Discuss what is meant by Fiscal Policy. What are the instruments of fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy involves the use of government incentives to address the amount of money in circulation. There are normally two types of fiscal policies. These are expansionary and contractionary fiscal policies. Expansionary fiscal policies are those policies meant to boost the disposable income of the citizens. Contractionary policies on the other hand help mob up an excessive amount of money in circulation (King, Stonecash Mankiw &, 2009).
Normally, they are used during times of inflation; the governments through its fiscal policies reduce the disposable income of individuals. The government aborts the development projects; this consequently cuts down the amount of money in circulation.
According to Stonecash, King, & Mankiw (2003), government spending, taxation, and borrowing are the three major instruments of fiscal policy. Government expenditure entails the initiatives used by a government to realize a given macroeconomic goal (Rao, 2006). The development of infrastructure is an example of government spending. Taxation is a way through which a government obtains its funds to use in the budget. Taxation helps control the amount of money in circulation. Borrowing entails the use of treasury bills by the government to control the amount of money in circulation.
With the aid of a diagram, show and explain how fiscal policy can be used to shift the aggregate demand. Evaluate the effectiveness of the policy used
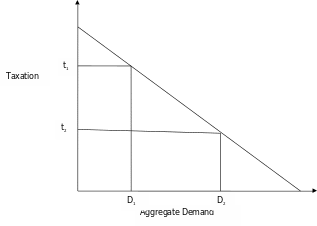
From the above diagram, I have used taxation as an instrument of fiscal policy to demonstrate how a fiscal policy shifts the aggregate demand. D1 and D2 represent aggregate demand while t1 and t2 represent taxation respectively. When economic inflation figures are high, the government increases taxation from t2 to t1. From the graph, when taxation is high (t1) the aggregate demand is low (D1).
This is so because taxation reduces the disposable income of customers hence reducing aggregate demand for goods and services. The expansionary policy helps increase the amount of money in circulation; this in turn increases the aggregate demand as the consumers have a lot of money to spend on products. Given the reduction of taxes, for example from t1 to t2, the aggregate demand increases from point D1 to D2. Taxation is a useful instrument that helps maintain sustainable inflation pressures.
Access the 20010-11 Australian Government’s Budget papers and with the aid of statistics, explain the fiscal policy stance adopted
According to the Australian 2011 – 2012 government’s budget paper, the inflation rate stands at 3.6%. To maintain sustainable inflation pressure, the government needs to tighten its fiscal policy stance. Tight fiscal policy measures however have adverse negative effects on the economy in the long run. To maintain price stability, for example, the government needs to reduce its expenditure, increase taxation, and increase internal borrowing. The aforementioned incentive reduces the disposable income that in turn decreases aggregate demand. With the economy having fewer amounts of money in circulation, prices of products will destabilize with some rapidly coming down.
What are the current inflationary pressures being experienced in the Australian economy? Evaluate the appropriateness of the government’s fiscal policy stance
To maintain a healthy economy, the Australian government needs to employ indirect fiscal policies which will ensure the government operations are kept running while price stability is maintained. This policy stance will help contain soaring inflation rates. To enhance economic growth, the government needs to ensure spending by citizens is not adversely affected by the tight fiscal stance employed.
In addition, sustainable inflation and confidence in the market are paramount for an economy to thrive in both growth and development (Rao, 2006). The Australian government, in her 2011 – 2012 paper, has helped nurture market confidence in their core healthcare and the country’s learning systems’ plans. This is an initiative in the right direction, as it will help the Australia economy grow while containing its inflation pressure at manageable figures.
Reference List
King, S. Stonecash, R. & Mannkiw, G., 2009, ‘Principles of economics.’ 4th ed. Sydney: Cengage Learning.
Rao, G., 2006. ‘Development ,poverty, and fiscal policy.’ New York: Springer.
Stonecash, R. King, S. & Mankiw G., 2003. ‘Principles of macroeconomics.’ Sydney: Harcourt-Brace.