PESTLE Analysis
Political factors affecting British Airways are Brexit and the removal of travel restrictions. Brexit may impose certain barriers to companies operating globally, including British Airways, forcing them to search for ways to overcome these barriers (Brezonakova, Badanik and Davies, 2021). In contrast, the removal of travel restrictions is a positive political factor. The restriction-free environment facilitates the aviation industry’s recovery and increases the demand for airline services (Department for Transport et al., 2022). Thus, British Airways’ situation is likely to improve with new regulations.
Economic factors include the pandemic’s impact and increasing fuel prices. The government measures taken to contain the virus caused British Airways to report a total operating loss of €7.4 billion in 2020 (Sweney and Topham, 2021). As for fuel prices, the International Air Transport Association (2022, p. 18) states that “in 2021, the airline fuel bill increased by almost 30%.” In 2022, fuel expenses will rise further due to a surge in oil prices resulting from the Russia-Ukraine conflict (International Air Transport Association, 2022). Since fuel is one of the key expenses in the airline industry, this change is crucial for British Airways.
The most important social factor is customer attitudes toward the brand. In the annual report, British Airways Plc (2021) regards the erosion of the brand and a failure to meet customer’s expectations as principal risks. This risk is significant because a recent survey of customer satisfaction revealed that British Airways was the second worst in a ranking of the six best short-haul airlines in the UK (Hobbs, 2022). Flight cancellations and refusals to refund damaged British Airways’ brand image, which may affect the company’s future profitability.
Technological factors include IT systems and IT infrastructure. The need to invest in solid IT infrastructure is driven by high fixed costs, security dependence, and competition intensity since technology assists companies in fleet planning, reservations, flight management, and other operations (Heiets, I. et al., 2022; Lubbe, B. and Potgieter, 2018). Flawed or obsolete IT systems in airline companies can lead to operational issues and a loss of competitive advantage.
The most important legal factor is non-compliance with laws and regulations. For example, in 2018, a data breach occurred in British Airways, affecting over 400,000 people and resulting in a fine of £20 million (BBC News, 2021). Although this legal claim was subsequently settled, it shows that a company’s failure to comply with laws and regulations can result in fines, financial losses, and reputational damage.
The most important issue among the environmental factors is decarbonization. Since airline companies are criticized for greenhouse gas emissions, many companies in this industry include emission-reducing activities in their corporate social responsibility agenda (Mayer, 2018). Thus, since British Airways has to comply with international environmental regulations and meet customers’ expectations regarding sustainability, the company is motivated to invest in developing fuel-efficient aircraft models and transitioning to carbon-neutral flights.
An analysis of different factors influencing British Airways suggests that political, economic, and legal factors seem to be the most important. In particular, Brexit influences how British Airways will operate on new terms with European countries. The consequences of the pandemic and an increase in fuel prices directly influence the company’s revenues and profitability. Finally, non-compliance with regulations can lead to substantial financial losses and reputational damage.
Financial Analysis
British Airways is a segment of International Consolidated Airlines Group SA (IAG). Its financial performance was stable until 2019; for example, in 2018, the firm’s net income was $3.4 billion, decreasing to $1.9 billion in 2019 (see Figure 1). In 2020, the company had a loss of over $7 billion and then began a slow recovery (Macrotrends, 2022). As Figure 1 shows, other companies in the industry also had negative net incomes in 2020-2021.
