Abstract
When customers in a business firm are loyal, they make the organization to attain uninterrupted flow of income and relatively lower costs of production due to favorable economies of scale. The improved income is usually as a result of increase in production whereas the cost of production is cut down due to the decrease in promotional expenses.
The whole process is triggered by high customer loyalty and optimal purchasing intentions which culminate into increase in the firm’s profits. It is important to note that customer loyalty does not grow by itself. As a matter of fact, it is a product of quality marketing strategies in today’s competitive markets.
For a company to achieve customer loyalty, it must create an exemplary value for all its consistent and potential new customers. This dissertation proposal paper seeks to examine how consumer based value at Michelin has succeeded in marketing in addition to creating a loyal customer relations at the Chinese market. A comprehensive framework that leads to desirable results has been formulated.
Based on ground findings and reliable literature reviews, the customer perceived firm value can be investigated and evaluated. This research study will conclude with solid findings which can be evaluated using specified standards rather than the common monetary scales.
Underlying principle
Studies reveal that customer loyalty is one of the basic elements which forms a stable foundation for business organizations to be operated successfully (Bloemer & Odekerken-Schröder 2002, p. 70). Indeed, the loyalty of customers plays a critical function in ensuring the profitability of a business.
Loyal customers are always ready to give a company a true and sincere feedback, make valid recommendations to the company, go an extra mile to try every new product which is on sale by the company and also buy the company’s products in spite of variety of products and services that are being supplied by competitors (Christopher 2012, p.99).
Bustillo and Lloyd (2009, p. 50) note that customer retention is a broad goal aimed at by all organizations. They add that this cannot be achieved without establishing a firm base in customer loyalty strategies (Bustillo & Lloyd 2009, p. 54).
In a bid to improve customer retention, companies like Michelin have to evaluate the environment of their operational markets. In order to be able to retain all new customers without incurring extra cost, firms need to research in a thorough way the dynamics of the principle of customer intentions and loyalty.
On the other hand, investment management firms have to understand the status of companies’ customer loyalty in order to be able to offer reliable services to them (Cengiz & Yayla 2007, p. 80). A good understanding of the importance of cultivating customer loyalty has been proposed in this study. It is worth noting that customer loyalty will often make companies to become more competitive when they adopt better programs.
As a matter of fact, the case study on Michelin in China provides very typical example on how business organizations ought to manage their markets as part and parcel of retaining their customers. The study will seek to highlight how Michelin has managed to dominate the Chinese market despite of the fact that there are other market players who are equally competitive and appealing to the targeted markets.
There are several benefits which are to be accrued by the analysis of Michelin’s customer loyalty performance in China. As already noted in the above introduction, the well established investment advisory companies will gain invaluable information. They will be placed in a strategic position to operate with a more streamlined focus.
Therefore, individual companies and the entire industry need to consider being involved in carrying the regular market research. To account for their importance, Chris, Greg and Suzan (2012, p. 145) are quite categorical that the only thorough explanation which elaborates poor customer loyalty among companies operating in China is poor research in the field of marketing.
Literature appraisal
Given that the primary objective of this research will be to improve customer loyalty for Michelin, adequate examination of several pieces of literature is inevitable. In this regard, several works of both empirical and theoretical literature have been analyzed. The empirical texts support the role of mediating influence in marketing to maximize customer loyalty.
The issue of customer loyalty has proved to be challenging to both researchers and marketers (Cronin, Brady & Hult 2000, p. 201). Despite of this challenge, it has continually been discussed since businesses have great interest in it. The case of Michelin’s customer loyalty has taken an approach of evaluating how they have managed to create value for themselves as well as for other external stakeholders of the company.
In addition, the relationship between customer loyalty and company value has been sufficiently supported by empirical studies rather than theoretical literature largely due to the credibility of information gathered from primary sources (Dick & Basu 2001, p. 110).
Donio, Massari and Passiante (2006, p.50) note that marketing is supposed to fulfill the desires of customers. This explains why marketing strategies are supposed to build long term as well as mutually benefiting relationships between customers and the firm. In other words, the firm is supposed to deliver a true and ideal value to the market so that the tastes, demand and preferences of consumers are met in a timely manner.
Marketing strategies survive through proper market analysis (Eakuru & Mat 2008, p.130). Besides, controlled market variables give a firm the foundation to pursue desirable levels of consumer satisfaction (Elliot 2010, par. 2). Positioning, targeting and segmenting will be described and evaluated in the case of Michelin. These are the specific marketing tools which yield customer retention and loyalty.
Precise utilization of product package differentiation and segmentation capitalize into dependable strategy (Haelsig et al 2007, p. 441). On the other hand, customer perceived value refers to the customers’ total assessment of the usefulness of products on the basis of perceptions of net benefit (Hemlock 2009, p. 55).
