Introduction
Innovations are an essential part of the natural development of any business. Companies need to deploy innovative concepts and equipment into their operation management processes to ensure the continuum of the economic growth. However, very few organisations view innovations as an inherent part of their corporate philosophy and a vehicle for improving every facet of their functioning, from sales to customer relationships (Kirkegaard Sløk-Madsen, Ritter, & Sornn-Friese 2017). Apple, Inc. is one of the corporations that have dared to venture into the domain of incremental innovations, making the very concept of innovative thinking an inseparable aspect of their decision-making.
Apple has always positioned itself as an organisation that has been viewing innovations as an aspect of the corporate philosophy rather than a tool for raising the number of customers comparatively quickly (Hsiao 2017). However, the link between the incessant inclusion of innovations and the rise in a firm’s profit margins requires further exploration. Although the concept of innovations is generally positive, utilising the philosophy of innovative thinking as the Apple policy suggests in contrast to non-incremental innovations used by other companies may put other companies under a significant strain, questioning their future existence in the global market.
Exploring the long-term effects of the innovation-driven policy and the correlation between the deployment of innovation-driven policies and the corporate performance would be a way of proving the connection between the two. An insightful look into the nature of Apple’s success streak and the factors that have facilitated its unceasing triumph in the global economy will assist in understanding the Apple phenomenon. The objective of the current study is to examine the correlation between the investment in the R&D management and the changes in the profit margins and the overall performance of an organisation, specifically, rise in its revenue, will be the main focus of the research.
Problem Planning & Definition
The analysis of the connection between investing in R&D as the key driver of innovative strategies in the organisational context and the corporate performance is the focus of this study. Determining whether the connection is present in case of Apple will allow stating several key facts about operating in global economy. For instance, one will discover the course that the organisation will have to take in the future, specifically, the approach that it should take in managing its organisational and performance-related processes. In addition, the route that other companies that function in the IT industry, especially the ones that have only recently been integrated into its environment, will be located (Masa’deh 2016). The outcomes of the problem analysis will determine the scope of an innovation-driven approach that firms need to use when entering the realm of the IT market.
To define whether investing in incremental innovations and the focus on R&D as the primary area of development should remain the priority for IT organisations, one will have to determine the correlation between the two variables. The next objective concerns inferring critical conclusions about the significance of innovative thinking and the focus on R&D. It is expected that the outcomes of the analysis will deliver the information that will be sufficient to predict the next changes within Apple. After receiving the results, the third objective will be to delineate the best course of actions for the company and determine whether the described approach will be applicable to other business settings (Kianto, Sáenz, & Aramburu 2017). Opportunities for introducing the notion of innovation-driven management into the framework of multiple organisations on a global level will emerge. The focus on an innovation-driven corporate culture will enhance the propensity in the target demographic to develop new competencies, simultaneously spurring the development of an organisation, in general.
Data Collection Methods
Since a quantitative assessment of the data to be represented in the study is the main objective, the analysis between the variables will require quantitative data. The dependent variable of the research includes the profit margins of the organisation, whereas the independent one will be represented by the expenses taken by the company to invest in its R&D processes. While it is expected that the expense rate has increased over time due to the changes in pricing and the exchange rate, the direct connection between the net income of the organisation and its focus on innovation as its corporate philosophy is yet to be determined.
The main information will come from statistics retrieved form online databases. At this point, it is worth noting that retrieving the described information, especially concerning changes in a company’s management processes and the effects that it has on the organisation’s performance, is rather challenging due to the understandable lack of disclosure. The described limitation was addressed after considering the data that is publically available on sites such as Statista.com (‘Apple’s net income in the company’s fiscal years from 2005 to 2018 (in billion U.S. dollars)’ 2019). Numerical information regarding the changes in R&D investment rates at Apple and the alterations in the company’s revenues was collected for the further quantitative analysis. The main advantage of the identified method is the availability and relatively high veracity of the information. However, the downside of the proposed data collection tool is the lack of opportunity for retrieving qualitative characteristics of trends associated with innovation in the context of a business organisation (Oflazoglu 2017). Since the selected approach implies quantitative analysis of data, no qualitative characteristics regarding the attitudes among staff members toward the implemented change can be obtained. The identified limitation sets the premise for a follow-up study that could help to explore the alterations in employees’ performance due to the changes in their perception of innovation as a concept that makes the bulk of the corporate philosophy.
With the help of a statistical sampling taken from the described data set, one will establish the presence of a correlation between the focus on R&D process as the primary management tool for integrating innovation into the corporate environment and the performance of the organisation. The outcomes of the data analysis will point to the importance of making innovation incremental in the organisational context and using it as a vehicle for encouraging a shift in corporate philosophies on a global scale. Developing an insight into the notion of organisational change is critical to encouraging the economic growth in companies worldwide.