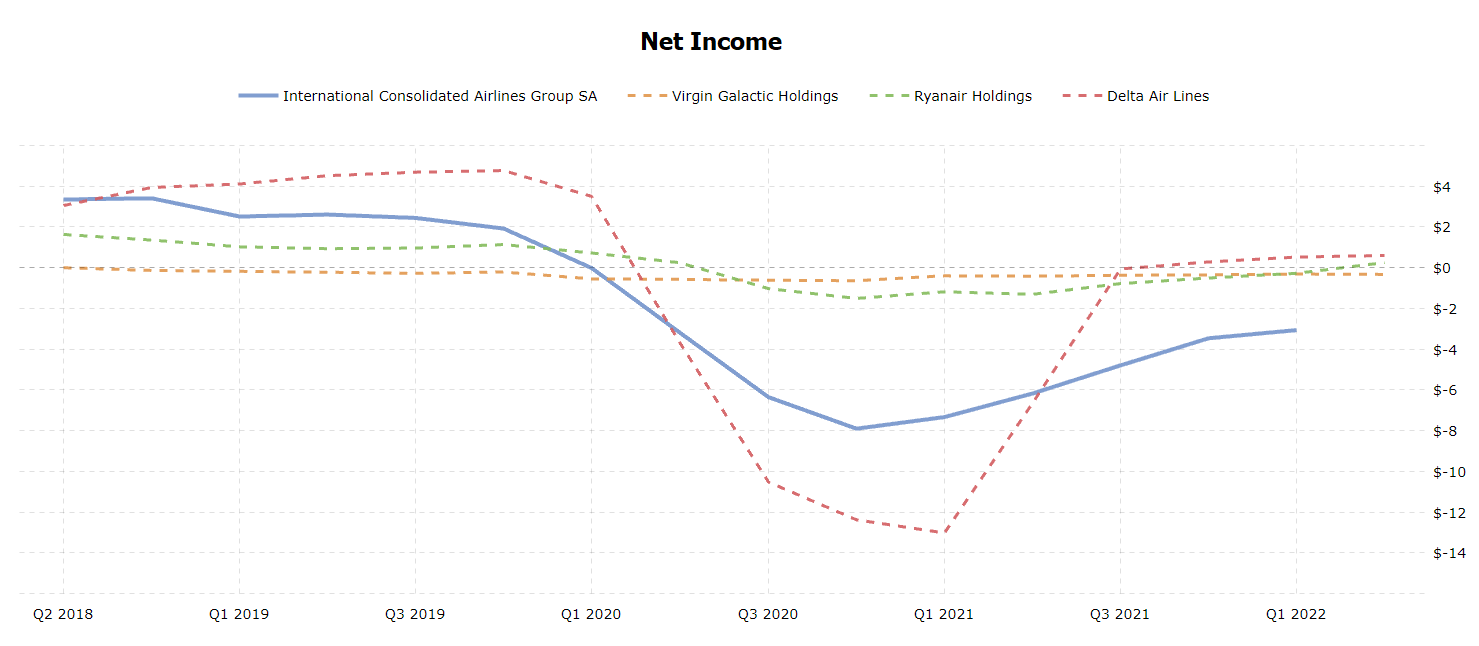
Further, some key financial ratios will be analyzed and compared. According to Perçin and Aldalou (2018), important solvency ratios include Quick Ratio, Current Ratio, and Debt-to-Equity Ratio, while profitability ratios are Return on Sales (Operating Margin) and Return on Assets. Quick Ratio shows the company’s short-term liquidity; in British Airways, this