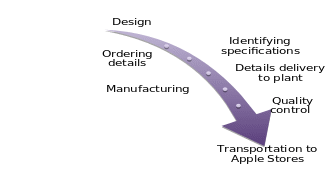
Apple products are assembled in China (Ross 127). The production operation process includes several interrelated steps (see Fig. 1 for the visual representation of the process). It begins with the design of the new product in California. Once a product is designed, and its specifications are identified, the needed details are purchased. The major provider of details is Foxconn (Hillsberg), and it is the manufacturer. After the required details are delivered to the plant, Apple products are assembled. The process is the combination of automation and human effort (Statt). Once the assembling process is over, all products undergo quality control procedures (Simon and Schmidt 73). After that, they are dispatched around the globe to official Apple Stores.
Resources Required
Regardless of the specificities of Apple’s manufacturing process, the resources necessary for the operation and production of the company’s products are the same for all industries. In general terms, several groups of resources are required. The first group of resources is equipment. It involves all technologies used at plants for manufacturing Apple products as well as those deployed for designing products. As for now, special attention is paid to the automation of the production process in the closest future (Statt). In this way, the group will be supplemented by one more resource – robots.
At the same time, equipment may as well incorporate details necessary for manufacturing Apple products. Another group of resources involves human resources. They are necessary for designing products, manufacturing, transporting, and distributing them. In addition, human resources are needed for fulfilling marketing, budgeting, and quality control functions (Dima 245; Kurbel 94). Finally, transportation resources are essential for distributing finished products to Apple Stores as well as delivering the purchased goods to customers who ordered them.
Activities Performed by Workers
Just like different resources are needed to drive the production operation process, it as well requires the fulfillment of different activities. These activities are performed by different groups of workers. For instance, the design group is responsible for developing new products and identifying their specificities. The software development team deals with upgrading software and guaranteeing its exceptional performance and stability. More than that, there are plant workers who are responsible for assembling Apple products.
It is essential to point to their role because the production operation process is still a combination of human effort and automated processes. In addition, some plant workers are involved in performing quality control functions in order to assure that the brand name will not suffer due to unexpected quality gaps. Another team of workers is responsible for marketing and budgeting activities. Finally, there are those involved in transportation activities to distribute the finished products. Here, it is paramount to specify that all of these groups were pointed to because, in the case of technology manufacturing, focusing on plant production only in an incomprehensive decision that does not represent the complexity of the production operation process.
Reflection
Reviewing the production operation process designed by Apple, for me, it is obvious that everything works well. The company has made the cost-effective decision to manufacture its products in the country known for a cheap but high-quality workforce that is a significant contribution to the exceptional performance of all Apple products and the company’s financial success. However, there is still one thing to improve – making a significant effort to hasten the process of automation in order to avoid human-related issues in the production.
Works Cited
Dima, Ioan Constantine. Industrial Production Management in Flexible Manufacturing Systems. IGI Global, 2013.
Hillsberg, Alex. “How &Where iPhone Is Made: Comparison of Apple’s Manufacturing Process.”CompareCamp. 2014, Web.
Kurbel, Karl E. Enterprise Resource Planning and Supply Chain Management: Functions, Business Processes and Software for Manufacturing Companies. Springer, 2013.
Ross, Celia. Making Sense of Business Reference: A Guide for Librarians and Research and Professionals. American Library Association, 2013.
Simon, Daniel, and Christian Schmidt, editors. Business Architecture Management: Architecting the Business for Consistency and Alignment. Springer, 2015.
Statt, Nick. “iPhone Manufacturer Foxconn Plans to Replace Almost Every Human Worker with Robots.”The Verge. 2016, Web.