Introduction
A well-known company in the organic food sector, Alce Nero is renowned for its dedication to ethical agricultural practices and premium goods. Since its founding in 1978, the business has grown significantly, diversifying its product line and entering foreign markets (Alce Nero International, 2023b). Products from fruits and vegetables comprise most of Alce Nero’s product line.
However, it has broadened to include categories like fresh and frozen food, released in 2015 and 2017 (Alce Nero International, 2023a). The surge in the organic food sector, further boosted by food safety crises like the mad cow disease epidemic and the Dioxin Affair instances around the turn of the century, has been a significant driver of the company’s expansion. The firm has progressed in foreign markets, notably Europe and Asia, and is expanding its product line.
Due to its closeness and the simplicity of selling through wholesalers and smaller stores specializing in organic and natural products, Alce Nero’s worldwide sales started in the early 1990s, particularly in Europe. The firm has primarily taken an opportunistic approach to the European markets, relying on unplanned possibilities rather than employing a defined market penetration strategy. The firm has a substantial presence in Asia, Alce Nero’s largest overseas market by revenue, particularly in Japan, Singapore, Malaysia, and Hong Kong. One of the founding members of Alce Nero, Lucio Cavazzoni, who saw the need for Italian goods and natural organic food in Japan, helped make this achievement possible (Massa, 2015). As a result, Alce Nero Asia was established, a long-term relationship to expand the brand throughout the area.
Alce Nero has established itself as a pioneer in the organic food sector thanks to its dedication to sustainable agricultural methods and organic farming. The company’s commitment to quality and sustainability is evident in its product line, which features a variety of organic goods, including fresh and frozen meals and fruits and vegetables. Alce Nero’s success in the organic food sector is evidence of its dedication to quality and sustainability and its capacity to innovate in response to changing market conditions and consumer needs.
Objectives of the Report
This report’s primary goal is to give Alce Nero a thorough strategic analysis and company transformation strategy. The business must comprehend the existing market dynamics, competitive environment, and prospective prospects for development and innovation as it works to increase its presence and impact in the organic food sector. The purpose of the research is to examine the current business strategy of Alce Nero, assess its advantages and disadvantages, and pinpoint opportunities for innovation and growth. It will also look into the external environment, including market trends, customer behavior, and competitive pressures, to give a complete picture of the industrial landscape.
The potential of the Danish market for organic food will also be examined in the paper, along with significant trends, market size, and development prospects. Additionally, it will evaluate Denmark’s competitive environment by identifying the main rivals and their business strategies. The final objective is to identify and assess prospective Alce Nero market prospects in Denmark while offering specific suggestions for market entrance and business model improvement. The report’s last section will be the report’s implementation plan, which outlines the actions Alce Nero should take to take advantage of these possibilities and achieve sustainable development.
Consultant Role to Alce Nero’s Senior Management Team
Our position is diverse and essential to the company’s strategic decision-making process as consultants and advisors to the senior management team of Alce Nero. We have been tasked with offering unbiased, data-driven insights and suggestions to steer the company’s future course, notably in its effort to enter the Danish organic food market. The first thing we have to do is thoroughly examine the existing market situation and business model of Alce Nero. To do this, it is necessary to assess the company’s SWOT and the competitive environment in its primary market, Italy. To give a thorough grasp of the external environment and the forces in action, we will employ a variety of analytical frameworks, such as Porter’s Five Forces.
The present work is looking into potential new markets and comprehending the environment. To do this, thoroughly examining the Danish organic food market must pinpoint significant trends, consumer tendencies, and prospective entry opportunities. The competitive climate in Denmark will also be evaluated by identifying the key rivals and their corporate strategies. These conclusions will be used to identify and assess prospective commercial prospects for Alce Nero in Denmark. This will entail evaluating each opportunity’s attractiveness while considering market size, development potential, degree of competition, and compatibility with Alce Nero’s strategic goals and critical competencies.
Finally, suggestions for market entrance and business model development will be given. This will contain a thorough implementation strategy describing the actions Alce Nero must take to take advantage of the opportunities found. Continuous communication with Alce Nero’s senior management team will be maintained throughout this process to guarantee that the recommendations align with the organization’s vision, purpose, and strategic goals.
Mapping Alce Nero: Analysis AS IS
Brief History and Background of Alce Nero
The history of Alce Nero may be traced back to the 1970s, when representatives from the cooperative Alce Nero in the Marche area and Conapi, the National Bee Keepers’ Association created in 1984 by the former Cooperativa Apistica Valle dell’Idice, met in Emilia Romagna (Alce Nero International, 2023c). Both organizations had the same goal:
- A strong feeling of obligation to the Earth.
- Seeing the planet as a fruitful, living creature.
