Introduction

The research topic of refractory superalloys presents many interesting challenges on how to improve the qualities of the existing materials of gas turbines. According to James Coakley currently, technological progress has reached a limit in terms of the materials for gas turbines (Cruz, 2022). Specifically, gas turbines require low-density materials which, simultaneously, have a high level of mechanical performance across temperatures and times and are resistant to corrosion and oxidation. The existing nickel-based superalloys have such qualities, yet there has been no progress in terms of their improvement over the past seven decades. As of now, the nickel-based superalloys can be utilized at 11,000C, and such a temperature level cannot be increased with the existing technology in different fields, including casting.
In order to overcome the established limit of capabilities of gas turbine materials, refractory high entropy superalloys can be used. The notable feature of such superalloys is that they have a body-centric cubic crystal structure which means that every crystal has one atom in the middle of it. The refractory high entropy superalloys have an ordered crystal structure which considerably improves the capability to withstand high temperatures by reinforcing it. Currently, the refractory high entropy superalloys are still being researched by scientists, yet there are already organizations which are interested in the use of such materials, including the Air Force. The researchers working on the new generation of superalloys will focus on two main issues in the future. The first aspect which scientists will explore is what deformation micromechanisms refractory high entropy superalloys tend to have. Another important issue which will be studied during the research is how stable the material will be during the period of exposure to a high temperature.
AI integrated composite additive manufacturing
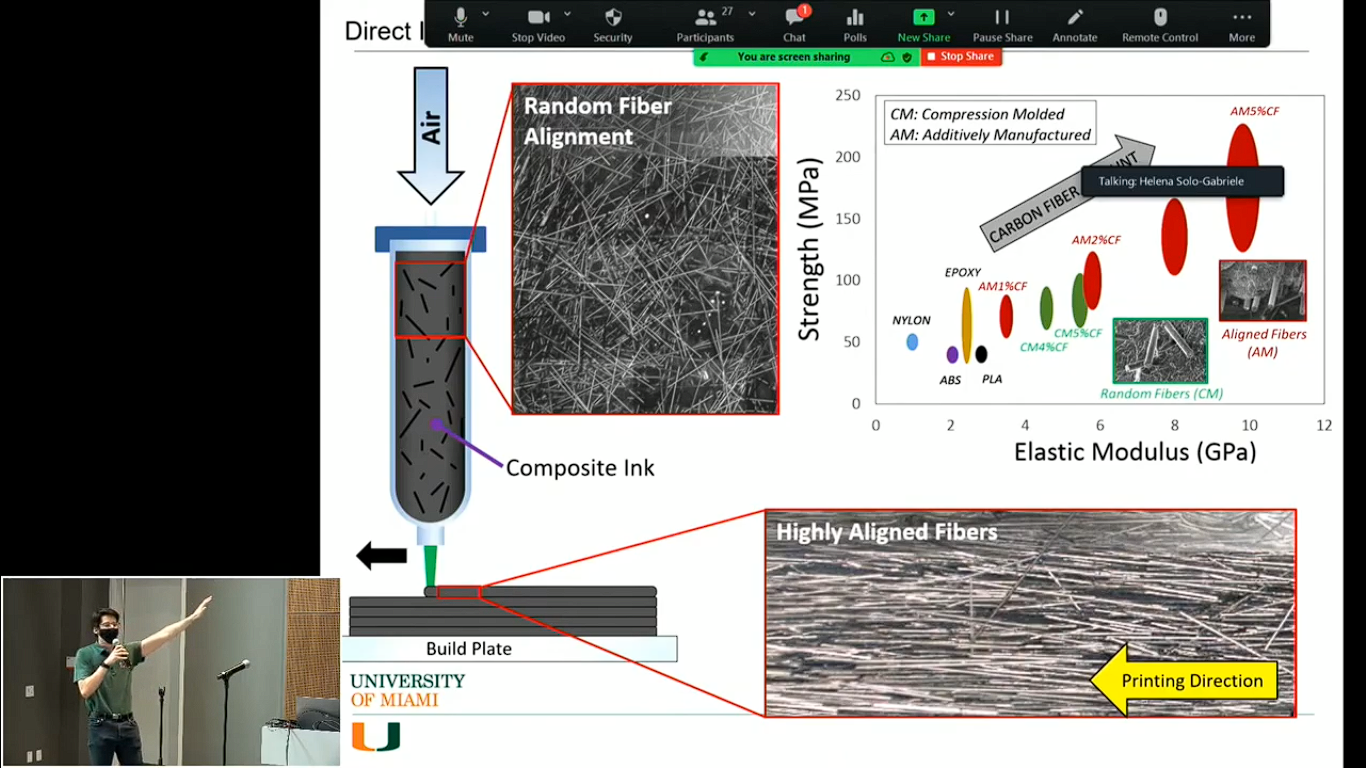
Another interesting research topic presented during the conference concerned the integration of artificial intelligence into composite additive manufacturing. Additive manufacturing is an alternative to the traditional methods of composite production (Cruz, 2022). The former methods, including compression molding and autoclave, require large and expensive machinery, which implies using molds to create simple geometries. Additive manufacturing such as direct ink writing, as opposed to the traditional one, involves 3D printing composites and creating complex geometries while minimizing material waste. Moreover, additive manufacturing considerably improves the composite microstructure making it more resilient and durable. The entire chain of additive manufacturing processes makes ink, which initially has randomly aligned fibers, stronger. As the ink goes through the nozzle of a 3D printing syringe, its fibers become highly aligned. As a result, the ink after the 3D printing procedure has much more superior qualities than that at the beginning of the process.
