New Mission
Atrium Health aims at:
- Patients’ wellness.
- Advanced technologies use.
- Care delivery by effective cross-functional teams.
- Collaboration and services co-production.
Atrium Health aims at the provision of healthcare services that will ensure the improvement of people’s health through the integration of advanced technologies, the collaboration within cross-functional teams, and their communication with patients. Co-production of services is one of the priorities as the company aims at addressing patients’ exact needs even before they are pronounced, which is an emerging trend in the healthcare system (Osei-Frimpong, Wilson, & Lemke, 2018). The use of IT systems is at the core of the implementation of the mission.

New Service
Proactive Health by Atrium Health:
- Regular checkups and standard healthcare services.
- Health advocate providing recommendations and health-related behavioral patterns.
- 90-day health programs to manage weight, hypertension, and other issues.
- Online community that shares the vision.
- 24/7 support and care.
Proactive Health is a new service offered by Atrium Health based on the innovate approach to the delivery of health care (Atrium Health, 2019a). Effective and almost instant communication is one of the pillars of the service as patients can access the health team through a mobile application or can benefit from their participation in an online community (Sullivan, Ibrahim, Ellner, & Giesen, 2016).The cross-functional team collaborates effectively to satisfy the needs of patients and improve their health status. The success of the teamwork is ensured by the atmosphere of equality, where every professional speaks freely and contributes to decision making (Pathak, Parry, Block, & Desai, 2016).

Service Delivery Enhancements: Atrium Health Board
- Eugene A. Woods – President and Chief Executive Officer;
- Armando L. Chardiet – President, Atrium Health Foundation;
- Anthony C. DeFurio – Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer;
- Jim Dunn – Executive Vice President and System Chief Human Resources Officer;
- Ken D. Haynes – Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer;
- Carol A. Lovin – Executive Vice President, Chief Integration Officer and System Chief of Staff;
- Scott Rissmiller, MD – Executive Vice President and Chief Physician Executive;
- Rasu B. Shrestha – Executive Vice President and Chief Strategy Officer;
- Keith A. Smith – Executive Vice President and General Counsel.
The leadership of the organization makes a lot of effort to ensure the implementation of the mission (Atrium Health, 2019b). The use of advanced healthcare equipment, which is facilitated by the utilization of the most recent information technologies is an integral component of the organization’s strategy. Human resources management is another area that received increased attention, and top executives allocate substantial funds to train and develop the staff.
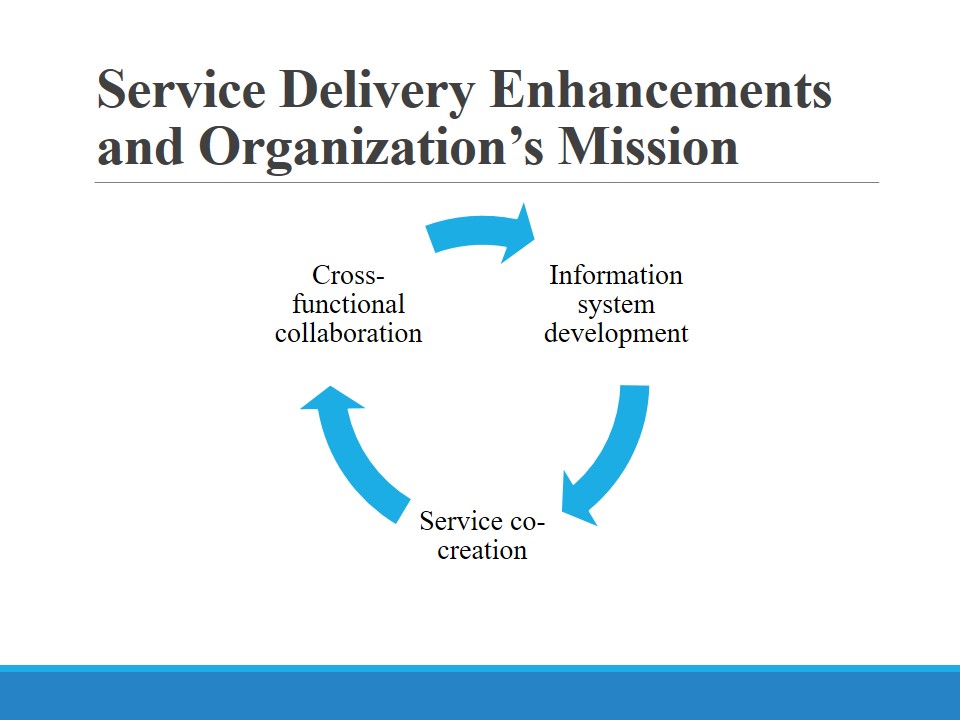
Service Delivery Enhancements and Organization’s Mission
The use of advanced technologies is one of the organization’s competitive advantages. However, the utilization of more sophisticated information systems (IS) can enhance service delivery and implement the new mission. Proactive Health is based on the principles of collaboration and close communication, so the use of the corresponding software is essential. Apart from the storage and processing of data, ISs should ensure the effective communication of the involved stakeholders (Wager, Lee, & Glaser, 2017). The interactions between the staff and patients and between different healthcare professionals should be managed (Sullivan et al., 2016). Atrium Health pays much attention to the areas mentioned above (E14: Proactive Health Part 2, n.d.). The project in question facilitates communication and knowledge sharing through the staff empowerment, so team members are willing to explore their creativity to develop new services and improve existing ones.
Advertisement
- A headline: We will take care of your wellness.
- A sub-headline: We will transform your wellness behaviors into your routine without the need to lose much time and money.
Advertisements are a part of communication strategy and aim at attracting more customers. When promoting the company’s products and services, it is beneficial to focus on such concepts as innovation, care, and affordability (Hillestad & Berkowitz, 2018). Therefore, the headline and sub-headline will include the information regarding the company’s focus on patients’ wellness that is promised to be maintained quite easily. Atrium Health should stress that the organization can help patients remain healthy for a prolonged period of time, which is one of the needs of young generations (especially young adults, as well as other age groups) (Poku, Behkami, & Bates, 2017). The company should articulate its capacity to cater to their potential patients’ needs.
A Brand–Positioning Statement
Concepts to concentrate on:
- Healthy lifestyle maintenance.
- 24/7 care provision.
- 24/7 communication and support.
- Saving customers’ time and money.
Atrium Health should position its Proactive Health project with the focus on several concepts. Modern people are becoming more conscious regarding their health, so wellness-related services are becoming increasingly popular (Poku et al. 2017). People also strive to remain connected through various channels, but digital platforms are preferred, so the company should use effective IT and utilize social networks as one of the primary communication instruments. Proactive Health can have the following brand positioning statement. Proactive Health ensures the maintenance of its customers’ wellness through the delivery of 24/7 care and support.

