceivable that an individual infected before or after immunization might show symptoms and get the illness. Notably, Vaccines are the best and safest method of disease protection, yet no vaccination is perfect. Vaccinated individuals may still get a disease but are less prone to becoming critically sick.
Vaccination acceptability remains high in most industrialized nations, but vaccine phobia has increased considerably over the last few years. Thus, this concern has led to dramatically higher rates of vaccination rejection in certain communities, linked with increases in sickness and mortality from vaccine-preventable illnesses and substantial health care and societal expenditures. Declining vaccination rates promote disease transmission and mortality from vaccine-preventable illnesses, not simply among people who have chosen not to get immunized. Vaccine rejection costs billions of money in health care expenses and public health expenditures to combat disease outbreaks (Edward-Isaac Dovere). Knowledge of the proof of vaccine safety has little effect on the dread of vaccines. In most regions where vaccination is well-established, immunization rates remain high. In many areas, however, vaccination rates have fallen below the levels required to sustain herd immunity, especially among youngsters.
The power of the government should be reassessed regarding its ability to force its’ citizens to receive medication. Vaccines are recognized as one of the most important public health achievements of the 20th century. Maintaining public trust in vaccines requires governments to communicate the benefits of vaccination and provide immunizations safely and effectively. Vaccines work to prevent disease by creating an environment in the body that is similar to that of an infection. The immune system is strengthened via this kind of simulated disease to better fight off future illnesses. Occasionally, the simulation of the sickness may result in mild adverse effects. No coercion should be involved in the choice to undergo drugs and therapies. Physicians must respect the right of competent patients to decline recommended treatments. Drugs and immunizations have dangers and might have varying effects on people. Vaccines and medications may cause adverse reactions, such as redness and soreness at the injection site. Since most patients are unaware of the adverse effects of their drugs, they must be informed.
Works Cited
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. “Understanding how vaccines work.”Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2022.
Chevallier, Coralie, Anne-Sophie Hacquin, and Hugo Mercier. “COVID-19 vaccine hesitancy: Shortening the last mile.” Trends in Cognitive Sciences, vol. 25, no. 5, 2021, pp. 331-333. doi:10.1016/j.tics.2021.02.002.
Edward-Isaac Dovere. “The Atlantic.”The Atlantic, 2021.
Grady, Denise. “A few people report delayed skin reactions to the Covid vaccine.”The New York Times, 2022.
Lane, Síle. “The Hidden Truth about Our Prescription Medications.”Ideas.ted.com, 2017.
Olejarczyk, Jacob P., and Michael Young. “Patient Rights and Ethics.”Nih.gov, StatPearls Publishing, 2022.
Wongtaweepkij, Kamonphat, et al. “Thai patients’ drug safety knowledge and perceptions relating to different forms of written medicine information: A comparative study.” Patient Preference and Adherence vol. 16, 2022, pp. 1141-1152. doi:10.2147/PPA.S361447.