Introduction
As derived by classical economists such as Adam Smith, classical economies are largely dependant on the market efficiency functioning (Jamesesz, 2008). The two influencing factors in classical markets structures are the influence of demand and supply on market prices.
Classical economists observe and indicate that microeconomics is based on market functioning and individuals, that is consumer and producers behaviors. These two variables usually control and affect the efficiency of markets. In this context, prices are dependants on the demand level and the supply levels.
At market equilibrium price, the level of supply equals demand level. When supply exceeds demand level, prices fall and when demand exceeds supply, the level of equilibrium rise. Markets function effectively due to the objectives of producer and consumers. Producers are there to maximize profits while consumers are there to optimize satisfaction on consumption.
In this respect, when prices rise in one commodity, profit driven market players will produce more of high priced commodity. In addition, producers will draw human capital, entrepreneurship, land and material capital (factors of productions) from low priced products to higher priced products.
Conversely, oils are key inputs production factors that influence production levels and market systems. Economists suggest that the current economic environment oils demand and supply, together with the oil prices influence markets structures and can be used as a predicting tool for markets systems (Jamesesz, 2008).
Today’s national and globalized economies have received the behavior of oil prices volatility with deep concern and consideration. From the experiences, oil’s prices volatility and rise in prices are common. It has come to economic believe that high oil prices have adverse effects to economic systems and equally derail economic growth.
In addition, the volatility in oil prices causes increase in uncertainty and risks, thus discouraging investments and reducing economic incentives for growth. Like other production inputs, high oil prices stimulates increase in production (supply increases) and causes decline to oil demand levels.
This paper will focus on the effects of rising oil prices to economic growth. Importantly, the paper will discuss on the micro economic impacts caused by oil prices and the effects to derailing economic growth. The paper will highlight on effects of oil price rise to gross domestic product, consumption and production.
Impact on gross domestic product
Oil prices affect the economic performances in a country. The mechanism to the impacts on performances exerted by the oil prices is very well recognized by most developed and underdeveloped countries. Many countries measure the impacts of the rising oil prices through estimating their Gross Domestic Products (GDP).
Economic growth is measured by the increase in the size of the economy GDP. A good and simple measuring approach to estimate economic size is its expenditures. According to Mankiw, 2008, gross domestic product is the market vale of all final goods and services produced within a country in a given timeframe. A concept is comprehensive and it includes the summation of all items produced and sold legally within an economy. There three ways of measuring GDP within countries borders.
These methods include use of expenditures approach, incomes approach, and the output approach. Based on the expenditures GDP measuring approach, it is the summation of all the countries consumptions, investments, net exports and the government spending.
Based on the other two, economists suggest that the approaches leave out many incomes and the outputs produced by illegal means. In addition, output and income aggregate economic measure of GDP does not reflect the equality principle to all country’s citizens.
Raise in oil prices affect many economic units of an economy. High price impact on an economy is attached to the reliance of a country to oil. Countries depending on oil translate impact on consumptions and other spillover effects to increase in cost of production (Jamesesz, 2008).
Economic sectors that depend on oil include the agriculture, transport, manufacturing and the government organs. Increase in price of oil will directly correlate positively to rise in costs of production. To cover production cost, prices of goods and services in the market increases.
This causes an increase in consumption at household level and industrial level. Increase in cost of production in all sectors translate to reduction of real household incomes forcing the household reduce its consumption expenditure proportionately.
As noted by Mankiw (2008), in real gross domestic product there is a relationship between the value of money and price level, and the quantity demanded at that level. This entirely sums up to decline in aggregate demand of an economy and cause an aggregate consumption decline.
Increase in production costs and the decrease in consumption expenditure caused by the rise in oil prices prompt producers to reduce outputs. Since transportation is affected by the raise in oil prices, distribution of products and services is equally affected.
Distribution and production costs cater a large percentage in agriculture and manufacturing sectors expenditures. For this reason, firms are induced to lower production levels and output. According to Skousen (2008), increase in production and distribution costs can also be from other factors such as the price rise expectation, wages increase demand from human capital and other production inputs costs.