- The notion of organic farming as an agronomic and environmental technique for producing food and nutrition for people.
Alce Nero became a standout on the market when no law governing organic practice defied the norm. Their logo illustrates this by showing the Black Elk, the spiritual head of the Sioux Oglala tribe, riding in the opposite direction while conveying his message with great vigor to other regions, beyond boundaries and restrictions, suggesting that fresh ideas and new visions are always conceivable. Alce Nero has consistently strived to rid the land of pollutants, protect biodiversity, and show respect for the Earth and its people (Alce Nero International, 2023e). They work diligently and responsibly, deciding to offer respect to the people and places that continue to define our shared past.
The principal interpreters of their cuisine are the founding members of Alce Nero, the farmers. They decided to work as a whole food supply chain in 1978, picking the location, the workers, and the products to support their operation from the farm to the pantry. Over 10,000 hectares of land have been converted to organic farming by Alce Nero in Italy, and this surface area is still expanding (Alce Nero International, 2023d). They have decided to innovate continually. They are an open business, and their trip has taken them to Italy, where they now operate with an increasing amount of land used for organic farming.
Analysis of the Existing Business Model Using Relevant Frameworks
Alce Nero’s current business strategy, combining conventional and cutting-edge techniques, has helped the company establish itself as a top name in the organic food sector. The organization functions as a full-service food chain by selecting the land, the people, and the ingredients to nurture their endeavor from field to pantry. Alce Nero can control the whole production process using this strategy, guaranteeing its products’ high caliber and genuineness. Sustainable business practices and fair trade are critical to the company’s strategy. Most equity partners supporting Alce Nero and its dedication to organic farming supply its goods (Massa, 2015). Alce Nero can guarantee the quality of its raw materials and preserve a reliable supply chain thanks to its tight relationships with suppliers.
One of the most critical aspects of Alce Nero’s business plan is its distribution strategy. The business offers its goods through several channels, such as specialty shops, big-box retailers, independent small businesses, and direct Internet sales. Specialized retailers have emerged as Alce Nero’s most dependable traditional distribution route since they were the first to recognize their dedication to fair trade (Alce Nero International, 2023c). Alce Nero has been looking at fresh approaches to improve its rapport with clients and give them a sense of involvement in the company’s objective. An example of one of these programs is the “producer partners point of sale” scheme, which enables customers to buy a restricted range of Alce Nero goods straight from farmers and processing partner businesses.
Additionally, the business has started a challenging initiative to increase ownership in the company. The new shares will not grant owners the power to vote or receive dividend payments; instead, they may only be purchased by Alce Nero’s customers. However, the business will provide Alce Nero goods directly to the new owners at a significant discount. It is anticipated that Alce Nero’s consumers will feel more like a part of the community and that sales will improve due to this creative financing strategy (Alce Nero International, 2023e). In conclusion, Alce Nero’s business model is distinguished by its dedication to environmentally friendly procedures, tight ties with suppliers, varied distribution plans, and creative consumer interaction efforts. These factors have helped the business develop a significant foothold in the organic food sector and set itself up for expansion.
SWOT Analysis for Alce Nero in the Italian Market
A SWOT analysis provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Here is a SWOT analysis for Alce Nero in the Italian market.
Strengths
- Strong Brand Recognition: Alce Nero has become a dominant brand in the Italian organic food sector. Customers like the company’s devotion to sustainable farming and high-quality goods, which has helped it build a solid reputation.
- Control Over Supply Chain: Alce Nero operates as a whole food chain by choosing the land, the people, and the ingredients to support their business from the field to the pantry (Massa, 2015). With this approach, Alce Nero can maintain complete control over the production process, ensuring the excellent quality and authenticity of its products.
- Diversified Product Portfolio: Fruits, vegetables, fresh food, frozen food, and other organic items are available from Alce Nero in various forms. The firm can serve a wide range of customers because of its diverse product portfolio, which also helps to reduce the risks brought on by reliance on a particular product category.
Weaknesses
- Dependence on External Suppliers: Despite having tight ties to its suppliers, Alce Nero relies mainly on them to supply raw materials. Any supply chain interruption might impact the firm’s operations.
- Limited Presence in Online Retail: Although Alce Nero distributes its products online, the firm has a relatively small presence there. Given the rising internet buying trend, this may impede the company’s ability to develop.
Opportunities
- Growing Demand for Organic Products: Italian consumers are becoming more aware of the advantages of eating organic food, increasing the demand for organic goods. For Alce Nero, this trend offers a considerable possibility for expansion.
- Expansion into New Markets: By entering new markets, Alce Nero has the chance to grow domestically and globally. Customers in new markets may be attracted to the company’s high-quality items and well-known brand.
