Proposal
The following paper will describe and cover various organizational aspects of the Bayerische Motoren Werke AG manufacturing company. BMW AG specializes in designing, developing, and producing automobiles, bicycles, engines, and motorcycles. It is a well-known manufacturer in the world market. The discussion below will focus on such factors of the given organization as its manufacturing process, suppliers, raw materials, professional equipment, quality of the products, technology, and other points regarding its approach to management and business in general. The BMW AG Company is famous for its high-quality sports cars and new technologies that its engineers develop every year. The upmarket vehicles manufactured at the Bayerische Motoren Werke factories are considered to be the most comfortable and technological automobiles in Europe.
Overview and Environment
As it is mentioned above, the Bayerische Motoren Werke Aktiengesellschaft specializes in producing revolutionary automobiles, motorcycles, combustion engines, and bicycles. It has a plethora of factories all over the world and its dealerships almost in every developed country (“Manufacturing Building a Better BMW” 1). The organization mentioned above follows the ownership structure of a joint-stock company. Its competitive advantages are the following:
- BMW AG produces high-quality sports automobiles.
- The company’s production always has a warranty (up to five years) after the purchase at one of its authorized dealer stores.
- The specific and aggressive design of the carriage body attracts the purposive audience.
- Innovative technologies implemented in the BMW vehicles improve the clients’ safety.
- The BMW cars’ productivity and acceleration dynamics are the best in the European market as their inclusion gives the customers unforgettable emotions.
The operations competitive advantages of the Bayerische Motoren Werke imply the fact that its employees are obliged to put all the parts of the cars together while the assembly line is moving. Such an approach to the manufacturing process requires every worker to be qualified and certified in a particular sphere (electrics, mechanics, and so on). The industry is very profitable and has great competition, especially in such countries as Italy, Germany, the USA, the UK, and Japan. However, only companies that have been working at the market for an extended period (over thirty years) are successful. Car manufacturing is essential in the twenty-first century as people seek means that save their time. The primary competitors of the BMW AG Company are the following:
- Daimler AG
- Porsche AG
- Audi AG
- Volkswagen AG
Every company’s (listed above) headquarters are situated in the territory of the Federal Republic of Germany. Therefore, they must compete to attract new clients every year. The competitive environment affects the operations of the BMW AG positively as its engineers and designers strive to make a better product than their competitors and foreign manufacturers (Krajewski et al. 36). Perhaps, this motivates them to create almost perfect cars (many clients have been complaining about their reliability recently). A recent operational decision of the Bayerische Motoren Werke was to deliver all the necessary parts to its factories all over the world from Germany to improve the quality of its production.
The infrastructural decision to develop the marketing strategy with the help of the M Performance significantly raised the organization’s income in such countries as the USA, Russia, Germany, Switzerland, England, and Hungary. In turn, the structural decision to build more dealerships in Asia did not show good results due to the high competition with the local manufacturers (Toyota, FAW, Hyundai, and so on). The latest radical innovation of the discussed company is the automobile with an electric engine that is called BMW i3. Although its design reminds of other BMW models, this vehicle has a different philosophy and confuses many fans of the brand. Indeed, the company was also inspired by radical innovations of Mercedes-Benz (such as air ionization in a car, luxurious interior, and other factors). Due to these disruptive technologies, BMW almost went bankrupt.
Process Description
The following paragraph is intended to describe the manufacturing process of the BMW M5. This sports automobile’s location in the product lifecycle is now at its growth stage. However, the era of electric vehicles slowly takes advantage of cars with combustion engines. Therefore, BMW M5 might also be at its highest point of the maturity stage (“Manufacturing Production Process” 1). As it is mentioned above, the assembly conveyor production process is used to create this revolutionary automobile. All the products that are developed, built, and tested at the Bayerische Motoren Werke factory are presented at the International Motor Show Germany in Frankfurt am Main. Many journalists and celebrities are invited to this event to share and discuss new inventions in the car industry.
The primary inputs in the process of the BMW M5 production imply financial investments (to pay salaries to professional engineers and designers), materials for the development of innovative technologies, and other supplies used in car manufacturing (metal parts, plastic, interior parts, glass, electric equipment, and so on). The discussed company uses such transformational activities as implementing the M Performance and showing high testing results to the customers to add value to its cars (“Manufacturing Building a Better BMW” 1). The outputs of the BMW M5 production process imply a material price list to show the value of particular raw supplies. Also, the workers at the BMW factory should make an inventory and production status reports to compare and calculate all the required expenses. The company uses proactive capacity strategy in its work.
