Background information
The industrial revolution brought forth with it huge benefits to humanity, several manufacturing industries emerged and the society experienced an economic growth, however, the revolution brought with it very serious ecological and environmental issues that still “haunt” humanity to date. Issues such as global warming and environmental pollution became common phenomenon..
Statement of purpose
Acidic rain has immense effects on the environment, when it falls on plant leaves, the leaves are corroded thus impacting heavily on the photosynthetic capacity of the plants, secondly, the acidic rainfall lowers the soil PH when it seeps into the crust of the earth leading-leaching. This obviously alters the ionic balance in the soil leading to an imbalanced chemical and nutrient content. This shall be the focus of this paper.
Preview
The interest of this paper is to explore the impacts of acidic rain on the PH of the soil and the leaching processes. The paper shall briefly highlight the remedies to global air pollution that causes acidic rain.
Acidic Rain
Dangerous acidic gases emitted in the atmosphere from industrial activities rise and mix with the atmospheric precipitation. They then fall back into the earth as an acidic rain.
Acid rain from Sulphur dioxide
Through combustion of fossil fuels containing sulphur, Sulphur dioxide gas is emitted in the atmosphere as a by product, coal combustion is the major source of this gas. The gas rises into the atmosphere and is further oxidised forming sulphur trioxide which reacts with atmospheric forming Sulphuric acid which falls back as acid rain.(Friesel 108)
Acidity levels are measured using the Ph scale which is a universal scale that determines the Hydrogen potential of any solution. It shows the alkalinity levels too. Pure water is considered neutral with a PH value that falls between 7.0-5.7.Above the value of 7 up to 14,the water is considered alkaline or basic.
Other compounds
Through fossil fuels, Nitrogen Oxide is emitted, its combustion releases nitric oxide which is further oxidised to Nitric oxide by atmospheric oxygen. This further reacts with atmospheric water to form Nitric acid which is an acidic rain. Some of the origins of this compound- nitrogen oxide emission are automobiles and fossil fuel burning power stations. (Friesel 111)
Carbon (iv) Oxide also plays a role in the formation of acidic rain when it reacts with the atmospheric water to form weak Carbonic acid that falls back as rainfall in the atmosphere.
Acidification of Soil
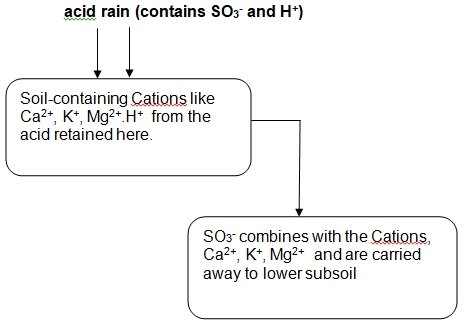
As earlier mentioned, the acidic rain lowers the soil PH when it falls on the ground. This is achieved through ion exchange where Hydrogen ions-prevalent in the acid rain, are interchanged with the cationic elements present in the soil. (Singh 15 )These elements are the positively charged nutrients like Calcium and Potassium.
When this occurs, the Cations are leached out of the soil together with the sulphate radical that is present in the acidic rain,this action eventually render the soil deficient of the nutrients but leave higher concentration of the Hydrogen ion in the soil. (Friesel 108) The Hydrogen ion is responsible for the acidity of the soil.
In a nutshell, the sulphuric acid that is present in the rain, shall “donate the Hydrogen ion in the acid to the Cations in the soil, the metal cations, on the other hand, is attached to the sulphate compound from the Sulphuric acid and transited to the sub soil where the plants cannot easily access them
Relationship between soil acidity and nutrients
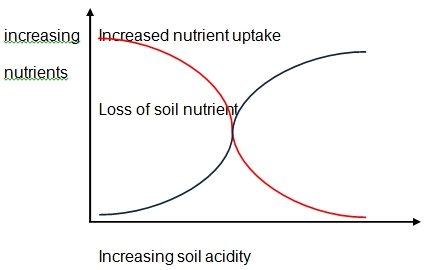
Research has proved that acid rain disrupts the regeneration of soil.This essentially means that the recycling of chemical and mineral nutrients by the plants is greatly impaired through the effects of acidic rain. (Xie 27)Acid rain are capable of disintegrating the bonds that exist between the crucial plant nutrients like magnesium which are bound to soil particles then transport them to sub soil. This will obviously interfere with the productivity of the plant as depicted by the graph below.