Nevertheless, a key problem with the direct ink writing technology lies in the fact that the properties of the ink change depending on the environment. Yet, artificial intelligence can help to determine the ideal material since researchers can train it to identify the required conditions for the ink. Essentially, artificial intelligence enables researchers to easily discover ideal process parameters, which saves many hours of work and makes the entire procedure more predictable. Since artificial intelligence makes it easier to find excellent conditions for the material, the quality of the end-product also improves. Moreover, the performance increase occurs across all of the fields, including mechanical, thermal, and electrical, making the printing process more efficient and effective. The newly discovered capacity of artificial intelligence can significantly enhance the quality of 3D printers and make them more accurate.
Micromechanics of high-temperature materials
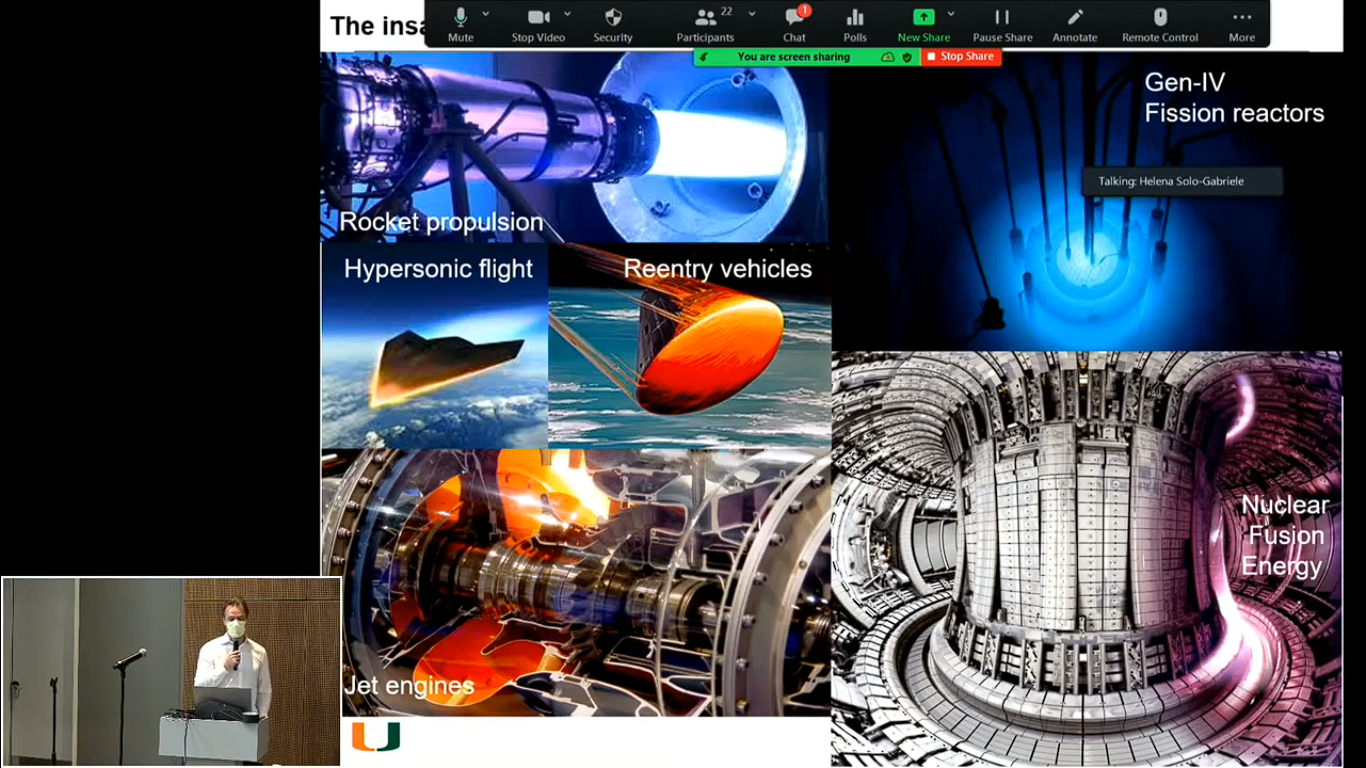
The report presents information on the topic of micromechanics of high-temperature materials, which have many technological applications. For instance, high-temperature materials are extensively utilized in the spheres of rocket science, hypersonic flights, the nuclear energy industry, and many others (Cruz, 2022). The current limits of the materials are dictated by the nickel-based superalloys, yet there are also ceramics which can operate at high temperatures. Both refractory metals and ceramics are crystalline materials which means that they have a crystal structure. The field of micromechanics is still emerging and developing, but it has already enabled researchers to make considerable progress in their understanding of the structures of different materials on their micro and nanoscale. Micromechanics also provides researchers with real-time data about the mechanical behavior at the precise locations of materials and prevents experimental errors. When conducting experiments, material properties of constituent phases can be easily extracted and modeled to assess the behavior of the materials.
The properties of crystalline materials are directly dependent on their defects which are studied as part of micromechanics. For instance, in order to study the strength of certain materials such as nickel-based superalloys, researchers utilize micromechanical modeling. By changing the microstructural parameters of the material, including the size, researchers can determine the