Advertisement: An Artwork
One of the most potent platforms for the promotion of healthcare services is the Internet. Social networks and digital advertising can be instrumental in communicating the necessary messages and attracting more customers (Hillestad & Berkowitz, 2018). Print advertisements in periodicals can also facilitate the promotion of the project. The visual messages should include the following concepts: collaboration, community, and wellness. The collaboration between healthcare professionals and patients, as well as the communication between the members of the medical staff, should be visualized. Pleased (smiling, interested, engaged) patients of different ages should be featured. Finally, the images of patients who do some exercise or do sport should be displayed.

Advertisement: A Layout (Major Features)
- 2-3 similar video clips are needed.
- Proactive Health logo is present.
- 3-minute long clips are optimal.
- All the concepts are included.
- Major stakeholders speak.
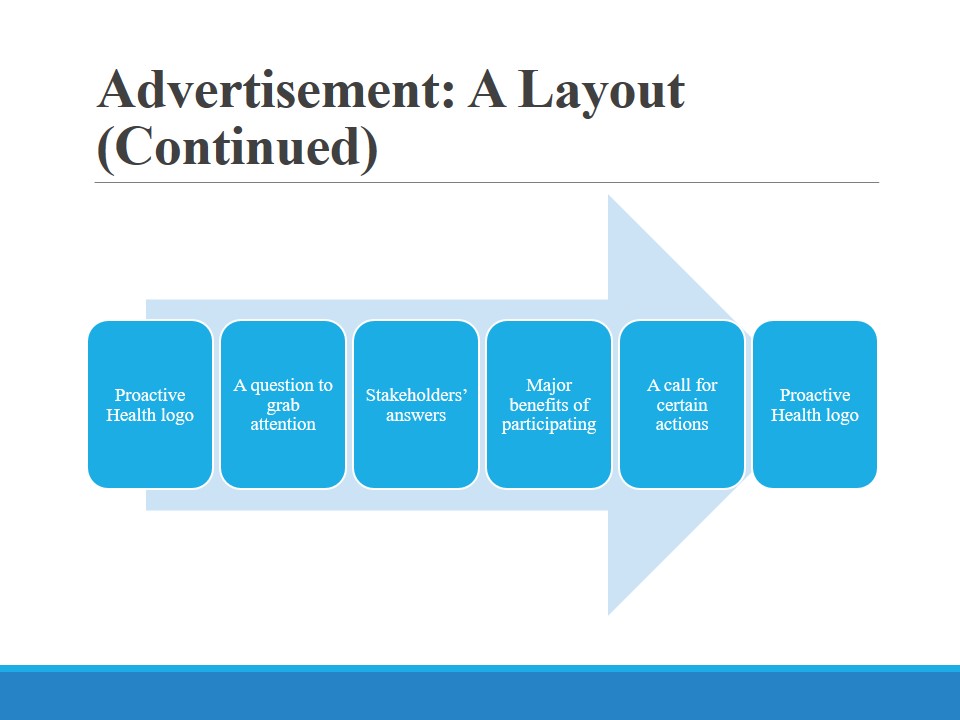
It is necessary to create two-three similar video clips that will have a number of features. Proactive Health logo should become recognizable, so it can frame the videos. The clips should be approximately 3-minute-long as this duration ensures that people will watch it, and the costs will not be excessive. It is essential to make sure that health team members and patients articulate certain messages. Existing patients should share their ideas as to the project and the reasons behind their participation. Such areas as professionalism, access to a wider community, and 24/7 support with advanced technologies use will be covered. Healthcare practitioners should put an emphasis on the provision of patient-centered care and the communication that is almost instant and endless.
As mentioned above, the project’s logo can frame the video clip, which will enhance its recognizability. After this component, a question should appear on the screen (with the background used for the brand’s logo). Some examples of the questions are: What is health for? Are you doing enough for your wellness? How can healthcare professionals provide innovative services to help people maintain proper health? Patients and health team members respond to these questions. They start their response with their names and age to make the information more credible. The stakeholders also mention the benefits of participating in the project. The call for action can be presented as a question against the background of Proactive Health logo. A stakeholder can also ask a question motivating potential customers to learn more about the project. The final image is the brand’s logo and contact information.

Pricing Objective
- Objective:
- Competition-driven objective;
- Increase market share.
- Rationale:
- Low representation across the country;
- Atrium Health is comparatively new in the market;
- High competition in the market.