Acid rain-soil interaction
Depending on the type of soil in an area, some are capable of resisting the precipitation or the leaching process, this ,as earlier mentioned, wholesomely depend on the type of the mineral that is present in the soil.(Xie 27)
Limestone
Soils formed from sedimentary rocks such as limestone are least affected by the leaching process. This is because limestone is basic in nature, it contains minerals such as calcite and dolomites which offer a buffer zone that neutralizes acidic rain.(Friessel 117)
Calcite and dolomite have Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Magnesium Carbonate respectively, these Carbon compounds possess Hydroxyl ions in them that react with the Hydrogen Ion from the acid to form water, a process referred to as neutralisation process.(Xie 27)
OH– + H+ —>H2O
Areas with limestone therefore are greatly protected from the leaching process through the buffering process as defined by the equation above.
Igneous and metamorphic rocks
Soils that are formed from the parent rocks of igneous and metamorphic rocks, lack the Hydroxyl ion needed to neutralize the Hydrogen ion from the acid rain, such soil therefore undergo leaching in large quantities. Soil types like Basalt and granite formed from igneous rocks experience very high levels of leaching. In addition, metamorphic rocks experience the same fate. (Friessel 117)
Acidic soils have numerous effects in the environment.Through leaching the mineral compounds invariantly find their way into the water bodies which interfere with the aquatic life.
The change in the soil PH has an enormous effect on the microorganisms that stay within the lithosphere. These microbes are very significant in the aeration of soil, the alteration of soil PH thus kills the microbes. (Friessel 122)
Acidic soils that emerge after the soil PH has been altered by the acidic
rainfall is very toxic to the plants,it leads to stunted growth of the plant roots.Some plants,however,are capable of mitigating the effects of acidic conditions through the secretion of very strong bases that neutralize the acid, such plants include, the leaves of Malanthora which add the ions of Potassium.
Mitigation
To reduce the effects of soil PH changes, it is very important to reduce the atmospheric pollution by eliminating the gases that lead to acidic rainfall. The gases can be transformed into less dangerous compounds whose environmental effects is less severe.
Conclusion
Humanity has perpetually contributed to the defilement of the environment through its activities. The acid raid formation is as a result of the uncontrolled emissions of gases into the atmosphere which in turn affects the soil PH hence degrading the soil.
The paper has conclusively explored the impact that the acid rain has on the acidity level of the soil. The phenomenon of leaching that invariantly affects the soil quality has been deeply dealt with. It is factual that the core role demerit of acidic rain,in terms of soil PH is the fact that it encourages the leaching process.
The formation of acidic rain has been conclusively highlighted.It therefore remains the duty of humanity to mitigate the effects of the acidic rain on lithosphere even as the human race explore industrial processes.
References
Friessel M.J., 1974, Simulation of accumulation and leaching in soils,Wageningen: Pudoc. 107-213.Print
Johnson, N & Parnell, R, 1986, ‘Composition, distribution and neutralization of acid rain derived from Masaya volcano, Nicaragua’, Tellus, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 167.print
Singh, A & Agrawal, M ,2008, ‘Acid rain and its ecological consequences’, Journal of Environmental Biology, vol. 29, no. 1, pp. 15–24.print
Xie Xhengua., 1998, Control Acid Rain and Sulphur Dioxide Pollution, Improve Environmental Quality, China Chemical Reporter. 1142 (4), 22-38.print