Introduction
Accor is a chain of hotels which operates in 92 countries around the world. The hotel has its headquarters in Paris, France. Founded in 1967 by Gérard Pélisson and Paul Dubrule, this hotel has over 3600 franchises in the five continents. It offers economy, budget lodging and luxurious accommodations in these facilities (Kwaku & Murray, 2004). This firm faced some challenges during its early years of operations, especially in attracting the high class customers into its stores. However, this changed in the 1980s and 1990s when it started experiencing rapid growth. The firm was able to expand its operations to other European nations and North America during this period. Currently, Accor has the largest number of hotels in various categories in Paris, France. This research seeks to investigate the marketing strategies that this firm has been using in the market, and how it has been able to manage the market competition.
Level of Analysis Statement
In this study, it was important to understand the strategies that Accor S.A. is using to manage the market forces within the home country and in the international market. According to Cook (2008), the external environment in the hospitality industry has remained very dynamic due to the changes that take place in the field of technology. In order to remain competitive, Accor must find a way of maintaining its internal environmental factors to be in line with the external environmental factors. In this report, therefore, the level of analysis will focus on both the internal and external factors. The analysis of the external factors will create awareness of the factors that this firm must be able to deal with in the market in order to remain competitive. On the other hand, the analysis of the internal factors will make it possible to understand how this firm is ready to deal with the external factors in order to achieve success (Cook, 2005).
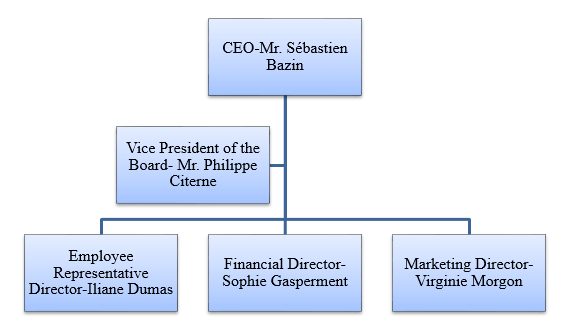
Situation Analysis
According to Nash (2000), the best way of understanding the forces that affect the normal running of a business entity is to conduct a situation analysis. The analysis involves investigating both the internal and external environmental factors (Bradley, 2005). In this study, it will be necessary to investigate the internal and external environmental factors that affect the normal operations of the firm.
Market Analysis
At this stage it is important to analyse the current position of this firm within the industry. The following graph shows the current position of Accor in its life circle.
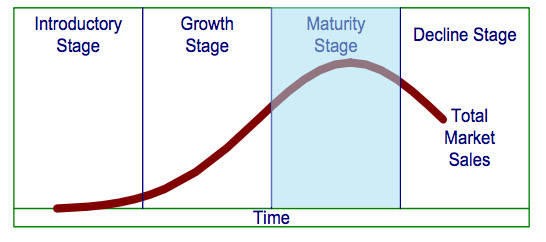
As shown in the diagram above, the firm has achieved maturity in its market growth. Although the firm has been making an effort to spread its operations to the emerging markets in Asia and Africa, its market in Europe has been invaded by other emerging firms. This means that the rate at which it is losing its market share in Europe is almost the same as the rate at which it is gaining market share in these emerging markets.
The model that will be used to investigate the external environment of Accor is the PESTEL Model

These factors can be summarised in the table below.
Table 1: Summary of PESTEL.
4Ps can be used to further strategies used by this firm to manage the external forces
Table 2: 4Ps.
It is important to understand the internal environmental factors that may affect the ability of Accor to deal with the external environmental factors discussed above. SWOT Analysis is one of the most effective tools that can be used to investigate these factors (Knox & Gruar, 2007). The table below shows the model, and some of the specific factors that relate to Accor. The SWOT Analysis below is based on a case study on the firm’s recent past operations.
Table 3: SWOT Analysis Model.
The table above has identified specific strengths and weaknesses that may affect Accor’s normal operations in various ways. The management should formulate a strategy that would enable it to use its strengths to overcome its weaknesses (Ansio & Mattila, 2009). The market also offers a series of opportunities that should be tapped in order to fight some of the threats that exists in the market.