variation in terms of the strength of the alloy. After conducting such experiments, the researchers discovered that the strain parameter was the most important one for the strength of the material. The researchers also utilized mechanical modeling in their study of the materials used in nuclear fusion reactors, namely, the refractory metals. Such materials have a different microstructure which consists of small loops and defects called dislocations, and by exploring them, the researchers were able to find how they contribute to the strengthening of the material.
Resolving safety issues of batteries

Today, batteries are utilized in many devices and appliances, while they are extremely effective in powering such gadgets, they also have many issues. The batteries’ common issue is the risk of them suffering a damage which can entail considerable injuries for people. Batteries contain toxic electrolytes which are highly flammable and therefore pose a risk of explosion and fire in the case if they leak (Cruz, 2022). At the same time, there is research on how safer batteries can be made and the aforementioned risks and accidents prevented. One of the possible solutions would be to replace batteries with liquid-state electrolytes with those which have solid-state ones. Moreover, the batteries with solid-state electrolytes can be produced with simpler fabrication techniques and have a smaller size. Nevertheless, there is a challenge with solid-state electrolyte batteries, which is the slow ionic conduct of solid electrolytes.
The researchers discovered a possible solution for the challenge by using a supersonic ceramic conductor, rubidium silver iodide, and subjecting it to several procedures. Specifically, the researchers conducted a solid-state synthesis, quenching, and annealing in order to improve the ionic conduct of the material. As a result of the experiment, the researchers were able to achieve one of the highest values in terms of ionic conduct for a solid-state electrolyte material. Based on the result of the experiment, the researcher managed to develop a solid-state battery composed of silver as anode and cathode as graphite, as well as rubidium silver iodide as the solid electrolyte. The battery demonstrated excellent results and even outperformed the traditional liquid-state batteries in a high-humidity environment. Thus, the researchers concluded that the properties of solid-state batteries could be used successfully in appliances even without special packaging.