Data Analysis & Presentation
To locate the correlation between the two variables under consideration, the regression analysis was used. The proposed tool has helped to establish a link between the changes in the investment in R&D and the rise in the annual revenue of the organisation (Dubey, Kothari, & Awari 2016). Opportunities for proving the importance of incremental innovation as an essential element of the corporate philosophy was studied profusely.
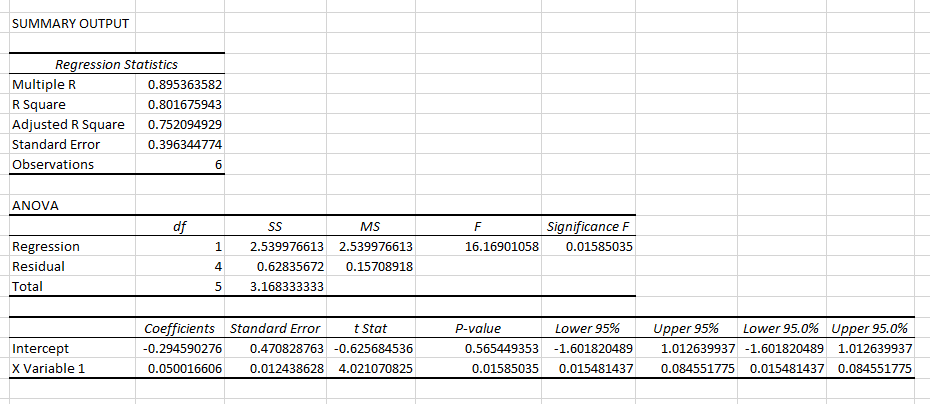
After a look at the available data, the exploration of its statistical meaning was started. The outcomes of the analysis showed that the multiple R reaches 0.89 in the case in question, whereas R square has amounted to 0.8. The variables under analysis show a moderately strong positive correlation in their value (Mertens, Pugliese, & Recker 2016). The derived data proves that the correlation between investment in R&D undertaken by Apple throughout the past five years has caused the company’s profit margins to increase systematically.
Additionally, the outcomes of the analysis prove that there is a considerably low range of variations in the net income of the organisation, which suggests that the degree to which Apple focuses on the introduction of incremental innovations into its organisational setting affects its performance in the global economy. The approximation of the research data also shows that the two variables are related. Finally, one should mention that the p-value of X variable 1 is approximately 0.01. Since p<0.05, the results of the test can be defined as statistically significant, which implies that the link between the two variables under analysis is direct and evidently present.
The analysis of the alterations in the company’s R&D and net income has supported the assumption that there is, in fact, a correlation between the two. The variables in question show the propensity toward growing in a roughly the same proportion, with the change in the first one causing an almost immediate response in the other. However, it is worth mentioning that the outcomes of the analysis have a crucial limitation, which is the standard error. According to the data obtained from the analysis, the standard error for the evaluation reaches a total of 0.56, which is rather high for a regression analysis (Jacobs & Levy 2016).
Arguably, the information produced in the course of the regression analysis may lack precision. The regression equation may require further adjustments in order to reflect the actual state of Apple, Inc. and the trend observed within the organisation. The conclusion regarding the importance of incremental innovation and the notion of innovation-driven management may need additional research. Due to the approximation of data, the actual correlation between the extent of efforts that Apple puts into the enhancement of its R&D and the change in the company’s profit margins may need a further exploration.
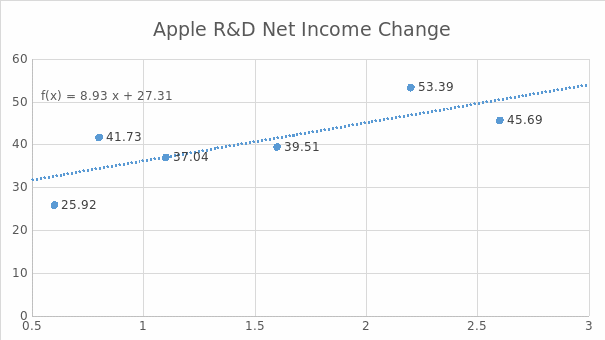
Nevertheless, the analysis has indicated that there is a distinct correlation between the extent of efforts and amount of financial resources that Apple, Inc. puts into the development of its R&D processes and the company’s revenues. The regression analysis has shown that the company’s income has grown visibly with the rise in the investments that Apple has been making in its R&D department. As Figure 2 indicates, the connection is direct, with the two variables being in nearly parallel connection to each other. In addition, the equation that defines the link between the variables under analysis points to the link between the enhancement of R&D processes and the rise in the organisation’s profit margins. The analysis has shown that the correlation between the variables under assessment can be defined with the help of the following expression: y=8.9267x + 27.305.