Problem Identification and Discussion
Accor has faced some major and minor problems that have affected its normal operations in the market. In order to understand some of the problems that this firm has faced in the market, it is necessary to use some theoretical models of marketing. Porter’s Five Forces will be an effective model to use at this stage (Cavusgil & Shaoming, 2004).
Table 4: Porters Five Forces Model.
Competitor Analysis
One of the main competitors of this firm is the Hilton Hotels & Resorts which also has global market coverage. Hilton Hotel offers several of services, including a variety of meals, accommodations, and tourism services. One of the main strategies that this firm uses is to offer its clients tour services, especially for those who register with them as tourists.
Proposed Alternative Solutions
According to Walker, Gountas, Mavondo and Mullins (2012), there are some problems that cannot be eliminated within the firm. In such cases, it may be necessary to come up with effective solutions that can address such problems in order to minimise their impacts within the firm. According to Aaker (2009), it is important to find a way of dealing with problems that cannot be avoided within the firm.
Internal capabilities
Financial strength from the past successful operations is one of the main strength of this firm. Effective human resource management and highly qualified staff have also enabled Accor to deal with its challenges in the market. The firm has also maintained regular research to improve its market operations. The following are some of the areas this firm should emphasize on.
- Segmentation: The marketing unit should identify segments that have the characteristics they desire in their customers (Aaker & Mills, 2005).
- Targeting: The marketing unit should target the selected segments with the most desirable products (Cravens & Piercy, 2009).
- Positioning: When the right market segment has been identified, it would be appropriate to position the products of this firm based on the characteristics of the customers.
Works Cited
Aaker, D.A & Mills, M. (2005). Strategic Market Management. New York: John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Aaker, D.A. (2009). Strategic Market Planning. New York: John Wiley & Sons. Web.
Ansio, T. & Mattila, E. (2009). Marketing Strategy Formulation: Pure versus Mixed Strategies. Strategic Management Journal, 30(12), 1097-1101. Web.
Bradley, F. (2005). International marketing strategy. New York: Prentice Hall. Web.
Cavusgil, S. & Shaoming, S. (2004). Marketing Strategy-Performance Relationship: An Investigation of the Empirical Link in Export Market Ventures. Journal of Strategic Marketing, 58(1), 1-21. Web.
Cook, J. (2005). Understanding Marketing Strategy and Differential Advantage. Journal of Business Strategy, 49(2), 137-142. Web.
Cook, V. (2008). Marketing Strategy and Differential Advantage. Journal of Marketing Management, 47(2), 68-75. Web.
Cravens, D.W. & Piercy, N. (2009). Strategic Marketing. Chicago: McGraw-Hill. Web.
Ferrell, O.C. & Hartline, M. (2011). Marketing Strategy. Mason: Thompson Learning. Web.
Gabrielsson, P., Gabrielsson, M., & Tomi, (2012). Marketing Strategies for Foreign Expansion of Companies Originating in Small and Open Economies: The Consequences of Strategic Fit and Performance. Journal Harvard Business Review, 20(2), 25-48. Web.
Hooley, G. Nicoulaud, B. & Piercy, N. (2011). Marketing Strategy and Competitive Positioning. New York: Pearson Education International. Web.
Jain, S. (2011). Marketing Planning and Strategy. Mason: Thompson Publishing. Web.
Kerin, R. & Peterson, R. (2010). Strategic Marketing Problems: Chicago: Pearson Education International. Web.
Knight, G. (2006). Entrepreneurship and Marketing Strategy. Journal of International Marketing, 8(2), 12- 32. Web.
Knox, S. & Gruar, C. (2007). The Application of Stakeholder Theory to Relationship Marketing Strategy Development in a Non-Profit Organisation. Business Strategy Review, 75(2), 115-135. Web.
Kwaku, A, & Murray, J. (2004). Antecedents and Outcomes of Marketing Strategy Comprehensiveness. Journal of Marketing, 68(4), 33-46. Web.
Lehmann, D. & Winer, R. (2008). Analysis for Marketing Planning. New York: McGraw-Hill. Web.
Nash, E. L. (2000). Direct marketing: Strategy, planning, execution. New York: McGraw Hill. Web.
Walker, O.C., Gountas, J.I., Mavondo, F.T., &, Mullins, J.W. (2012). Marketing Strategy: a decision-focused approach. Melbourne: McGraw-Hill. Web.