How glasses creep
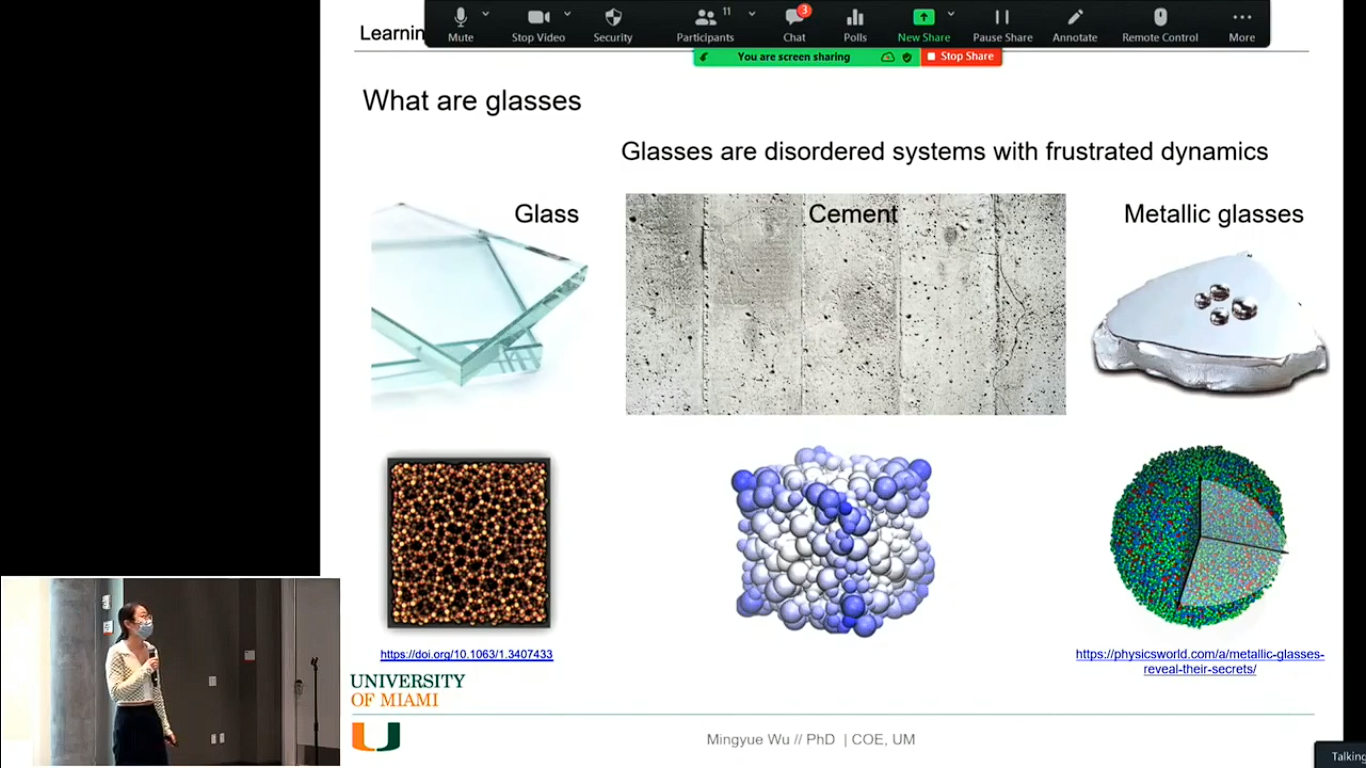
The report presented by Mingyue Wu provides an account of glasses and their property of creeping. The researcher defined glasses as disordered systems which have fractured dynamics. The study explored not only those glasses which people interact with on a daily basis but also metallic ones (Cruz, 2022). The phenomena of creeping can be defined as a long-term plastic deformation which occurs to glasses and other materials such as cement in the situation when they are subject to a sustained load. In order for the glass or cement to experience the creep effect, it must be subject to a load for a considerable period of time. After the load is lifted from the system, permanent deformation will be formed compared to the initial state of the system. The creep phenomenon affects all glass and concrete structures and presents a challenge to scientists and engineers. There is no knowledge on how the creep relaxation dynamics are related to the glass structure.
In order to tackle the creep problem, researchers decided to switch from studying large structures such as concrete bridges to small ones. In fact, the creep behavior can be discovered on the microscale, where it becomes visible that it is dependent on the microscopic displacements of the nanoparticles forming the cement matrix. The research conducted by Mingyue Wu and other scientists demonstrates that machine learning can be used as a tool to identify complex structural metrics which correlate with creep behavior. Specifically, the researchers used molecular dynamics simulations and viewed displacements of particles as a function of time, as well as utilized machine learning to predict particle displacements. Such an experiment enabled researchers to get a better insight into how the creep phenomenon occurs.
Reference
Cruz, W. (2022). CoE research day – Feb 25/2022 [Video]. YouTube. Web.