Interpretation of Data
As the analysis results have allowed to state, the connection between the enhancement of incremental innovations, as well as the interpretation of innovations as an inalienable part of the corporate philosophy, has proven to cause a positive effect on a company’s profit margins. The correlation between the two concepts implies that introducing the principles of innovative thinking into the management of all corporate processes, ranging from production-related to organisational ones, is paramount for a firm’s operations in the global context (Nambisan et al. 2017). The described component of the corporate philosophy will allow affirm to build a substantial competitive advantage by setting its quality standards very high and increasing the levels of customers’ expectations.
The observed phenomenon is very easy to provide a commentary on since the information obtained from the research is quite self-explanatory. The integration of the corporate philosophy based on the notion of innovation into the workplace environment affects the extent to which the organisation meets the ever-changing quality standards of the global market. However, on closer scrutiny, one will notice that the effects of innovation management need to spread into every area of a company’s performance and affect the very process of decision-making (Pérez-González, Trigueros-Preciado, & Popa 2017). The introduction of innovative technological solutions alone will not have a profound effect on a company’s functioning. Instead, one needs to engrave them into the corporate philosophy and ensure that the idea of the continuous change is seen as the incentive for deploying innovation-based management into every facet of the company’s operations.
The described necessity particularly concerns the domain of organisational management as the area that requires the consistent focus. Apart from incorporating the latest tools into the organisational processes, one will also need to encourage the effective education of staff members and advance the notion of professional growth among them to incite a positive shift in the organisational environment (Naranjo-Valencia, Jiménez-Jiménez, & Sanz-Valle 2016). Without the proposed step, the resistance to change, to which staff members are typically inclined, will be barely possible to overcome.
The data clearly indicates that the integration of incremental innovation into the corporate philosophy affects a company’s performance to a large extent. The described process is fuelled by the change in employees’ perspective, which shifts from the idea of meeting their basic workplace responsibilities to the deployment of Corporate Social Responsibility. These changes also include constructing the standards for decision-making based on corporate values such as the close and constant focus on customers’ requirements and the necessity to use culture-specific approaches when communicating with key stakeholders (Fraj, Matute, & Melero 2015). Arguably, the selected approach will establish the competitive advantage of a business due to its capability of adapting to the ever-changing needs of buyers.
Overall, innovation-driven management seems to have a vastly profound effect on the rates of organisational performance and the productivity of an organisation, in general. When implemented properly, the principles of innovation-based management allow staff members to utilise numerous opportunities for increasing the range of their competencies and update their skills by integrating the latest technological advances and strategies into the process of managing their tasks (Goffin & Mitchell 2016).
Additionally, the incorporation of innovation management will entail a greater cohesion between the functioning of different departments due to the rise in interdisciplinary cooperation between employees working in them. The described change is attributed largely to the integration of the latest tools for maintaining communication between employees (Azar & Ciabuschi 2017). With a more consistent information flow between the departments, the threat of an error or an instance of miscommunication drops greatly, leading to a systematic and immediate increase in the quality of a firm’s performance, in general. Thus, the principles of innovation-driven management should be integrated into the corporate setting of any company that is striving to develop a competitive advantage, which will allow a firm to remain relevant in the global market.
Conclusion
Apple has been a doubtless leader in the realm of IT for decades and still manages to retain its competitive advantage. Among the key factors that facilitate the firm’s progress, one should list the presence of an innovation-driven culture. The integration of management strategies based on the promotion of innovative thinking in the corporate setting has proven to have a directly positive impact on the extent of the organisational performance of a business. The levels of the firm’s revenue have increased along with the rise in the degree to which the R&D processes have been upgraded.
However, one will have to admit that the innovation-driven philosophy of Appel goes beyond the mere notion of introducing technological advances into the corporate setting. While the described step is an intrinsic part of the organisation’s policies and the idea of progress, the concept of innovative thinking is stretched beyond the enhancement of IT tools. In addition to the described change, Appel has been focusing on the integration of ground-breaking strategies for managing internal and external factors that define its successful functioning in the context of the global market. In addition, the very principles of decision-making at Apple, Inc. as the process driven by innovative concepts and notions has affected the way in which the organisation is perceived by its customers.
The importation of innovation-based management has allowed Apple to cement its image of a company that is willing to invest in its continuous development in an endeavour at meeting the most challenging demands of its customers. By setting the quality bar very high, Apple, Inc. has created a foundation for keeping its competitive advantage growing. Apple. Inc. has been challenging itself with its innovation-driven policy and the management principles rooted in the concept of the constant improvement. While the described approach appears to be quite strenuous and demanding a significant effort from staff members, it proves to be very gratifying. The rise in performance rates among staff members and the increase in their engagement with the organisation and its business success are expected. Maintaining the levels of enthusiasm among employees and ensuring that they follow the set guidelines for quality management are crucial steps in building the competitive advantage of a business in the setting of the global economy. Following the example of Apple, Inc. should be deemed as a sensible step in promoting the corporate progress and institutionalising change within a company’s environment.