It can be explained using an assessment criteria involving feedback from customers after a particular product has been used, evaluation during transaction and the general expectation before making a purchase. Customers need quality, monetary suitability in terms of price and non-monetary worth in terms of effort and time to develop interest in specific products of a firm.
It will therefore be critical to point out the level of loyalty among customers of Michelin products. The research will obtain clients’ first hand information for the sake of accuracy and credibility of data.
Studies indicate that the most typical and approved way to assess the customer perceived value of a company is to employ the buyer response research method which will of course be used in this case (Hennig-Thurau, Gwinner & Gremler 2002, p. 239).
Difference between the policies and rules that Michelin initiates in Europe and China
After expanding to the Chinese market, Michelin had to modify its policies and rules in order to fit within the new market. While the company had been practicing strong values in terms of organizational culture in order to attract and retain customers, it was necessary for its management in China to evaluate as well as understand the new environment especially in regards to culture.
For instance, Michelin in China has endeavored to cherish and relentlessly pursue its revamped organizational culture that seeks to uphold optimum respect for the environment, facts, shareholders, people and customers.
The company’s operation in China has also witnessed a decent career management model that seeks to improve the capacity and training of its employees. The model is divided into four phases namely individual’s view, manager’s view, career manager’s view as well as periodic development review.
In addition, Michelin in China has adopted a robust performance appraisal system as well as a development process unlike in Europe. It is carried out both annually and periodically. The latter was found to be necessary in the new market in order to boost the performance of employees and overall brand image of the company in the new competitive and dynamic market.
Study matters
Most studies in the business field of customer loyalty outcomes dwell on the complainant behavior of customers, their specific purchase intentions and sensitivity to a company’s prices (Huddleston at al 2009, p. 71). This has been proven to be insufficient in investigating the conclusive loyalty exercised by companies’ consumers (Ibrahim & Najjar 2008, p.32).
This research seeks to investigate the loyalty depicted by Michelin’s customers specifically in the nation of China. It seeks to find out how the company has managed to attract and retain a lot of loyal customers. The specific market strategies which have succeeded or failed in different situations are also a major concern.
The study seeks to find out the criterion which has been used by companies in the Chinese market to make their goods in relation to convenience, price and quality. Convenience is taken as the effort and time which customers spend.
Elements of market mix are the antecedents to value (Kanagai 2009, p.18). The quality of products will be evaluated in terms of monetary sacrifices made by customers. The efforts made by clients to do business will be discussed and researched as well. This will help in explaining how the company has been able to attain and retain loyal customers.
Reasons for study
This study investigates and explores how the business organization has maintained competitiveness. It investigates the challenges towards expansion and maintaining a stable share market. Globalization and innovations in technology has enabled consumers to become more informed (Kerin, Hartley & Rudelius 2009, p. 101). It has given consumers more alternatives and opportunities of doing their purchases.
This has called for customers to become more careful by making their choices become the most paramount aspect in the market (Kanagal 2009, p.11). It is important to study the behavior of customers. The study of a specific company like Michelin is a typical base to evaluate the price relationships in the market. This research seeks to explore the market of China.
It will also help to highlight the most effective ways of capturing the loyalty of the dynamic Chinese market. It will investigate how the customers are able to keep on purchasing a product which is believed to be highly priced.
The suspicion of customers will be considered and different persons will be given a chance to explain why they consider the use of complaints as the most effective way of communicating to their suppliers (Kotler 2005, p. 150).
The positioning of Michelin in the market will also be investigated. An exploration on how the company positions itself in making market strategies will be carried. The manipulation of all market elements to exceed the value of other competing firms is a strategy of establishing consumer loyalty (Kotler & Armstrong 2008, p. 200). The use of mass marketing in China will be studied.
Basically the general market environment which surrounds the firm will be scrutinized in detail. The study is therefore done to collect sufficient data which will be used by firms, the government and individual investors to make appropriate decisions in regards to the market. It aims at creating an ultimate awareness of the major factors which should be considered by any stakeholder in the Chinese market.
The choice of one company will ensure that the others are able to learn without the formulation their own interventions. The management of Michelin will be placed in a good position to make better strategies in terms of making new business moves.
Scope and compass of the study
It has been found out that in the global industrial sector, the chances of running a successful business depend on the advance understanding of the general attitudes of the target customers (Kotler & Keller 2006, p.70). On this note, this study is formulated to describe the ways of exerting an influence which yields customer loyalty. Customer intentions are critical in driving the market.
The efforts put by a company to get into good relationships with customers have been realized to be the ones which make a firm more successful than others. Business principles in the industrial sector dictate that companies must ensure customer satisfaction in order to attain sustainable profitability (Mabel & Aihie 2012, p.97). The government ensures that all consumers are supplied with good quality products and services.
