Introduction
Apple Computers was founded by Steve Wosniak and Steve Jobs in 1976. In 1996, the Company was transformed to Apple Inc. under Steve Jobs. Its products were highly sophisticated non-PC electronics. By 2010, it became a competitive mobile and PC devices vender.
In 2009, its PC market share was 8% in the United States. In 2010, Apple’s market share was $220 billion. Apple’s success is rooted over its constant innovation and wide marketing.
Its quality products, such as the computers and tablets, have enabled the company to expand fast, despite the stiff competition in the industry. Apple conducts thorough promotions under its slogans, such as “think different” and “the greenest lincups of notebooks”.
Apple has a wide target market. It includes education sector, home users, industrial and business sector, creative groups and young people. Apple has its stores all over the world trying to enhance customers’ accessibility in such a way.
Apple shops are staffed by skilled individuals who help customers get and enjoy Apple’s experience. Apple shops also provide their customers with opportunity to choose between different products and services (Janko, 2012).
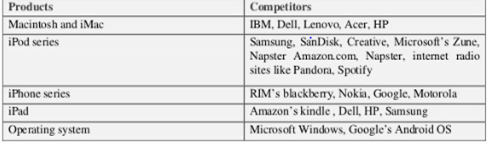
Apple’s high innovativeness has made the company stand a stiff competition in the industry. It faces a lot of competitive pressure concerning its differentiated products. Some of the major competitors are shown in the table below.
Apple’s major competitors
Apple’s SWOT Analysis
Like any other company, Apple has its own strengths and weaknesses. This paper analyses each and every capacity of the company to invest in decision making process.
Apple’s strengths are based on several factors. Innovativeness is Apple’s core strength. The company’s wide researches in technological field make it stand out from the other companies in the market as the pioneer in the industry.
Apple’s Mac, iPhone, iPad and iPod are produced with a lot of high technology innovation. Apple has also created a good brand name in the market. Apple brands are known and easily recognized across the world (Lashinsky, 2012).
Due to the strong brand image, ‘Apple culture’ has been created and promoted among loyal customers. The company is always involved in active research and implementation of new developments. Its researches are carried out by highly skilled workforce.
Apple offers its employees continuous education and constant organization improvement. Consequently, Apple stores across the world are aesthetically designed to appeal to the customers. Lastly, Steve Jobs was a genius, which made the company rise to such a height (Lashinsky, 2012).
Apple Inc. still enjoys a lot of opportunities in the field. The company has good relationship with most players. This allows joint ventures and sharing some ideas. Consequently, the company plays in gradually growing industry.
Mobile and PC industry is growing fast because there is an ever-rising demand for its products. Apple also has the capacity to meet the ever-changing demands in the market. Subsequently, Apple has a strong basis for expansion in Asia, Europe and Africa.
Apple production of energy is efficient because it is cloud based, moreover, its music products keep it a head among competitors in meeting customers’ demand (Schneiders, 2012).
On contrary, Apple has some weakness in its production. Apple TV and Mac Mini seriously suffered a blow in the market. The products sent a bad picture of Apple that is why the company lost many customers.
Compared to the competitors, the company’s products are highly priced, which lowers its competitive advantage. Consequently, The Apple has a small market share as compared to its competitors’ ones.
Finally, there are many risks facing the company, that’s why it should not rely too much on the innovative and management power of one person (Yukl, 2010).
Despite its tactics, Apple is threatened by high competitors in the market. Giant players like Nokia, Dell, Samsung, HP, Toshiba and Lenovo offer stiff competition in the industry. The company also suffers from high pricing against its competitors.
Consequently, Mobile and PC industry is very dynamic that calls for constant innovation. As result, cost of maintaining market demand is very high. Some of Apple products become less competitive in the market due to their incompatibility with Windows platform (Janko, 2012).
Apple has many stakeholders. Some of the stakeholders, such as shareholders and employees, operate directly within organization. Apple also has its manufactures and subsidiary companies with their subsequent employees.
It has the music industry, which enables it to develop music products. The company has various software developers who assist in its production.
Apple Inc. attracts customers from all over the world. Other stakeholders include their lenders and suppliers. Apple enjoys good relationship with its stakeholders due to its well-structured operating system (Robbins & Judge, 2011).
Conclusion
However, the company has not successfully met its customers’ need. Apple has failed in production of affordable products. Many people are locked out of its market due to high prices. Consequently, Apple has failed in expansion to attract new customers and enter the markets across the world.
Most customers need the experience provided by Apple stores. On the other hand, most Apple products are incompatible with Windows. As a result, some customers prefer companies like Nokia and Samsung that provide compatible with Windows platform products.
To counter its challenges, Apple is fighting to meet the customers’ demand for compatible with Windows products though it has failed in lowering product prices.
Despite the challenges, Apple strengths and opportunities still overweigh its weakness and threats making it still a lucrative investment company.
References
Janko, G. (2012). The marketing of Apple Inc.: a success story analyzed in a traditional marketing model. Saarbrücken: VDM, Verlag Dr. Müller.
Lashinsky, A. (2012). Inside Apple: the secrets behind the past and future success of Steve Jobs’s iconic brand. London: John Murray.
Robbins, S., & Judge, T. (2011). Organizational behaviour (14th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Yukl, G. (2010). Leadership in organizations (7th ed.). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Schneiders, S. (2012). Apple’s secret of success traditional marketing vs. cult marketing. Hamburg: Diplomica Verlag.