indicator was at its lowest in 2020, similar to Ryanair (see figure 2).
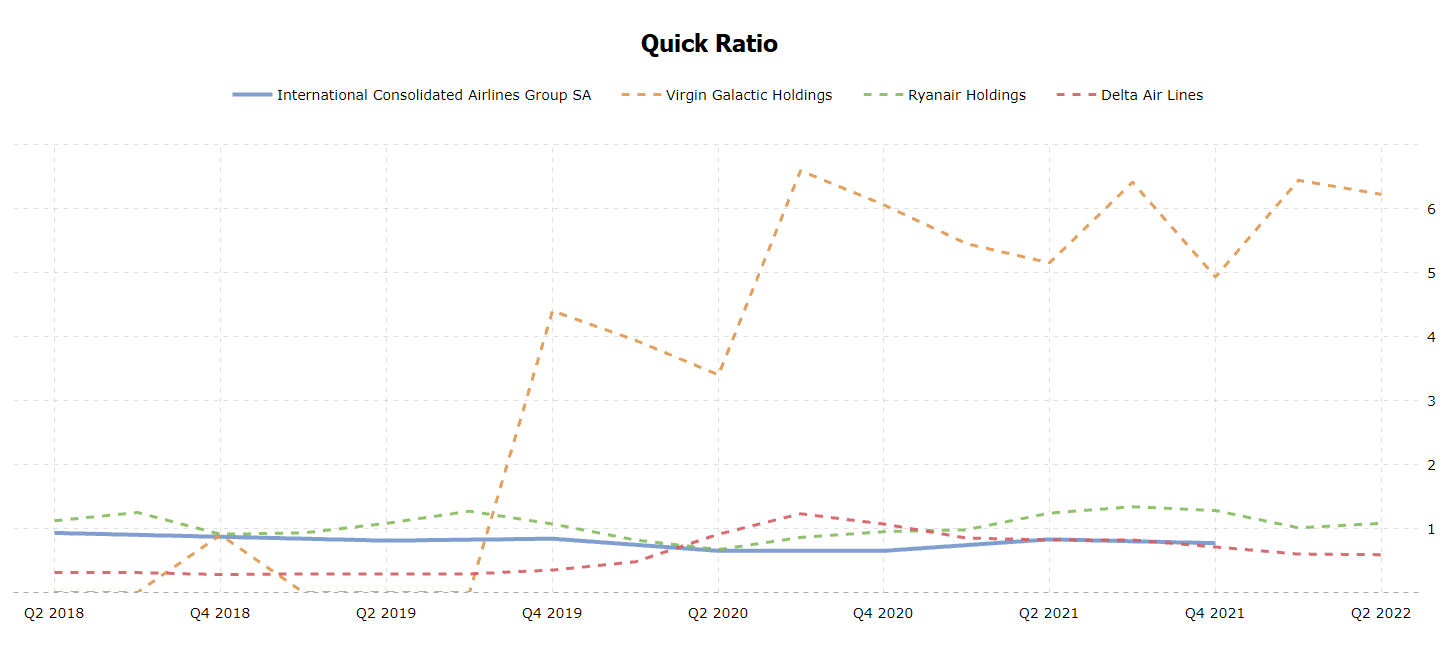
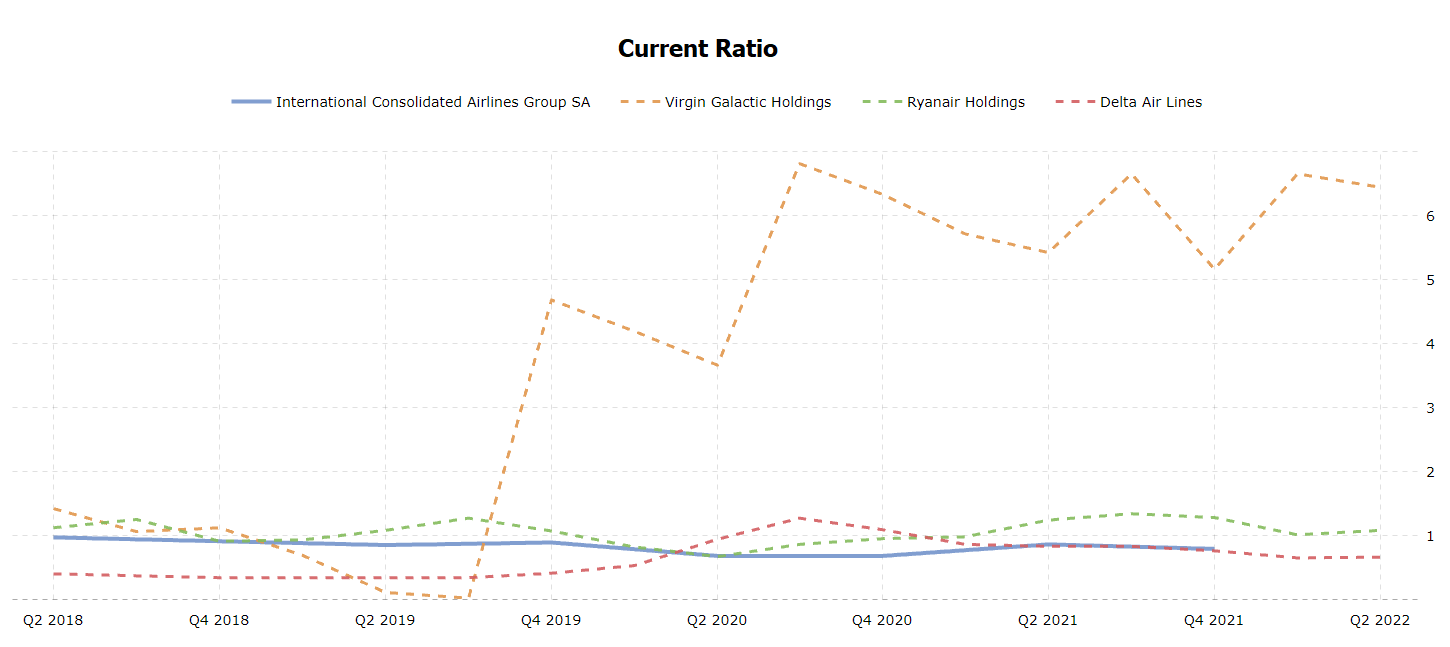
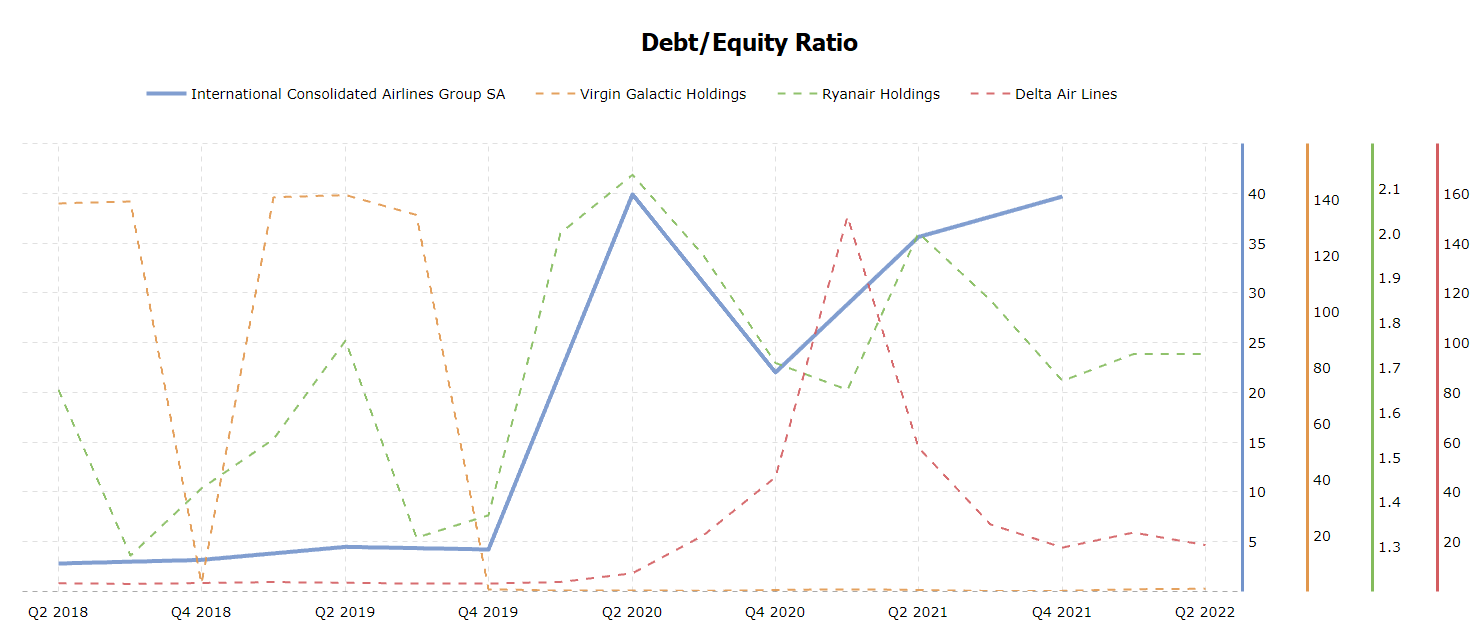
While both Quick Ratio and Current Ratio measure liquidity, the former refers to highly liquid assets, while the latter considers current assets. British Airways’ Current Ratio changed over time similarly to its Quick Ratio, like in other airline companies (see figure 3). Since 2019, airline companies have increased their reliance on debt (see figure 4). Figure 5 demonstrates that since 2020, British Airways and similar companies have begun to earn less money on their assets. Finally, figure 6 indicates that in 2020, airline firms had a low proportion of revenues available for covering non-operating costs.