Threats
- Intense Competition: Italy’s organic food market is highly competitive, with many companies selling comparable goods. This fierce rivalry may harm Alce Nero’s market share and profitability.
- Regulatory Changes: The organic food sector is governed by strict laws. Any modifications to these rules may affect Alce Nero’s business practices.
Porter’s Five Forces for Alce Nero in the Italian Market
The organic food market, where Alce Nero works, is known for its fierce rivalry and strict rules. The framework provided by Porter’s Five Forces analysis helps to comprehend the competing forces at work and how they affect Alce Nero’s operations in the Italian market.
- The threat of New Entrants (Moderate): The demand for organic food has increased, bringing in new competitors. However, joining this industry requires significant investment in brand development, supply chain management, and organic certification. The well-known brand, vast supply network, and devoted customer base of Alce Nero act as entrance obstacles for potential rivals.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers (Low): Most of Alce Nero’s suppliers are equity partners who support organic farming and share the company’s principles. This intimate contact diminishes their ability to negotiate. Furthermore, the supply of organic raw materials has expanded due to the development of the organic farming industry, further weakening the negotiating position of suppliers.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers (High): The market for organic foods offers various options, giving consumers more negotiating power. However, this can be mitigated by Alce Nero’s excellent brand awareness and the perceived quality of its products.
- The threat of Substitute Products (High): Organic food may be substituted for in various ways, including conventionally cultivated foods and “natural” foods that do not fulfill organic certification requirements but are frequently seen as healthier than conventional alternatives. The high cost of organic goods also exacerbates the threat compared to these alternatives.
- Competitive Rivalry (High): The market for organic foods in Italy is very competitive, with several businesses offering similar products. Alce Nero competes with these companies based on product quality, brand familiarity, and dedication to sustainability. The business can keep a competitive advantage because of its reputation and devoted clientele.
Market Analysis of the Organic Food Industry in Italy
The COVID-19 outbreak considerably influenced the Italian organic food business, but the sector started to recover as customers began to demand organic goods again. Two thousand twenty-three, several trends will influence the Italian organic food market (Massa, 2023). These include:
- Food Traceability: Traceability is becoming critical for restaurants and customers, particularly meat products. Companies that are open about their procedures are more appealing.
- Technological Advancements: The sector has changed due to the growth of eCommerce, which has increased the variety of items accessible and improved B2B logistics. The technique may potentially be used in the actual manufacturing of food.
- Fast Delivery: Thanks to advancements in GPS applications and delivery drones, perishable Italian delicacies can be delivered faster to clients. This allows eateries to purchase fresh goods and serve them that same day.
- Demand for Shelf Life: The demand for food with an extended shelf life has increased. This presents a dilemma for producers of organic goods, as they must figure out how to extend the shelf life of their products without using chemicals.
Mapping the Landscape of the Danish Market Value Chain
Overview of the Organic Food Market in Denmark from Alce Nero’s Perspective
From Alce Nero’s perspective, Denmark’s organic food sector offers an extraordinary chance for development and growth. Denmark is seen as having a solid devotion to sustainable agricultural methods and organic farming, giving it a market that might be open to Alce Nero’s goods (Massa, 2023). The organic food industry in Denmark is established and developed, and organic goods are well recognized and welcomed by consumers. Denmark has one of the world’s highest per capita organic product consumption rates, which reflects this (Sørensen et al., 2020). The Danish organic food industry is characterized by intense rivalry, with several domestic and foreign businesses providing a broad selection of organic goods. Alce Nero’s distinctive value offer, which combines premium organic goods with a solid dedication to sustainability and fair trade, can help the business stand out in this cutthroat industry.
Alce Nero also needs help in the Danish market. It could be challenging for Alce Nero to take a significant market share because of the intense rivalry in the industry. Alce Nero may also need help due to Denmark’s strict requirements for organic certification, as the firm would have to ensure that its goods adhere to these requirements. Despite these difficulties, Alce Nero has a substantial possibility in the Danish organic food industry (Massa, 2023). Danish customers love strong brands, high-quality products, and a dedication to sustainability; thus, Denmark may provide Alce Nero’s expansion opportunities because of these factors.
Market Size, Expected Growth, and General Trends
With the most significant organic share and a steady growth tendency, the Danish organic food sector is one of the most developed in the world. Three out of four Danes purchased organic food weekly in 2020, and organic food sales climbed by 14% (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). Denmark had the most outstanding market share for organic products in 2020 (12.8%) compared to other nations; in 2020, Denmark’s organic sales totaled DKK 18.3 billion (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). Bananas, plant-based dairy, carrots, oats, natural yogurt, root crops, cabbage, milk, wheat, and eggs were the top-selling organic items in Denmark in 2020 (Organic Production and Trade, 2023). Dairy products made up one-fifth of all organic sales in the retail sector, followed by fruit and vegetables, which made up more than one-third.
