Executive Summary
Security is one of the main issues to address in e-commerce. For BookMart the security issues became a major area of concern after a hacker attack that was performed due to a security breach. As a result of the attack, customers’ confidential information was at risk of being exploited by the hacker. Three alternatives were outlined for the company to choose as a response for such attack. One alternative focused on making sure that no information will be disclosed to the public, while all efforts of the Information Technology (IT) department directed toward eliminating the results of the breach. No commercial activity is conducted during such period. The second alternative implies focusing on providing full disclosure while targeting the consequences of the attack. The third alternative was recommended to be implemented, which main focus is investigating the root of the security breach, and developing corresponding new security policies. The implementation plan for such option is focusing in the creation of two independent work groups, one of which will develop new policies focusing on eliminating human mistakes and providing a risk management system.
The Situation
Background
One of the key factors that impact developments in the sphere of e-commerce is security. Despite the fact that major respectable brand names appeared in the sphere of e-commerce, there are nevertheless, existent concerns on the security issues when using online shops. For BookMart, a major online, movie, and CD store, such concerns occurred right after the company’s merger with a recent merger with a medium-sized virtual music site. For a company which business success was largely dependent on the loyalty of their customers, the issue of protecting customers’ privacy as well as retaining their previous purchase history and bonuses was of vital importance. Accordingly, Lois Fairchild, the Chief Information Officer (CIO) of BookMart implemented many security measures to protect the firm, specifically during the process of integrating the equipment of the platforms of the merged companies. Nevertheless, a breach of security occurred in the company’s systems, as a result of which customers’ confidential data was posted on the company’s website. Accordingly, BookMart had to shut the systems for an indefinite period.
With the necessity to provide a response to security breaches, BookMart faces a dilemma of what option to select in handling the security situation. According to the details of the case, three distinct problems can be outlined, assessing the damage and patching the breach in security, providing a response to the media to the customers, and preventing such breaches in the future. A suitable strategy should be selected in order for the company to be able to address each of the aforementioned areas. The present report will provide an analysis of the alternatives available, providing recommendations on the alternatives to choose as well as an implementation plan.
Criteria
The criteria of the decisions that should be taken as a response to the hackers can be seen in the order of their priority as follows:
- Eliminating the breach
- Restoration of the store’s security environment and normal functionality.
- Containing negative publicity.
- Solve the root of the problem.
- The learning process
The first two criteria are associated with each. It is stated that the negative publicity regarding security breaches is associated with the market value of the announcing firm (Cavusoglu, Mishra and Raghunathan), with the main concern being the fear of sharing (selling, renting) personal information to other companies (Miyazaki and Fernandez).
Thus, the first criteria for the decision are to be able to eliminate the breach and restore the normal functionality of the website. Containing the negative publicity, in that regard, can be seen as a major criterion in such decision.
Instantaneous actions are directed toward the current impact on the breach. However, eliminating the root cause of the breach, e.g. the insecure authentication processes, the human factor, the lack of personnel qualification, etc, can be seen as important criterion as well. Finally, the last criterion implies that the decision selected as a solution should provide a learning opportunity for the organization, as a result of which knowledge will be gained and new policies will be formulated.
Alternatives and Recommendations
Alternatives
It should be stated that the alternatives discussed are largely based on common actions which differ mainly in the order of the implementation. The mutually exclusive elements in the alternatives to be suggested are related to the way information should be disclosed.
The first option can be seen as the most radical one. Such option implies closing all electronic operations on the website and making an announcement that the website is closed for maintenance. The company should establish a deadline through which the issue is to be resolved. During such period all the staff of the IT department will work on eliminating the breach in the security, while all commercial activity will be directed toward providing support. In that regard, no information will be disclosed to the public, referring to internal hardware failures as the cause of the maintenance.
The main points of the second alternative can be seen the necessity of fully disclosing the details of the breach to the public. In such case, commercial activity might be stopped for a certain period, during which customers will be provided information on incident, while changing the security information on their card will be suggested. In such way, in case confidential customers’ confidential information will be used by hackers, it will be of little or no use. On the security aspect, the company will target the consequences of the problem, i.e. closing the breaches in the system, putting the latest patches on the system and providing a full check of the system’s vulnerability. After the issue will be solved, the website of the company will return to its normal functioning, with all customers being informed through newsletters and website announcements.
The last option can be seen through targeting the internal root of the problem, which might be seen as requiring for the most details. The main focus of such approach is targeting the security policies in the organization and the human factor as the root of the breaches that did occur in the organization. The results of the investigation will lead to a restructuring in the security policy of the organization, in which mistakes and the drawbacks from the experience will be considered. Such policies are related to the authentication system within the organization for customers and employees, as well as to the development of a risk management system that will handle the consequences in case such incident occurs again.
Such “policies can help to minimize the disruption that security breaches can cause for organizations where information has been defaced, data lost, the company profile damaged or work time has been lost — this all results in eventual financial loss” (Tomlinson 12). Accordingly, a full disclosure of the breach will be provided to the public and to the customers. The consequences of the breach will be managed through a full investigation, during which access to the internal network will be highly limited to the majority of employees.