Figure one shows changes in outputs and the demands in an economy as affected by fuel prices. The actual supply and demand for a particular commodity is as shown by S and D respectively. The supply curve shows economic output. Increase in energy cost prompt an increase to production cost.
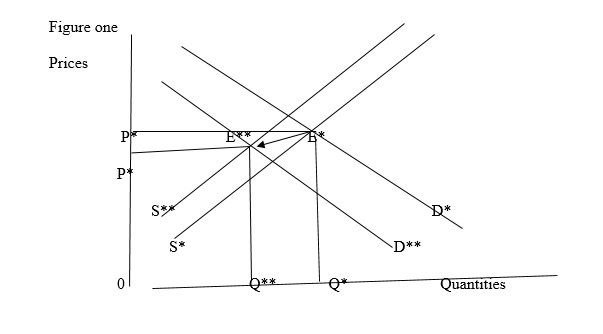
The supply curve will thus shift down wards. The demand of commodities will reduce due to increased cost transferred to prices. Subsequently, the economy will gain a new market equilibrium that is lower than the previous equilibrium. That is from E* to E**. If prices increase for a long time, the other economic sectors are affected thus derailing the economy growth (Jamesesz, 2008).
The concept of absolute advantage force countries with labor intensity, produce labor-intensive products for exports and for domestic consumption. Countries with capital intensity will produce capital-intensive products and exports to the labor-intensity countries. Developed countries or countries selling oil in the global markets capture this absolute advantage.
These countries will produce capital-intensive goods and export at low cost to underdeveloped countries, lacking oils or affected by oil prices. The net exports of such underdeveloped country will be adversely affected turning to negative balance of payment, consequently slowing growth and reducing gross domestic products. Export intensive countries will be faced by a drastic reduction in exports. This is caused by decline in exports demand from the developed countries leading to slow growth (Jamesesz, 2008).
Impacts on consumer budgets
As discussed in the impact to the gross domestic product, consumption level affect household consumer significantly. In this response, consumer will be forced to adjust his budget proportionately and attain new purchasing power. High oil prices increase causes an inflationary gap to consumers.
The rise in oil prices lead to rise in cost of productions hence rise in goods and services price increase. Inflation caused by the energy price increase, increases cost of living. Increase in cost of living reduces expenditures and reduce savings. Savings in an economy stimulates economic growth. With low savings, the economy stagnates or derails economic growth.
There are several reasons that affect the consumption budget of an individual. Generally, they comprise on factors affecting the cost of living and the welfare an individual. First, household’s large budget is spent on food and other essential services such transport.
Secondly, most of the consumption budgeted goods and services are not own produced but depend on other production costs. Increase in production costs lead to higher prices and thus increased consumption budget. In this respect, there is a negative or derailed gross domestic growth rate contributed by high oil prices through individuals’ consumption effects.
As noted in the GDP discussion, many economic analysts argue that rising in energy prices particularly oil prices will affect real individual incomes and growth. Therefore, tendency arises of changing from fuel using goods to most efficient non-fuel and cheap goods and services.
In fact, the relationship between the real gross domestic products and the raise in fuel prices clutch at the consumption level. There is a major challenge on consumption relationship with energy price increase. When prices of fuel rise, consumption is affected negatively while a decrease in fuel prices does not affect consumption. Like wise, consumption effects on durable items are not affected adversely than the consumption of frequent essential commodities.
Rational consumer depends on the real incomes for consumption. Real incomes at the individual disposal bring about consumption pattern and the utility level. Increase in prices reduces real incomes or erode purchasing power. Consumption budget line reacts to the increase or decrease in disposable real income.
Figure two shows this reaction. The figure shows changes due to increase in prices induced by fuel price increase. This implies that consumers do not spend more that what their have as disposable incomes. In the figure, consumer has $60 to spend on transport and food daily.