Danish organic products are not just sold for household use. Danish organic goods were exported for DKK 2.8 billion in 2020 (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). Germany accounted for 44% of all exports for Danish organic enterprises, with Sweden, the Netherlands, and China rounding out the top five. The COVID-19 epidemic has presented difficulties for the Danish organic market, notably in the food service industry. However, the retail sector, which includes internet sales, continues to expand and now accounts for most organic sales. The demand for organic foods is anticipated to increase going forward, both locally and internationally. Danish businesses are in an excellent position to benefit from this trend because of Denmark’s strong standards for food safety and quality, its distinctive “farm-to-table” management system, and its capacity for innovation.
Description of the Industry Ecosystem and Its Composition
The Danish organic food sector is a dynamic ecosystem with high levels of integration and collaboration among its numerous players. In this ecosystem, organic farmers, food processors, merchants, consumers, and regulatory organizations are essential to the sector’s success. Organic farmers at the center of this ecosystem are dedicated to environmentally friendly agricultural methods that respect animal welfare (Alce Nero International, 2023d). They are backed by a network of wholesalers and processors that guarantee that organic products get to customers quickly and in good condition.
Online and offline retailers are essential to providing customers access to organic goods. In addition to selling organic goods, they also inform customers of the advantages of eating organic food, which increases demand. Danish consumers strongly favor organic goods, as evidenced by the fact that 13% of the country’s retail food industry comprises organic foods (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). The Danish organic food business is expanding because of consumer demand. There is a rising demand for organic products because of their increased awareness of their dietary choices and their effects on health and the environment. Because of this need, Denmark now imports more organic goods than it exports.
Retailers, both online and offline, greatly influence the availability of organic products to customers. They promote the advantages of eating organic food to customers and selling organic goods, increasing demand. Denmark’s retail food sector accounts for around 13% of all organic food sales, showing consumers strongly favor organic goods (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). The organic food business in Denmark is expanding primarily due to consumer demand. As a result of their rising awareness of their food choices and their effects on health and the environment, there is an increase in the market for organic goods. Danish imports of organic goods now outnumber exports due to this demand.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis for the Danish Market
The Danish organic food sector is marked by fierce competition because there are so many domestic and international rivals. This competition is driven by several factors, as outlined by Porter’s Five Forces model:
- The Threat of New Entrants: The Danish market for organic foods faces a comparatively high threat from new competitors. The industry has grown significantly over the past several years, drawing numerous companies (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). The market is appealing to new entrants due to the Danish government’s support for organic farming and the rising consumer demand for organic products. However, strict guidelines and certification standards for organic goods may be a barrier to entry.
- Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Suppliers in the Danish organic food industry need better negotiating power. Many suppliers are small-scale farmers who may have little negotiating power. However, the restricted supply of organic raw materials and the rising demand for organic goods may give them more negotiating power.
- Bargaining Power of Buyers: Consumers have significant negotiating power in the Danish organic food industry. Danish consumers are pretty picky about the foods they buy, and they are prepared to switch brands in exchange for more excellent quality, a lower price, or ethical reasons. The availability of various organic products from different companies further boosts customers’ negotiating power.
- The threat of Substitute Products: Substitute items provide a modest hazard. Although conventional food items are widely accessible and frequently less expensive, the rising knowledge of organic products’ health and environmental benefits makes these alternatives less appealing. However, replacements are available, such as locally sourced food or fair-trade goods.
- Competitive Rivalry: The Danish organic food industry is highly competitive. Numerous domestic and foreign brands are present and competing for market share. Price is only one aspect of the rivalry; other elements include product quality, brand reputation, and sustainability policies.
Top Competitors in the Danish Market and Analysis of Their Business Models
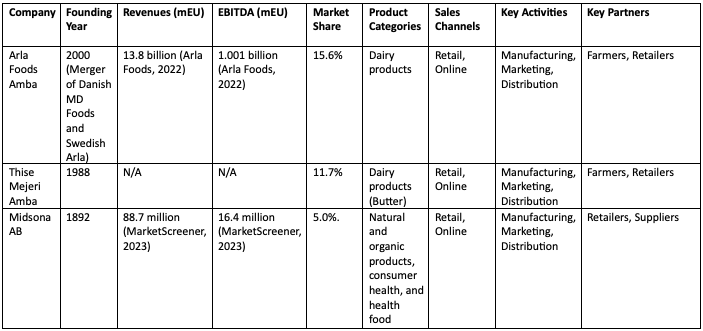
A multinational cooperative with a basis in Denmark is called Arla Foods. It is Scandinavia’s most prominent dairy product producer. Arla Foods emphasizes organic products and provides many organic dairy items like milk, cheese, and yogurt (Arla Foods, 2023). The firm is based on cooperative principles, with farmers serving as the company’s shareholders. As a result, Arla Foods can directly monitor the quality of its raw materials and guarantee that its goods are made sustainably and ecologically responsibly.