The pricing objective that can improve the organization’s performance and ensure its secured position in the market should target competition. Pricing objectives that concentrate on competition are instrumental in increasing companies’ share in the market and improving its competitiveness (Hillestad & Berkowitz, 2018). Atrium Health will benefit from the use of this pricing objective as it is poorly represented in states, which has a negative effect on its performance. People and ensures choose other healthcare providers with lower prices. Since the company is comparatively new, it has a limited number of customers so far.

Pricing Strategy
- Ensure high quality.
- Introduce innovative services.
- Lower down prices.
- Develop effective communication strategy.
In order to be more competitive, Atrium Health should undertake several steps. Atrium Health should consider lowering down prices to make their services more competitive. The modern healthcare industry is characterized by a high competition, and customers are rather price-sensitive these days, which makes lower prices a competitive advantage (Hillestad & Berkowitz, 2018). Costs reductions can be achieved through enhanced performance, the use of latest information technologies, and effective human resources management. The introduction of new and innovative services is a part of this strategy as innovation is the driver of competition. The company should also ensure the provision of high-quality services, which is another competitive advantage attracting more customers. Finally, an effective communication strategy will help the company improve its presence across the country, as people will learn about the organization’s services and associated advantages.

Conclusion
- Proactive Health is an innovative service aimed at improving people’s health status.
- The focus should be on gaining a competitive advantage.
- Advertising campaign will be mainly held with the help of Internet and periodicals.
- Collaboration, communication, co-creation are the principles of the project and its promotion.
Atrium Health is still rather new in the healthcare market, so the organization should aim at attracting more customers. Proactive Health is an innovative project that introduces people to a new type of care, which can become a considerable competitive advantage. In order to promote the brand, it is possible to resort to the Internet and periodicals as these means will reach a wide audience. Such components as collaboration, communication, and service co-creation are the features making the project capable of winning the competition and helping the organization to develop and grow in a sustainable manner.

References
Atrium Health. (2019a). A new kind of healthcare experience. Web.
Atrium Health. (2019b). Atrium Health leadership. Web.
E14: Proactive Health Part 2 – Creating a New Frontier. (n.d.). Web.
Hillestad, S. G., & Berkowitz, E. N. (2018). Health care market strategy (5th ed.). Burlington, MA: Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Osei-Frimpong, K., Wilson, A., & Lemke, F. (2018). Patient co-creation activities in healthcare service delivery at the micro level: The influence of online access to healthcare information. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 126, 14-27. Web.