Recommendation
Considering the strengths and the weaknesses of all alternatives, it can be stated that the last alternative, which focuses on eliminating the roots of the problem, can be seen as the most balanced. It can be understood that despite the negative consequences of security breach disclosures, such steps cannot be avoided from ethical and legal perspectives. Similarly, it can be understood from the case that the human factor plays a major role in the occurrence of the breach in the first place, which makes it feasible to handle only the consequences of hackers’ actions.
Additionally, such option conforms best to the criteria established for the decision, where it handles the situation through a learning process, tackling the root of the problem, and restoring the situation to normal functioning. Accordingly, the three problematic areas outlined in the problem statement will be addressed, although in a priority differing from other options. It can be stated that the order of such priorities, i.e. preventing the problem from occurring in the future, a response to the media, and patching the breach. As for the disclosure aspect, the role of the company will be ensuring that no harm will be done to the customer. Trust in the context of e-commerce is “a judgement made by the user, based on general experience learned from being a consumer and from the perception of a particular merchant” (Hanlon 36). Thus, it can be assumed that customers’ trust can be destroyed through a negative experience of e-shopping, rather than knowing about the fact of the breach itself.
Implementation Plan
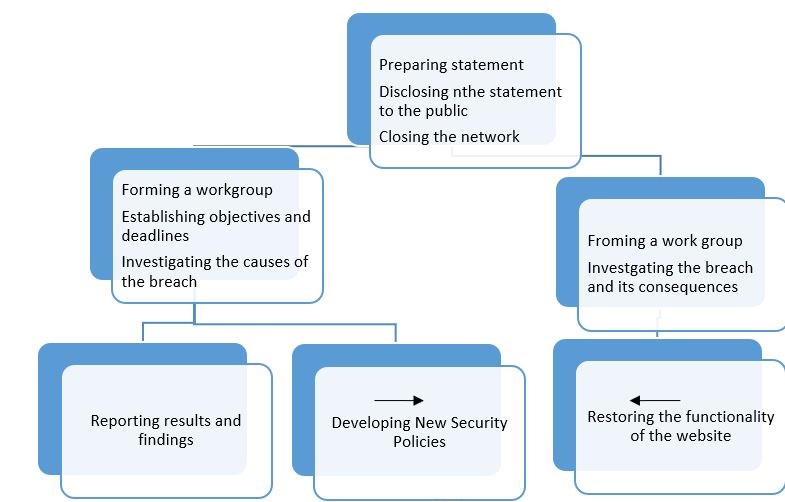
The plan for implementing the selected recommendation can be seen through the following steps:
- Preparing a statement to be released on the breach.
- Disclosing the statement to the public through a website announcement and through warning and precautionary letters sent to the customers.
- Closing the internal network from the web, and aborting any electronic transaction activities.
- Forming a working group to investigate the causes of the breach.
- Establishing objectives for the group and deadlines for results.
- Another group will be established to restore of the functionality of the website.
- Reporting results and findings of both groups.
- Developing security policies.
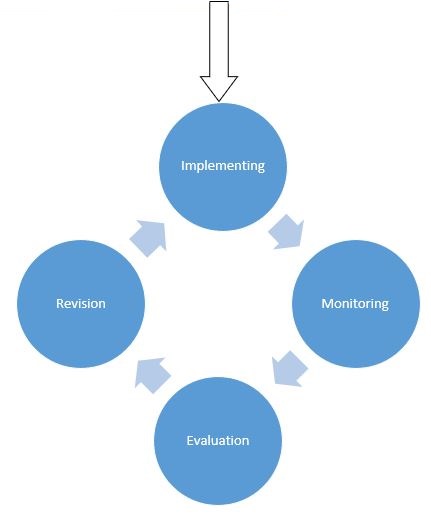
- Implementing the plan.
- Monitoring.
- Evaluation
- Revising the policy.
It can be seen that the implementation plan is concerned with two parallel work groups and continuous process of monitoring and evaluation. According to such continuous process, the learning process in the company should occur. A representation of the plan can be seen through Figure 1. It should be noted that according to the case, it is expected that the results of the investigation will reveal that the human factors contributed to the security breach, namely the password system within the organization as well as the system of sending passwords to customers by email. In that regard, it is not expected that new hardware investments will be required, rather than the introduction of new security processes and regulations in the system. The timelines for the plan can be divided between the two groups, where the group focusing on the restoration of the website’s functions will have a deadline of 3 to four days. The investigation group, on the other hand, will have a longer deadline, estimated between 14 and 20 days. The evaluation and the revision process will be conducted every six months.
Works Cited
Cavusoglu, Huseyin, Birendra Mishra, and Srinivasan Raghunathan. “The Effect of Internet Security Breach Announcements on Market Value: Capital Market Reactions for Breached Firms and Internet Security Developers.” International Journal of Electronic Commerce 9.1 (2004): 69-104 pp. Web.
Hanlon, Lynsey. “Ecommerce Services & Security”. Glasgow, 2005. Department of Computer and Information Sciences. University of Strathclyde. Web.
Miyazaki, Anthony D., and A. N. A. Fernandez. “Consumer Perceptions of Privacy and Security Risks for Online Shopping.” Journal of Consumer Affairs 35.1 (2001): 27-44. Print.
Tomlinson, Matt. “Tackling E-Commerce Security Issues Head On.” Computer Fraud & Security 2000.11 (2000): 10-13. Print.