Danish dairy firm Thise Mejeri focuses on organic and biodynamic products. Since its founding in 1988, the business has become one of Denmark’s top organic dairies. The business strategy of Thise Mejeri is based on quality and sustainability. To achieve high animal care and environmental sustainability standards, the firm works closely with its farmers. The variety of goods available from Thise Mejeri includes milk, cheese, yogurt, and butter. A Swedish business with a focus on health and well-being is called Midsona. The business sells various organic goods, including food, health foods, and cosmetics. The core of Midsona’s business strategy is the provision of goods that support healthier and more environmentally friendly lifestyles. The business is well-established in the Nordic area and consistently extends its product line and market penetration.
Table 1 – Business Models of Top Three Competitors.
Opportunity Generation and Assessment
Identification of Potential Market Entry Opportunities for Alce Nero in Denmark
Alce Nero has several potentials to expand its footprint and grab a grip on the Danish organic food industry. Denmark, which has the largest market share in the world for organic food, has a receptive customer base that values sustainability, quality, and transparency—values consistent with the brand spirit of Alce Nero.
- Product Differentiation: Alce Nero may make use of its Italian history to promote distinctive, premium organic goods that are not already offered in the Danish market. This can include certain Italian product lines that set Alce Nero apart from its rivals (Alce Nero International, 2023b). Danish customers are recognized for appreciating high-quality foods, so they could be open to new items that combine the charm of Italian food with the advantages of organic food.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Alce Nero could consider partnering with Danish businesses or merchants in the area. Alce Nero might hasten its debut into the market by teaming up with companies with a presence and distribution system. Alce Nero’s dedication to organic and sustainable farming might be shared by retailers or other organic food brands, which could strengthen the company’s reputation and marketability.
- Private Labeling: Alce Nero may look at the potential to develop organic private-label goods for Danish merchants, given the popularity of private-label goods in Denmark. Taking use of the retailer’s well-established brand and client base can offer a way to join the market at a cheaper marketing and distribution cost.
- Online Sales and Direct-to-Consumer Channels: Alce Nero should consider creating an online presence in Denmark, given the growth of e-commerce and online buying. Alce Nero could reach a larger audience and satisfy the growing number of customers who prefer the ease of online purchasing by selling items directly to customers through an online store or well-known e-commerce platforms.
- Sustainability and Transparency Initiatives: Danish customers may be drawn to Alce Nero by their unwavering dedication to ethical business conduct and sustainable farming. These characteristics may act as Alce Nero’s distinctive selling factors in the Danish market due to rising consumer knowledge of, and concern about, sustainability and transparency in food production.
Alce Nero should consider the cultural, commercial, and legal distinctions between Japan and Denmark while replicating the Japanese experience. While specific tactics could be transferrable, a customized strategy that takes into account the unique traits and preferences of Danish customers is likely more successful. Alce Nero could have to modify its current business strategy to take advantage of Denmark’s prospects. This can entail creating brand-new goods for Danish customers, partnering with regional companies, investing money into online sales channels, and boosting its sustainability and transparency programs (Massa, 2023). These possibilities need to be further assessed for viability, possible ROI, and compatibility with Alce Nero’s larger company goals.
Analysis of Competitor Business Models in Denmark and Identification of Innovation Opportunities
The organic food market in Denmark is a vibrant ecology that is constantly changing. A wide range of stakeholders defines it, such as growers, processors, merchants, consumers, and regulatory organizations. Farmers who grow organic food and raise organic livestock are the foundation of the environment (Ditlevsen et al., 2019). They uphold rigorous organic agricultural guidelines that forbid using artificial fertilizers and pesticides and support environmental sustainability. Danish farmers are devoted to attaining the global sustainable development goals of the UN, with a heavy emphasis on enhancing sustainability on farms and sustainable production.
Raw agricultural output is transformed by processors, including food and beverage producers, into a wide range of organic goods. These include processed foods like dairy, meat, packaged meals, and fresh fruits and vegetables. The expansion of organic food production in Denmark has been facilitated by several small, innovative firms as well as significant multinationals with strong organic reputations (Ditlevsen et al., 2019). In the ecosystem, retailers are essential because they act as a conduit between organic farmers and customers. They include grocery stores, farmers’ markets, and specialty organic stores. Consumers in Denmark lead the globe in organic food consumption. Compared to any other nation in the world, Denmark has the most significant market share for organic food, and annual consumption is rising.