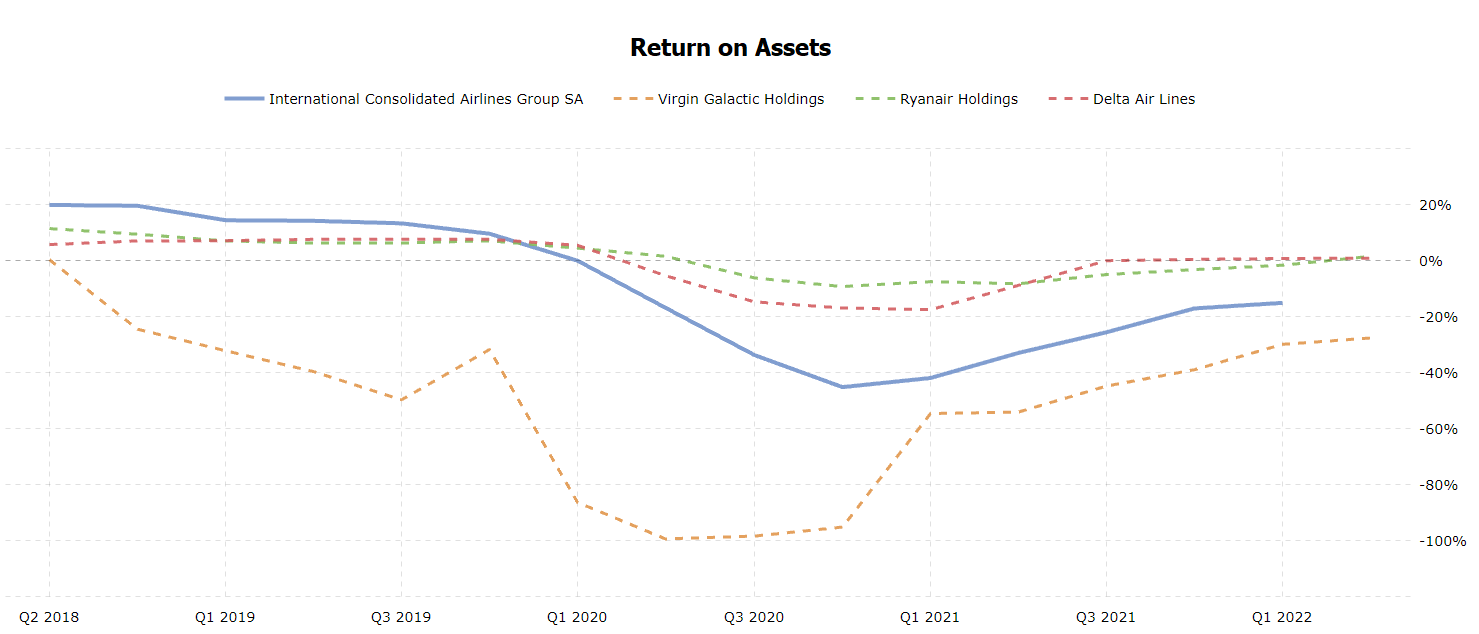
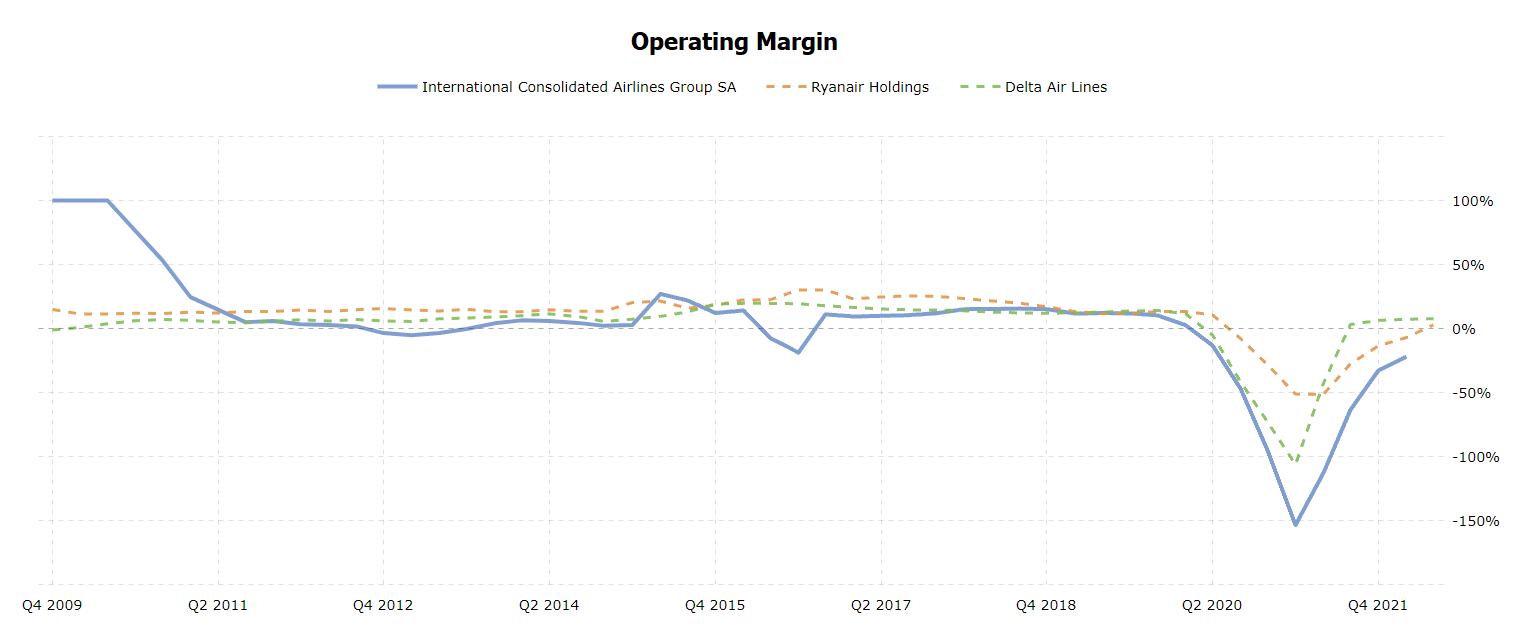
The real-world events explaining these changes are related to the COVID-19 pandemic. This crisis led to lockdowns and travel restrictions, anxiety in global financial markets, and a reduction in workforce and fleet in airline companies (British Airways Plc, 2020; Institute for Government, 2021; Maneenop and Kotcharin, 2020). From the figures, one may conclude that the pandemic led airline companies to financial losses. The graphs also reflect that the situation improved in 2021, and the airline industry is experiencing a recovery.
Reference List
BBC News (2021) ‘British Airways data-breach compensation claim settled’, Web.
Brezonakova, A., Badanik, B. and Davies, R. (2021) ‘Brexit in Air Transport after 2020’, SHS Web of Conferences, 92(09001), pp.1–8.
British Airways Plc. Annual report and accounts: year ended 31 December 2020.Web.
British Airways Plc. Annual report and accounts: year ended 31 December 2021. Web.
Department for Transport et al. (2022) ‘All COVID-19 travel restrictions removed in the UK’,GOV.UK, Web.
Heiets, I. et al. (2022) ‘Digital transformation of airline industry’, Research in Transportation Economics, 92, p.101186.