BMW M5 Manufacturing Process Description
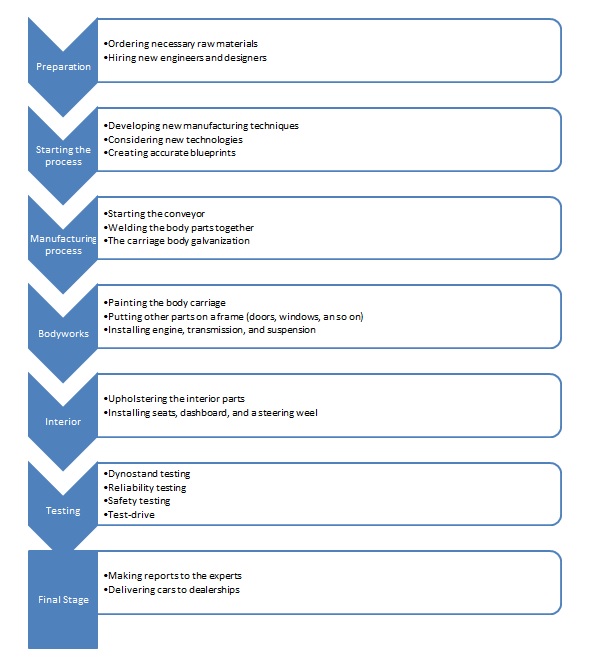
Inventory
Although there are a plethora of necessary raw materials required for the car manufacturing process, there are few unique elements that remain permanent: steel, high-quality plastics, aluminum, and rubber. The work in process (WIP) goods used at the BMW AG factories usually include different mechanical parts, transmission elements, engines, wheel webs, and so on. Maintenance, repair, and operations (MRO) imply different parts of the BMW cars that are delivered to official dealerships all over the world in case of some issues with warranty vehicles. The finished goods of the BMW Company are all analyzed and tested before their transportation to the factory yard. When some dealers sell their automobiles, they request more cars from the yards mentioned above. However, the most luxurious models are kept in large garages to preserve their general appearances (“Manufacturing Building a Better BMW” 1).
Modern factories implement various robotics to build their cars because this method is more efficient and faster than human labor. The plusses of such inventory holding are evident as they do all the work accurately and quickly. However, there are some disadvantages that people are obliged to cope with. For instance, programmed machines sometimes cannot reach certain spots when painting a car. Therefore, workers should eliminate every error (“Manufacturing Building a Better BMW” 1). The management department of BMW is supposed to forecast the demand and the market’s trends in every season to create enough cars for their customers. To reach this goal, employees analyze their sales and incomes for previous seasons. According to the gathered data, all the information about future purchases becomes predictable. The organization does not use any just-in-time or lean practices as car manufacturing imposes a tremendous responsibility on the BMW Company’s employees.
Quality
The BMW AG organization’s approach to the quality of their automobiles is not precise. Approximately thirty years ago, the car brand gained its popularity for high-quality and reliable products. Unfortunately, nowadays the company uses specific methods to limit their automobiles’ exploitation terms. This strategy brings more profit to BMW as the clients are required to pay for service more often than usual (“Sustainability Corporate Sustainability” 1). An average model released by the BMW Company since the year of 1990 cannot be considered fail-operational. However, the quality of various comfort devices (upholstery materials, plastics, paint, and so on) is always high to attract more clients. BMW factories ensure the quality and safety of their cars by testing them with specific equipment.
The total quality management (TQM) of the organization implies the frequent exploitation of the vehicles it produces during the warranty term. The quality is adjusted to the needs of an average person (uses one car for two years and sells it at the secondary market. Despite all the issues discussed above, BMW AG is ISO certified as it is obliged to provide proper safety standards to its customers (“Sustainability Corporate Sustainability” 1). Moreover, every car manufacturing department implements the Six Sigma technique to reduce the number of particular mistakes or discards. The BMW Company uses such tools (discussed in the class) as Bottleneck Analysis, Jidoka, and Kaizen. The following lean concepts are used by BMW during the manufacturing process:
- Standardized Work
- Mistake Proofing
- Total Productive Maintenance
- Problem Solving
Technology
Unfortunately, the BMW AG Company does not use any tools discussed in the class. Nevertheless, it uses other important supply chain management tools in the manufacturing process. For instance, its employees establish contract relationship management with the suppliers to ensure a permanent delivery of raw materials to the factories (“Production Overview Manufacturing” 1). Also, BMW uses shipping status tools always to monitor and control various logistic procedures that deliver their goods or other necessary items. Another supply chain management technology that the German company uses regularly is the Bid and Spend tools. Sometimes, it is essential to make records of the less significant expenses and costs. This strategy helps to save more finances for the organization’s benefit.