Consumers make up the demand side of the ecosystem; they strongly prefer organic goods due to worries about their health, the environment, and animal welfare. Every other liter of milk drank by students in Danish schools bears the red organic label, and one in three liters of milk purchased by Danish customers is organic. Additionally, demand for organic fruits and vegetables has increased among consumers. Regulatory organizations keep an eye on the organic industry and ensure all rules and regulations are followed. The first country to adopt an organic label, organic standards, and open inspections was Denmark (Ditlevsen et al., 2019). It was the first country to create an organic action plan. The creative political strategy has fueled the growth of the organic industry in Denmark as well as new markets and expertise.
Assessment of Opportunity Attractiveness
Alce Nero must take into account several essential aspects when determining how appealing the Danish organic food industry is to him. An attractiveness map, which maps future possibilities depending on their level of difficulty and potential effect, can be used to illustrate these characteristics.
- Market Size and Growth: In terms of market share, the Danish organic food industry is the biggest in the world, with organic foods accounting for around 13% of the overall retail food market in 2020 (Kaad-Hansen, 2022). This is encouraging for Alce Nero since it shows a substantial degree of customer acceptance and demand for organic products. Moreover, this indicates that Alce Nero has room to develop and diversify in this market.
- Consumer Preferences: Danish customers strongly choose organic goods, which is a result of their concerns for the environment, human health, and animal welfare. They like organic milk, eggs, oats, wheat flour, carrots, and bananas over conventional counterparts. The products offered by Alce Nero, which include organic fruits, vegetables, cereals, and honey, go well with this. This shows that Danish consumers’ preferences and the items offered by Alce Nero are a good fit.
- Regulatory Environment: Denmark has a strict regulatory structure, with frequent inspections and high requirements, for organic goods. Alce Nero may find this difficult since it must assure adherence to these criteria. However, it also offers a chance since it can increase customer faith in Alce Nero’s goods.
- Competition: There are numerous well-established businesses in the competitive Danish organic food sector. Alce Nero may be able to set itself apart and acquire a competitive advantage, nevertheless, thanks to its strong brand and reputation for producing organic goods of the highest caliber.
- Distribution Channels: With a well-established distribution network, the Danish organic food industry offers a wide range of organic foods in supermarkets, specialized organic stores, online merchants, and farmers’ markets. Alce Nero now has the chance to connect with a variety of customers.
These elements make the Danish organic food sector a compelling business potential for Alce Nero. The market size, growth potential, consumer preferences, and distribution channels all point to Alce Nero having a good chance of succeeding in this market despite certain obstacles, including the competitive climate and regulatory compliance. To increase its chances of success, the firm will need to carefully analyze all aspects of its market entrance plan, including product selection, price, distribution, and marketing.
How to Play: Implementation and Recommendations
Arguments Supporting the Selected Opportunities and Key Assumptions
Alce Nero’s potential in the Danish organic food industry is supported by a number of solid justifications and fundamental presumptions. The quality organic products Alce Nero offers, and its Italian heritage give it a competitive edge in the Danish market (Massa, 2023). The justification for this chance rests on the supposition that Danish customers, who are renowned for their high standards and desire for quality, will be drawn to Alce Nero’s distinctive and genuine offers. In a market where customers are increasingly concerned about the environmental and social implications of their food choices, the company’s dedication to sustainable farming and open business procedures further increases its attractiveness.
Alce Nero may be able to gain access to established distribution networks and a local client base by establishing agreements with Danish businesses or merchants in the area. The justification for this chance is predicated on the supposition that Danish businesses and merchants would be amenable to working together and see the advantages of doing business with a respected worldwide brand like Alce Nero. Danish consumers’ preference for private-label products gives Alce Nero the opportunity to enter the market with lower marketing and distribution costs (Massa, 2023). The case for this possibility is predicated on the notion that Danish merchants are receptive to private-label cooperation with Alce Nero and are interested in extending their selection of organic goods.
Alce Nero now has the chance to reach a larger audience and appeal to the rising number of customers who prefer the ease of online buying thanks to the growth of e-commerce and online shopping. On the premise that Danish customers are at ease with online buying and that Alce Nero can successfully handle the logistics of online sales and delivery, the case for this possibility is made. Alce Nero might have an advantage in the Danish market thanks to its steadfast dedication to ethical business conduct and ecologically friendly farming (Massa, 2023). The rationale for this opportunity is based on the notion that Danish consumers value sustainability and openness and will gravitate toward a company that succinctly and clearly communicates its dedication to these principles.