In order to comply with the regulative activities of the ministry of trade and commerce, a company must ensure that it examines all the variables which interact with its customers. To be able to continue being profitable, Michelin has to emulate the viewpoint of both the government and the industrial researchers.
Furthermore, the size of the company being investigated is very important. It has to be clearly understood that economies of scale come with a variety of other factors. Large companies need to have relatively sufficient knowledge of the details of the customers in their markets.
This is because slight changes in the loyalty of clients result into relatively huge losses given that the company operates in a mode which yields high returns. Researcher studies have stated that large scale companies have a greater need of ensuring customer relations (Mabel & Aihie 2012, p.98).
This is explained by the fact that apart from being loyal to a particular firm, consumers attached to such companies often become loyal to specific brands manufactured by the same companies (Kanagai 2009, p.16). Indeed, it is very essential for all multinational companies to participate in this important research. The workers of a given company are well positioned to have access of customer responses.
This is because customers find themselves in discussions which give honest feelings towards a company. In this scope of the matter, the employees have been used as very resourceful participants in investigating the loyalty of Michelin’s customers in China.
Research methodology (Exploration and sampling strategies, data collection, analysis, validity and reliability)
In order to make sure that the study achieves credible and reliable findings, interplay of data collection and research methodology has been used in investigating customer loyalty at Michelin. Both inductive and deductive strategies have been employed.
The research exploration strategies used are a case study of Michelin in China, concept and semantic webbing, debating discussions with other scholars in the same field, open-ended questions, active assessments and theatrical questioning of customers in the market.
The internet has been used to enrich the secondary findings of the research. The findings will also be collected widely and compiled. The combination of information from both online and offline sources will offer valuable and reliable data store formed during this research study (Dick & Basu 2001, p. 110).
The use of action study methodology is approved in business research studies. According to Bustillo and Lloyd (2009, p. 54), the two major approaches of researching have been employed. By using the citizen based style, the research is aimed at empowering the customer.
This has been incorporated with bringing the desirable change. The participatory action research method will be used to recommend changes that ought to be executed at Michelin and any other interested company. The participatory research model will also ensure that outcomes offer guidance in the best way to trigger and nurture customer loyalty.
Nonetheless, this action research style raises several challenges. For instance the issues of validity, credibility, generalization, document value and reporting errors will have to be addressed. This particular method will enable this company to improve the practices which have direct impact on the loyalty of customers. In addition, keen attention will enable understanding of the changing situations in the competitive Chinese market.
Companies which will choose to take part in the research at that time will be in a better position to boost their customer loyalty status. Using the instructional strategies which prompt action immediately after making findings will play a role in suggesting post research actions by the firms.
Data will also be collected using observer notes. The practitioners will participate in the day to day activities of the company. This will enable them to make first hand observation on customer reactions and general responses.
Establishing collaboration will help in ensuring trustworthiness of data. This will be cultivated through the use of data triangulation which is expected to create collaborating evidence on all findings (Dick & Basu 2001, p.111). The qualitative technique will be employed in ensuring effectiveness and consistency in the multiple customer evaluations.
In other words, the solid findings collected directly from the market situation will be tested for validity using business principles. Testing datum will be applied to any data before it is validated for use. Strict interpretation against other findings will be used as a tool for increasing credibility (Elliott, 2010).
Access
Several challenges are expected in the execution of this study. These are basically some of the inevitable difficulties that may be encountered in the due process of conducting the research study. It is important to note that all factors which limit the accessibility of participants have a great impact on the overall research findings. The research is therefore going to be done with various restrictions in mind.
In any case, the lack of adequate access to information in the process of conducting research will be alleviated by ensuring that all possible barriers are indentified early in advance (Swoboda, Morschett & Schramm-Klein 2007, p. 339). Measures will be taken to review all arrangements of data collection and analysis. The key area of access should be maintained as a pivotal mark.
This will ensure that quality findings are fully and accurately compiled. The final reports given by all participants will be treated keenly to ensure that the respondents do not have a feeling of being used by researchers with no gain (Chris, Greg & Suzan 2012, p.150).
In order to ensure that the participants are fully accessed, Michelin or any other party which decides to do this research should aspire to cover the nationwide market in China.
This is the reason why the research is open and allows the input of all interested parties. Moreover, a reliable Gantt chart (shown on the next page) has been formulated to give the research schedule which will be followed during the research process.