Hobbs, G. ‘Best and worst airlines in 2022’, Which?, Web.
Institute for Government (2021) Timeline of UK government coronavirus lockdowns and restrictions. Web.
The International Air Transport Association (2022) Global outlook for air transport: times of turbulence. Web.
Lubbe, B. and Potgieter, T. (2018) ‘The role of technology in airline management and operations’, in Halpern, N. and Graham, A. (eds.) The Routledge companion to air transport management. New York: Routledge, pp.331-343.
Macrotrends (2022) International Consolidated Airlines Group SA net income 2010-2022 | ICAGY. Web.
Maneenop, S. and Kotcharin, S. (2020) ‘The impacts of COVID-19 on the global airline industry: an event study approach’, Journal of Air Transport Management, 89, p.101920.
Mayer, R. (2018) ‘Airline sustainability and corporate social responsibility’, in Halpern, N. and Graham, A. (eds.) The Routledge companion to air transport management. New York: Routledge, pp.277-296.
Perçin, S. and Aldalou, E. (2018) ‘Financial performance evaluation of Turkish airline companies using integrated fuzzy AHP fuzzy TOPSIS model’, International Journal of Economic and Administrative Studies, 18, pp.583-598.
Sweney, M. and Topham, G. (2021) ‘British Airways owner IAG hit by record €7.4bn loss’, The Guardian, Web.