Concrete Actions and Recommendations for Alce Nero to Implement the Chosen Opportunities
Based on the identified opportunities and their attractiveness, the following concrete actions and recommendations can be proposed for Alce Nero:
- Alce Nero needs to use its Italian ancestry and premium organic products to set itself out in the Danish market. The business may achieve this by conducting market research to see which specific organic items from Italy Danish customers would be interested in. By creating these goods next, ensure they adhere to the excellent standards for which Alce Nero is renowned. Marketing campaigns should emphasize how these items’ unique Italian history sets them apart from other options in the Danish market.
- Alce Nero ought to try to work with local Danish companies or traders. This can include looking for partners that are well-known in the Danish market and who share Alce Nero’s appreciation of organic and sustainable farming. Alce Nero might propose cooperation to these potential partners and outline the advantages that could be gained by both sides. This can entail teaming up on marketing initiatives, gaining access to existing distribution networks, and providing customers with a broader selection of organic goods.
- Alce Nero could look at options to make organic private-label goods for Danish stores. This would include finding merchants that share Alce Nero’s beliefs and are eager to increase their selection of organic goods. Then, Alce Nero may collaborate with these merchants to create private-label goods and make sure they adhere to the same high standards as Alce Nero’s own goods.
- Alce Nero should consider setting up shop in Denmark. This may mean opening an online store or selling products via reputable Danish e-commerce platforms. Building a user-friendly website and a successful internet marketing strategy would require investment from Alce Nero. Email marketing, social media, and search engine optimization may all be necessary to connect with and engage Danish consumers.
- Alce Nero could use its dedication to ethical business conduct and sustainable farming as a selling point. This might entail making sure to inform Danish consumers about the company’s environmental activities and practices online and on product packaging. To further boost its reputation, Alce Nero can think about gaining certifications or endorsements from reputable sustainability groups in Denmark.
Roadmapping the Implementation Process Considering Value Proposition, Main Assumptions, and Potential Challenges
The implementation of the chosen opportunities for Alce Nero in the Danish organic food market can be road-mapped as follows:
- Conducting market research to discover certain Italian organic items that Danish customers would be interested in would be the first stage in this process. Alce Nero can start working on creating these items once they have been identified. This can entail finding the required components, putting product formulas through testing, and making sure the goods live up to Alce Nero’s high standards. The items can be introduced to the Danish market once they have been created. The distinctive Italian heritage of these products should be highlighted in the marketing campaigns as a way to differentiate them from competing products in the Danish market.
- Finding suitable partners would be the first step in creating collaborations with local Danish businesses or stores. After locating suitable partners, Alce Nero can approach them and suggest working together. If the idea is approved, the following stage would be to iron out the specifics of the partnership, such as the terms of the contract, the obligations of each party, and the anticipated results. Alce Nero can start selling its products through its partner’s distribution channels once the collaboration is created.
- Alce Nero would first need to find Danish shops interested in increasing their selection of organic goods in order to take advantage of this potential. After seeing these merchants, Alce Nero can approach them and offer a private-label collaboration. Alce Nero can start creating and developing private-label products if the request is approved. To do this, it would be necessary to guarantee that the goods adhere to the same high standards as Alce Nero’s own goods.
- Setting up an online store or selling goods through well-known e-commerce platforms in Denmark would be required to establish an online presence in Denmark. This would need spending money on creating a user-friendly website and putting up a successful internet marketing plan. Alce Nero can start selling its items online once the web store is set up.
- In order to take advantage of this potential, Alce Nero must effectively inform Danish customers about its environmental goals and practices. This can entail promoting Alce Nero’s environmental activities through both online and offline marketing strategies, as well as revising product packaging to incorporate information about these programs. Alce Nero can think about getting accreditations or support from respectable sustainability organizations in Denmark to enhance its standing even more.
Conclusion
Key Findings
- According to market share, the Danish organic food market is the biggest in the world, which shows that there is a high degree of consumer demand and acceptability for organic goods. With annual growth rates of 20% in the food service industry during the last 10 years, the market is also expanding.
- Because of their concerns for the environment, human health, and animal welfare, Danish consumers strongly favor organic products. Compared to their conventional counterparts, they prefer organic milk, eggs, oats, wheat flour, carrots, and bananas.
- In the cutthroat Danish organic food market, there are several well-known companies. However, with its strong brand and reputation for creating the best organic products, Alce Nero could be able to differentiate itself and gain a competitive edge.
- For organic products, Denmark has a stringent regulatory framework with regular inspections and rigorous standards. Since it must ensure adherence to these criteria, Alce Nero might find this challenging. But it also presents an opportunity because it can boost consumer confidence in Alce Nero’s products.
Recommendations
- To make a name for itself in the Danish market, Alce Nero must use its Italian heritage and high-quality organic products. This may entail creating specialized organic products from Italy that Danish customers would find appealing and successfully selling them.