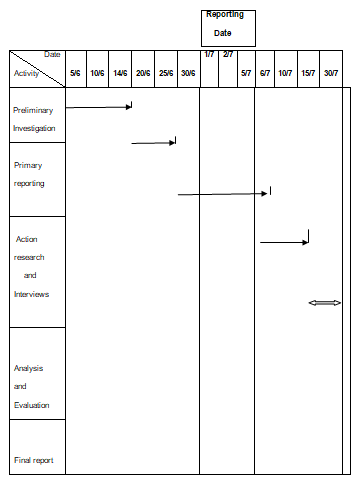
Figure 1: Gantt chart
Conclusion
The most dependable definition of customer loyalty establishment in regards to this study is the process of attracting customers, persuading them to buy a company’s products and services as well as hospitable treatment. The aforementioned practices within an organization will definitely attract customers and sway their purchasing needs towards particular products.
The study will achieve typical and useful information since it will focus on Michelin’s email marketing which has been appealing to customers. The manner in which the team in China has been treated over time determines how they have been treating customers.
This is not preconceptions bearing in mind that studies have shown that if a company cares for its employees, it directly and positively affects how customers are served on a daily basis. The choices made by customers and clients at Michelin are not beyond the control of the company.
In addition, the company will be able to come up with appropriate market strategies after doing an assessment of its customer relations in China. The company also needs to get the facts on the loyalty of its customers in order to come up with inspirational and motivational activities.
References
Bloemer, J. & Odekerken-Schröder, G 2002, “Store satisfaction and store loyalty explained bycustomer- and store-related factors,” Journal of Consumer Satisfaction, Dissatisfactionand Complaining Behavior, vol. 15 no. 2, pp. 68-80.
Bustillo, M. & Lloyd, M 2009, “Best Buy seeks female shoppers,” Wall Street Journal, vol. 17 no.3, pp.45-68.
Cengiz, E. & Yayla, H 2007, “The effect of marketing mix on positive word of mouth communication: Evidence from accounting offices in Turkey”, Innovative Marketing, vol. 3 no. 4, pp. 73-86.
Chris, B., Greg, E. & Suzan, B 2012, “Modeling customer satisfaction and loyalty: survey data versus data mining”, The Journal of Services Marketing vol. 26 no. 3, pp. 148-157.
Christopher, B 2012, “The dynamics of satisfaction and loyalty after relational transgressions”, The Journal of Services Marketing vol. 26 no. 2, pp. 94-101.
Cronin, J., Brady, M. & Hult, G 2000, “Assessing the effects of quality, value, and customer satisfaction on consumer behavioral intentions in service environments”, Journal of Retailing, vol. 76 no.2, pp.193-218.
Dick, A. & Basu, K 2001, “Customer loyalty: Toward an integrated conceptual framework”, Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, vol. 22 no. 2, pp. 99-113.
Donio, J., Massari, P. & Passiante, G 2006, “Customer satisfaction and loyalty in a digitalenvironment: An empirical test,” Journal of Consumer Marketing, vol. 23 no. 7, pp. 445-457.
Eakuru, N. & Mat, N 2008, “The application of structural equation modeling (SEM) indetermining the antecedents of customer loyalty in banks in South Thailand,” The Business Review, Cambridge, vol. 10 no. 2, pp. 129-139.
Elliott, C 2010, Confessions of a frequent-flyer program skeptic. Web.
Haelsig, F. et al 2007, “An intersector analysis of the relevance of service in building a strong retail brand,” Managing Service Quality, vol. 17 no.4, pp. 428-448.
Hemlock, D 2009, “What’s next for Saturn?” South Florida Sun-Sentinel, vol. 10 no.5 pp.34-57.
Hennig-Thurau, T., Gwinner, K & Gremler, D 2002, “Understanding relationship marketing outcomes: An integration of relational benefits and relationship quality,” Journal of Service Research, vol. 4 no.3, pp. 230-247.
Huddleston, P. et al 2009, “Customer satisfaction in foodretailing: Comparing specialty and conventional grocery stores. International’, Journal of Retail & Distribution Management, vol. 37 no.1, pp. 63-80.
Ibrahim, H. & Najjar, F 2008, “Relationship bonding tactics, personality traits, relationshipquality and customer loyalty: Behavioral sequence in retail environment,” The Icfai University Journal of Services Marketing, vol. 6 no. 4, pp. 1-37.
Kanagal, N 2009, “Role of relationship marketing in competitive marketing strategy,” Journal of Management and Marketing Research, vol. 2 no.4, pp. 1-17.
Kerin, R., Hartley, S. & Rudelius, W 2009, Marketing, McGraw-HillIrwin, Boston.
Kotler, P & Armstrong, G 2008, Principles of Marketing, Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Kotler, P & Keller, K 2006, Marketing Management (12th ed.), Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River.
Kotler, P 2005, According to Kotler: The World’s Foremost Authority on Marketing Answers Your Questions, AMACOM, New York.
Mabel, K. & Aihie, O 2012, “Remedy or cure for service failure?”, Business Process Management Journal vol. 18 no. 1, pp. 82-103.