View Description
Communication between computing devices is crucial because it allows the transmission of information between computing devices. Communication View recognizes the protocols required to initiate and implement data flow between a source and destination (Architecture Reference for Cooperative & Intelligent Transportation [ARC-IT] 1a). Architecture Reference for Cooperative & Intelligent Transportation (ARC-IT) terms the protocol stacks as solutions and consists of a collection of standards to regulate the communication process (ARC-IT 1a). Each information flow triple from the Physical View is attributed to one or more solutions (ARC-IT 1a). However, each solution or component can be evaluated differently within the ARC-IT framework. Overall, protocol stacks required for communication should be associated with one or more solutions.
Communication protocols are assembled following specific models to ensure the transmission of information. The ARC-IT communication model is utilized to assemble a triple solution (ARC-IT 1a). The framework also assigns components of a solution to different parts based on their roles. Standards are employed in all aspects of the model, and some might appear more than once if they satisfy various aspects. A triple solution can be accessed from different avenues, but they are commonly located in the service package (ARC-IT 1a). Protocol stacks are assembled according to different models defined by varying standards.
Figure 1 represents a typical example of a sample tiple solution. Standards are sometimes hyperlinked, and clicking them provides expanded details or alternatives (ARC-IT 1a). The solution also consists of ‘info’ buttons that provide pop-ups with details about a standard (ARC-IT 1a). Gap icons indicate problems, such as failure to meet some requirements defined by the standards (ARC-IT 1a). The severity of the issues is also defined, which can either highest, high, high-moderate, moderate, moderate-low, low, and lowest based on the number of issues (ARC-IT 1b). Overall, a typical triple solution comprises ‘info’ buttons, ‘gap’ icons, and the degree of severity of any issues.
An appropriate framework can be employed to manage communication models and multiple assignments. ARC-IT uses an intermediate construct referred to as profile to regulate, provide security, and enable an exchange of information between devices (ARC-IT 1a). Communication View defines various communication profile links, which are abbreviated as n2m (ARC-IT 1a). The symbols n and m represent either center of support (C), field (I or F), vehicle (V), traveler, or person (P) (ARC-IT 1a). Therefore, a V2V model represents the communication link between vehicles (ARC-IT 1a). ARC-IT uses the n2m framework to define different communication links.
Viewpoint Specification
Protocol stacks are essential to execute communication between devices. Communication Viewpoint provides a framework for defining different protocols needed to allow transmission of information between Physical View (ARC-IT 1b). The protocols should meet the identified interoperability, performance, functionality, security, pertinent policies, environmental requirements, and operation difficulties (ARC-IT 1b). A Communication Viewpoint also addresses different concerns that enable seamless communication between physical objects (ARC-IT 1b). The protocol stacks utilized by Communication Viewpoint are defined by different requirements, which should be addressed.
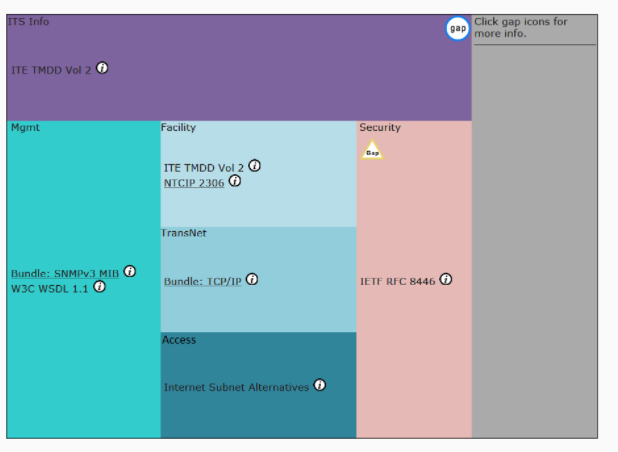
Different frameworks are integrated to develop efficient and effective communication models. The ARC-IT communication program incorporates varying models, such as the Open System Interconnection (OSI) and the IS Station architecture (acquired from ISO 21217) (ARC-IT 1b). The framework comprises six main elements (ITA application-, facilities-, TransNet-, access-, management-, and security-layer), which are summarized in Figure 2. The communication model enables the transmission of information between physical objects.
Works Cited
“Architecture Reference for Cooperative & Intelligent Transportation (ARC-IT). Communication.” 2021, Web.