- Alce Nero should look to collaborate with regional Danish businesses or merchants. This may entail seeking out partners that value organic and sustainable farming as much as Alce Nero does and who is well-known in the Danish market.
- Alce Nero might consider producing private-label organic products for Danish retailers. This would entail locating retailers that are willing to expand their inventory of organic products and who hold similar values to those of Alce Nero.
- Alce Nero ought to think about creating a website in Denmark. This can entail establishing an online store or selling goods through well-known Danish e-commerce websites.
- Alce Nero might leverage its commitment to sustainable farming and moral business practices as a selling advantage. This may mean making sure that Danish customers are aware of the company’s environmental policies and initiatives both on the company’s website and on the packaging of its products.
Overall Summary of the Strategic Innovation and Business Transformation Process
Alce Nero’s possible entry into the Danish organic food market has been the subject of a strategic innovation and business transformation process that has involved a thorough investigation of the Italian and Danish markets as well as the company’s own strengths and shortcomings. An extensive review of Alce Nero’s present business model, including its product offers, value proposition, and market position in Italy, served as the starting point for the procedure. Alce Nero has a strong brand and a reputation for producing organic goods of the highest caliber, which might provide a robust platform for its entry into the Danish market.
The Danish organic food market’s geography was mapped in the following stage. Understanding the market’s size, growth trends, customer preferences, and competitive environment was necessary for this. With a sizable and expanding demand for organic goods and a customer base that values sustainability and transparency, the Danish market was found to be quite alluring (Hurtado-Barroso et al., 2019). Alce Nero was given a number of opportunities as a result of this agreement. These included efforts to differentiate products, form alliances and partnerships, use private labels, sell products directly to consumers online, and promote sustainability and transparency. Each of these chances was assessed for appeal and viability, resulting in a list of specific suggestions for Alce Nero.
Utilizing Alce Nero’s distinctive advantages and matching them with the prospects in the Danish market are the advised tactics. Alce Nero’s Italian origin and premium organic products, for instance, may be leveraged to set its offers apart in the Danish market. Similar to this, Alce Nero’s dedication to ethical business conduct and sustainable farming might be used to win over Danish customers. These plans will need to be put into action with careful preparation and coordination. Alce Nero will need to create particular goods for the Danish market, form alliances with regional businesses or shops, look at the potential for private labeling, establish a web presence, and successfully promote its environmental goals. There will be difficulties associated with each of these processes, but with proper preparation and execution, they may be effectively overcome.
In conclusion, the process of corporate transformation and strategic innovation for Alce Nero’s introduction into the Danish market is challenging but worthwhile. It entails comprehending the market dynamics, spotting opportunities, coming up with plans, and successfully putting them into action. Although there are obstacles in the road, the potential benefits are substantial. Alce Nero has the potential to build a significant position in the Danish organic food industry and find long-term success because of its powerful brand, top-notch goods, and dedication to sustainability.
References
Alce Nero International. (2023a). Alce Nero International. Web.
Alce Nero International. (2023b). About us. Alce Nero. Web.
Alce Nero International. (2023c). Our shareholders. Alce Nero. Web.
Alce Nero International. (2023d). Our farmers. Alce Nero. Web.
Alce Nero International. (2023e). Our Sustainability Report. Alce Nero. Web.
Arla Foods. (2022). Annual Report 2022. Arla. Web.
Arla Foods. (2023). Arla. Solid performance and sustainability action in another volatile year. Web.
Ditlevsen, K., Sandøe, P., & Lassen, J. (2019). Healthy food is nutritious, but organic food is healthy because it is pure: The negotiation of healthy food choices by Danish consumers of organic food. Food Quality and Preference, 71, 46-53. Web.
Hurtado-Barroso, S., Tresserra-Rimbau, A., Vallverdú-Queralt, A., & Lamuela-Raventós, R. M. (2019). Organic food and the impact on human health. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, 59(4), 704-714. Web.
Kaad-Hansen, L. (2022). Facts and figures about Danish organics. Organic Denmark. Web.
Massa, L. (2023). Alce Nero – looking at the Nord to transform the business.
Massa, L. (2015). Alce Nero – Towards a New Business Model for Organic Food. IESE Publishing.
MarketScreener. (2023). MIDSONA AB (PUBL): Financial data forecasts, estimates, and expectations. Web.
Organic production and trade. (2023). Statistics Denmark. Web.
Sørensen, N. N., Sørensen, M. L. K., Trolle, E., & Lassen, A. D. (2020). Organic food in public catering: How the Danish organic cuisine label may maintain organic food production in the longer term. Journal of Culinary Science & Technology, 18(4), 255-269. Web.