The evolution of Amazon’s distribution systems and supply chain
The evolution of Amazon’s supply chain and distribution systems in the United States was caused by several internal and external forces. First of all, the sales rate of this company rose significantly, and this organization had to improve its capacity to process the orders that customers placed.
Secondly, Amazon faced the competition of such retailing companies as Barnes & Noble or CDNow. Amazon’s responded to these problems by increasing the number of items that it sold to customers and improving its internal operations. This strategy required the development of supply chain and distribution systems.
On the whole, one can argue that Amazon acts as a part of two-tier distribution network distribution when there are intermediaries between manufacturers and customers. Amazon has established partnerships with wholesalers and some of the most important publishers. It is possible to use a diagram to illustrate American distribution network of Amazon
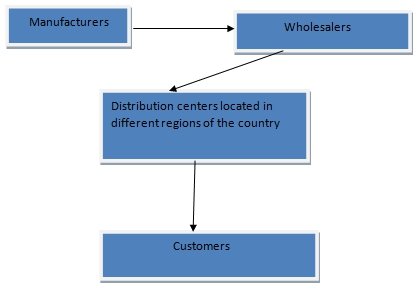
This diagram shows that Amazon can be regarded as a second-tier company that does not deal directly with producers. They interact primarily with various wholesalers that provide Amazon with a variety of goods. At the beginning, when Amazon was only a book retailer, the company attempted to procure books directly from publishers, but these organizations could not ensure the fast delivery of goods.
Additionally, one can say that Amazon pays close attention to the performance of its distribution centers. Moreover, the company makes significant investments its information system that ensured the fast delivery of goods to the customers.
The inventory management policy of the company
The inventory management policy of Amazon has several distinctive elements that are aimed at reducing the operational costs. For example, one can speak about such a technique drop-ship orders which means that wholesalers delivers goods directly to buyers without storing them at the distribution centers of Amazon.
Secondly, the company adopts software solutions that enable them to forecast the demand for different types of products. Additionally, Amazon has a set of rules according to which various wholesalers are evaluated. The most important evaluation criteria are the delivery options and the price. Overall, their policy is aimed at reducing the volume of goods that are stored directly at the distribution centers of Amazon. This approach is quite suitable for the needs of a large online retailer that has to sell a variety of goods.
There are several models that can be partly applicable to Amazon. In particular, one can speak about Economic Order Quantity or EOQ model. This model is based on a formula which enables a company to estimate the quantity of goods that a company should hold in order to avoid two extremes, oversupply and shortage of good. Amazon does apply software solutions that help to estimate the demand for a certain product.
Nonetheless, one should note that EOQ approach has several limitations. It is based on the assumption each supplier meets its schedule and that the demand curve does not have significant deviations. However, these requirements are not always met. Another approached adopted by companies is a saw-tooth inventory model.
According to it, the company’s stores should be replenished at certain intervals; moreover, these intervals can be accurately estimated. Yet, this approach is not quite relevant to Amazon, because this organization relies on the quick transfer of data from customers to suppliers, rather than the estimation of demand.
Another strategy that can be discussed is periodic inventory management. According to it, managers should count the items stored at a warehouse and compare their findings with the receipts or electronic data. In this way, they can determine whether there are goods that have been taken into account. This method can be relevant to a company like Amazon since this organization operates a variety of distribution centers and it is possible that there databases were not properly updated.
The problems that Amazon faced in Europe
There were several supply management issues that Amazon faced when it began to operate in the European market. First of all, the number of wholesalers in Europe was much smaller, especially in comparison with the United States. For instance, one can mention that in Germany there was only one book wholesaler.
Thus, it means that this organization could easily dictate its terms to Amazon. In order to mitigate this risk the company established many partnerships with publishers and distributors. Secondly, Amazon had to ensure the speed of delivery in order to gain the loyalty of European customers.
This is why the management of Amazon decided to cooperate with national postal services. These organizations functioned very efficiently, especially in such countries, as England, France, or Germany. Nonetheless, a significant problem remained unaddressed, because these postal carriers were not effective in cross-border logistics.
In effort to address these problems, Amazon enabled its customers to choose the distribution center from which the ordered goods could be delivered as soon as possible. These are the ways in which this company attempted to resolve the problems that it encountered in Europe.