Recommendation for Decision Making
Given the direct correlation between innovation management and the increase in the efficacy of Appel’s performance in the global IT market, it would be the most responsible step for the organisation to continue its innovation-driven management policy and ensure that the principles of innovative thinking should remain the basis for decision-making in the organisational context. The described approach should be implemented at all levels of management, including communication with stakeholders, production issues, and the management of a firm’s supply chain. Organisations that are forced to face stiff competition in the setting of the global economy should pay especially strong attention to the example set by Appel since it invites them to reconsider their priorities and re-evaluate their assets.
Indeed, while the current innovation management strategy used by Apple, Inc., has its focus mostly on the integration of the latest IT ideas into the development of its products, the notion of innovation management is stretched to the idea of rebuilding relationships with key stakeholders within the firm. Taking the example of Apple, Inc. in their efforts to pursue innovation-driven management, organisations need to shape their approach toward their HR assets and focus on the introduction of new tools for talent management. Keeping the levels of loyalty high among employees is an essential step for companies that are willing to introduce innovation-driven principles into their functioning. The use of appropriate strategies for decision-making aimed at addressing specific needs of staff members are essential.
For organisations operating in the IT industry to remain competitive and gain a substantial advantage in the global market, the principles of innovation management set by Apple. Inc. should be followed closely. Once the notion of innovation as the platform for improving the management processes is institutionalised in the corporate setting, gradual positive changes in the overall performance of a firm can be expected. However, for the described objective to be attained, the concept of innovative management should be included into every facet of a firm’s operations, ranging from HRM to public relations to production processes. The incorporation of innovative tools into the SCM domain should be paralleled with the investment into the HRM processes and the enhancement of the production cycle. Once all of the organisational processes are set in motion at the required pace and the idea of the constant progress is firmly engraved into the corporate culture of a firm, a public success is guaranteed.
Reference List
Apple’s net income in the company’s fiscal years from 2005 to 2018 (in billion U.S. dollars) 2019, Web.
Azar, G & Ciabuschi, F 2017, ‘Organizational innovation, technological innovation, and export performance: the effects of innovation radicalness and extensiveness, International Business Review, vol. 26, no. 2, pp. 324-336.
Dubey, U, Kothari, DP & Awari, GK 2016, Quantitative techniques in business, management and finance: a case-study approach, CRC Press, Chicago, IL.
Fraj, E, Matute, J & Melero, I 2015, ‘Environmental strategies and organizational competitiveness in the hotel industry: the role of learning and innovation as determinants of environmental success’, Tourism Management, vol. 46 pp. 30-42.
Goffin, K & Mitchell, R 2016, Innovation management: effective strategy and implementation, Macmillan International Higher Education, New York, NY.
Hsiao, K 2017, ‘What drives smartwatch adoption intention? Comparing Apple and non-Apple watches’, Library Hi Tech, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 186-206.
Jacobs, BJ & Levy, KN 2016, Equity management: the art and science of modern quantitative investing, 2nd. ed., McGraw Hill Professional, New York, NY.
Kianto, A, Sáenz, J & Aramburu, N 2017, ‘Knowledge-based human resource management practices, intellectual capital and innovation’, Journal of Business Research, vol. 81 pp. 11-20.
Kirkegaard Sløk-Madsen, S, Ritter, T & Sornn-Friese, H 2017, ‘Commercialization in innovation management: defining the concept and a research agenda’, Academy of Management Proceedings, vol. 2017, no. 1, p. 15880.
Masa’deh, R 2016, ‘The role of knowledge management infrastructure in enhancing job satisfaction at Aqaba Five Star Hotels in Jordan’, Communications and Network, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 219-240.
Mertens, W, Pugliese, A & Recker, I 2016, Quantitative data analysis: a companion for accounting and information systems research, Springer, New York, NY.
Nambisan, S, Lyytinen, K, Majchrzak, A & Song, M 2017, ‘Digital innovation management: reinventing innovation management research in a digital world’, MIS Quarterly, vol. 41, no. 1, pp. 223-238.
Naranjo-Valencia, J, Jiménez-Jiménez, D & Sanz-Valle, R 2016, ‘Studying the links between organizational culture, innovation, and performance in Spanish companies’, Revista Latinoamericana de Psicología, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 30-41.
Oflazoglu, S 2017, Qualitative versus quantitative research, BoD – Books on Demand, New York, NY.
Pérez-González, D, Trigueros-Preciado, S & Popa, S 2017, ‘Social media technologies’ use for the competitive information and knowledge sharing, and its effects on industrial SMEs’ innovation’, Information Systems Management, vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 291-301.