Supply Chain
It is a well-known fact that BMW AG is one of the most popular businesses in the world. Therefore, their supply chain requires extra attention. The organization signed long-term contracts with approximately thirteen thousand suppliers around the world from seventy different countries (“Supplier management” 1). The BMW Group Supplier Sustainability Standard is intended to test various businesses and choose the most reliable and trustworthy partners. The most important organization’s suppliers are the following:
- Bridgestone
- Brembo
- Harman/Kardon
- Delphi
- Guardian
- Mahle
- Hirschvogel
The main clients of the BMW AG are the citizens of such countries as Russia, the UK, the USA, India, Brazil, and Germany. The company uses outsourcing because it lets the organization control and work with its dealerships and factories in different parts of the world, which is very convenient. As it is mentioned above, BMW uses many supplier strategies.
Global
The Bayerische Motoren Werke manufacturing company has many global components. One of the most popular methods is to make the presentation of their vehicles all over the world to attract foreign clients and demonstrate particular results of the organization’s work. Another strategy that BMW implements are inviting and financially supporting journalists and reporters from particular states. These people tell their subscribers about new features and technologies installed in the vehicles (“Production Overview Manufacturing” 1). Also, the bloggers’ viewers might be considered potential clients of BMW as it is the only automobile manufacturer that works with popular people on the YouTube video hosting website. Moreover, the Bayerische Motoren Werke dealerships from different parts of the world always order some parts’ or vehicles’ deliveries from Germany as to their clients’ requests. BMW has its sports team in the Gran Turismo yearly competition that is sometimes hosted at the German Nürburgring (the most dangerous and the hardest track).
Recommendation
As it is mentioned above, the automobiles produced the Bayerische Motoren Werke Company have a lack of reliability and quality. Therefore, my operational recommendation to the organization’s factories would be to change some suppliers as the raw materials they provide are not adjustable to the powerful engines of the BMW cars (Paul 660). Another operational recommendation to the German manufacturer is to monitor their sales in every state of the world. This strategy would be helpful to forecast the market trends in a particular region (Smith 251). Basing on the acquired information, the factories might deliver their products to these countries beforehand to reduce their emergency shipping expenses in the future.
Conclusion
The Bayerische Motoren Werke AG Company specializes in cars, motorcycles, bicycles, and combustion engine manufacturing. It has more than fifty thousand dealerships and several factories in different parts of the world. The organization of its production process is fast and efficient due to the robotics equipment and the assembly conveyor strategy. To support the factories’ workers with the required parts and materials, the BMW established partnerships with approximately thirteen thousand suppliers. The quality of the cars released by BMW used to better three decades ago. Unfortunately, today, the company builds unreliable automobiles that work without any errors during the warranty period. The German joint-stock organization implements various global operations to promote and popularize its product among potential buyers. It would be proper to mention that BMW attracts its clients by the interior comfort and the quality of the materials used for seat upholstery and other parts of an automobile. BMW always uses new technologies in the production process to make the work more efficient and accurate. To check the quality and safety of their vehicles, the factories hire experts and other employees who are supposed to test every example of their products.
Works Cited
Krajewski, Lee J., et al. Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains. Pearson Learning Solutions, 2014.
“Manufacturing Building a Better BMW.” BMW US Factory, 2017, Web.
“Manufacturing Production Process.” BMW US Factory, 2017, Web.
Paul, Sanjoy Kumar. “Supplier Selection for Managing Supply Risks in Supply Chain: A Fuzzy Approach.” The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, vol. 79, no. 1-4, 2015, pp. 657–664.
“Production Overview Manufacturing.” BMW US Factory, 2017, Web.
Smith, Laura, et al. “Servitization and Operations Management: A Service Dominant-Logic Approach.” International Journal of Operations & Production Management, vol. 34, no. 2, 2014, pp. 242–269.
“Sustainability Corporate Sustainability.” BMW US Factory, 2017, Web.
“Supplier management.” BMW Group, 2017, Web.