There were other challenges that were indirectly related to supply chain management. This company had to operate in countries with different cultures and labor relations. The employees had to have knowledge of various suppliers that could operate in France, Germany, or England. For instance, they hired people, who had worked in the French media industry, in order to establish better relations with suppliers.
PRM and CRM of Amazon
The success of Amazon can in part be explained by its policies on customer relations management (CRM) and partner relations management (PRM). The first term refers to the practices that a company adopts in order to manage its relations with clients and retain them. In turn, the second term can be defined as a set of strategies that facilitate their interactions with suppliers or distributors.
These tasks are of great importance to Amazon, because this organization has to make sure that customers could receive the purchased goods as quickly as possible; at the same time, they helped wholesale vendors or manufacturers better distribute their products.
In order to improve its CRM and PRM the management had to find a way of integrating these activities and improve the flow of information between suppliers and clients. To a great extent, this goal was achieved through the use of EDI (Electronic Data Exchange).
This system was used to transfer the information about the orders directly to the suppliers. When a person placed an order at Amazon, this application sends a request to one of suppliers and this organization could either confirm a request or reject it when a certain product is out of stock. On the whole, this interaction can be illustrated with the help of a diagram:
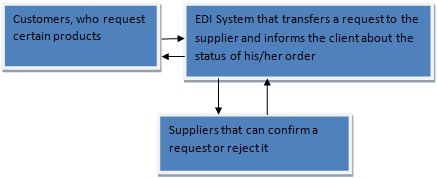
Suppliers that can confirm a request or reject it
One can argue that EDI system is supposed to act as an intermediary between suppliers and clients. Overall, this application is instrumental for sales automation of sales and effective interaction with clients who want to know whether Amazon has already processed their orders.
Pull-push strategy
Push-pull strategy is one of the concepts that play an instrumental role for marketing and supply chain management. The term push strategy means that a manufacturer or distributor makes an offer to the customer who can either accept or reject it. The main peculiarity of this approach is that a buyer is not able to contact the company and place an order.
In contrast, push strategy means that a buyer first makes a request and only later his/her order is processed by producers or distributors. Each of these models has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, push strategy can often result in oversupply of materials and inventory, while pull strategy can make the company unable to meet the demand of the clients. These are the main factors that should be taken into account.
Overall, one can argue that Amazon adopts a pull strategy and their work is demand-driven. There are several reasons why this organization adopted this strategy in the United States and abroad. The main factor is the inability to forecast the demand for goods. Admittedly, Amazon used software solution that could estimate approximate demand for product, but these tools were not always accurate.
Secondly, this management of Amazon wanted to reduce its inventory levels to the minimum. This was possible only if the company adopted push strategy. Certainly, the policies of Amazon could be affected by other factors such as the number of wholesalers in a country or the level of demand. They had to increase the number of distribution centers in order to avoid the undersupply of goods. Nevertheless, in most cases, this organization relied on the pull strategy.
Facilitators in the Amazon’s supply chain
One can identify several facilitators that improve the work of Amazon’s supply chain. In particular, special attention should be paid to the role of various software solutions that helped Amazon to process customers’ orders as quickly as possible. Secondly, it is important to speak about the presence of many distribution centers and warehouses. In this way, this retailer was able to decrease the time it took to deliver the order to buyers.
One of the practices that Amazon can adopt is cross-docking. This term is used to describe a logistics method according to which the products are directly transferred by a manufacturer or wholesaler to the customer. In most cases, they are not stored or handled by a retailer.
Additionally, this approach implies that goods are stored at distribution centers or warehouses for a minimum amount of time. In part, Amazon adopted this practice. If a wholesaler has an opportunity to reach the buyer, Amazon only provides this organization with the address of the client without handling or storing the product. This method helps Amazon to decrease the delivery time. Overall, the following diagram can better illustrate this interaction.
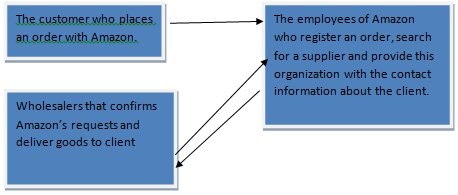
Thus, Amazon often acts only as an intermediary and in such cases the operational costs of this company are reduced to the minimum. Yet, cross-docking is possible only when wholesalers and customers are located in one geographic area. In other cases, Amazon has to store and handle the purchased items.