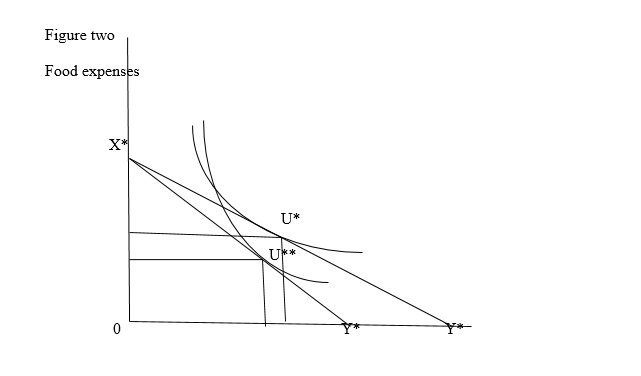
Restaurant cheapest food is $18 and transport is $42 daily. The utility for the day is at point U*. Assuming there is increase in fuel prices. Increase in transport cost is transferred to individual passenger by increasing fare by $3 per passenger. The budget line will change from y* to y**.
The individual’s disposable incomes will not change in short run. The increment in transport costs will force an individual to reduce either food expenses or travel to work less days. Due to fuel prices increase, restaurants sales will reduce and this translate to negative economic growth in the sector. Individual’s utility curve will also change to U**.
Alternatively, suppose household consume 20 litters of gasoline in a month. Suppose the prices of oil are up by 20 percent. This implies the amount of gasoline consumed in a month will increase by 20 percent. Suppose also, that the individual saving was 30 dollars for every 100 dollars got.
The price of gasoline will reduce the savings of an individual. The propensity to consume for an individual will not change in short run but the propensity to save will change drastically (Melvin et al., 1983). In the short run, individuals or the household will not respond to the increase of gasoline from the amount they purchase.
Economy will not have an impact on the same. This is because consumers in the short run do not respond to the reduction in supply or increase in price. Fuel prices will not alter individuals going to work in short run. Neither individuals driving lifestyle nor the consumption level will change in short run.
Economic growth is based on an annual timeframe. In the long run, consumers, both industrial and individuals feel the impact on purchasing power eroded and on the propensity to save and consume.
Equally, manufacturer sales reduce forcing them to lower output. Decrease in output and consumption level induced by fuel prices signals inefficiency in the market structure functioning (Melvin et al., 1983). It also signals symptoms to derailed economy growth.
The consumption on individual is thus affected by the prices increase. The reduction in restaurant demand or profits will be solved by increasing prices of food also or reduce their outputs. Agricultural sectors and manufacturing being fuel guzzlers will increase their production costs also.
The increment will further be transferred to either the industrial or the individual consumer. Reduction in individual’s expenditure due to energy price increment causes the output reduction and decrease in economy’s overall gross domestic product.
Future planned consumption depends on the anticipated values of resources. Anticipated value of resources is actually incomes and wealth of an individual at predetermined date (Bhattacharya, 2000). Incomes and wealth of individuals dictate the consumption level for the economy in future date.
Incomes and wealth can be changed in long run and this affects the consumption level. Increase in fuel prices causes a decrease in wealth, increases cost of production, thus reducing wage rates in an economy. This causes a low economic growth.
Conclusion
Rising in oil prices slows down economic growth rate. This reduces the economy output leading to recession. Fuel prices lead to increase in commodities price level and the increase in price in particular timeframe cause inflation. The largest expenditure of an economy goes to fuel.
An increase in oils price will lead to economic shock and inflationary tendency. Escalating oil shocks to the developed world is transferred to the developing and underdeveloped countries. Outcomes as discussed above are a threat to economic growth or recovery.
Consumption is the largest variable in the economic growth measurement. In this regard, increase in oil prices affects both the microeconomic and macroeconomic growth. Microeconomic units such as the industry and the households are the variables of macroeconomic unit. This means, once micro economic variables are affected by fuel prices, economy growth rate derail causing unemployment and inflation.
References
Bhattacharya, J. (2000). Consumption budget line. Web.
Jamesesz, P. (2008). Impact of High Oil Prices on the Malaysian Economy. Web.
Mankiw, N. G. (2008). Principles of economics. Cengage Learning. Web.
Melvin, J. R., Scheffman, D. T., & Ontario Economic Council. (1983). An economic analysis of the impact of oil prices on urban structure. Toronto: University of Toronto Press.
Skousen, M. (2008). Economic Logic. Regnery Publishing. Web.